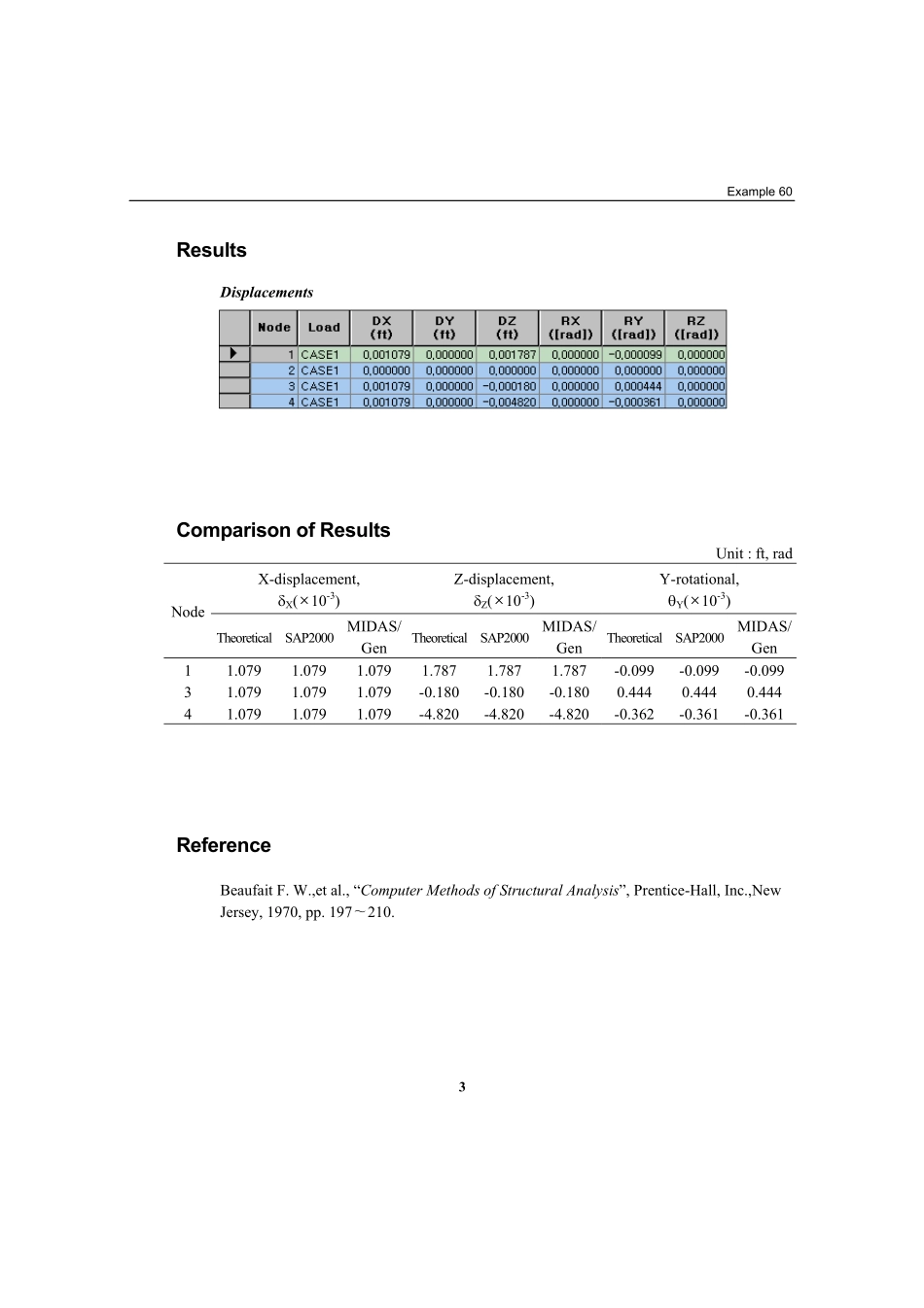
1Example7TitleBeamwithelasticsupportsandaninternalhingeDescriptionDeterminethedisplacementsofastructuresubjectedtotwoconcentratedloads.Structuralgeometryandanalysismodel2ModelAnalysisType2-Dstaticanalysis(X-Zplane)UnitSystemft,kipDimensionLength54ftHeight12ftElementBeamelementMaterialModulusofelasticityE=4.32×106ksfSectionPropertyElementsand-AreaA=0.125ft2MomentofinertiaIyy=0.263ft4Element-AreaA=0.175ft2MomentofinertiaIyy=0.193ft4BoundaryConditionNode2;ConstrainallDOFs.Nodes1and4;Springconstant(Zdirection),K=1200kips/ftReleaseRyofthenode3oftheelementintheelementlocalcoordinates.LoadCasesAconcentratedload,P1=5kipsisappliedtothemid-pointoftheelementintheXdirection.Aconcentratedload,P2=15kipsisappliedtothemid-pointoftheelementinthe-Zdirection.Example603ResultsDisplacementsComparisonofResultsUnit:ft,radX-displacement,δX(×10-3)Z-displacement,δZ(×10-3)Y-rotational,θY(×10-3)NodeTheoreticalSAP2000MIDAS/GenTheoreticalSAP2000MIDAS/GenTheoreticalSAP2000MIDAS/Gen11.0791.0791.0791.7871.7871.787-0.099-0.099-0.09931.0791.0791.079-0.180-0.180-0.1800.4440.4440.44441.0791.0791.079-4.820-4.820-4.820-0.362-0.361-0.361ReferenceBeaufaitF.W.,etal.,“ComputerMethodsofStructuralAnalysis”,Prentice-Hall,Inc.,NewJersey,1970,pp.197∼210.