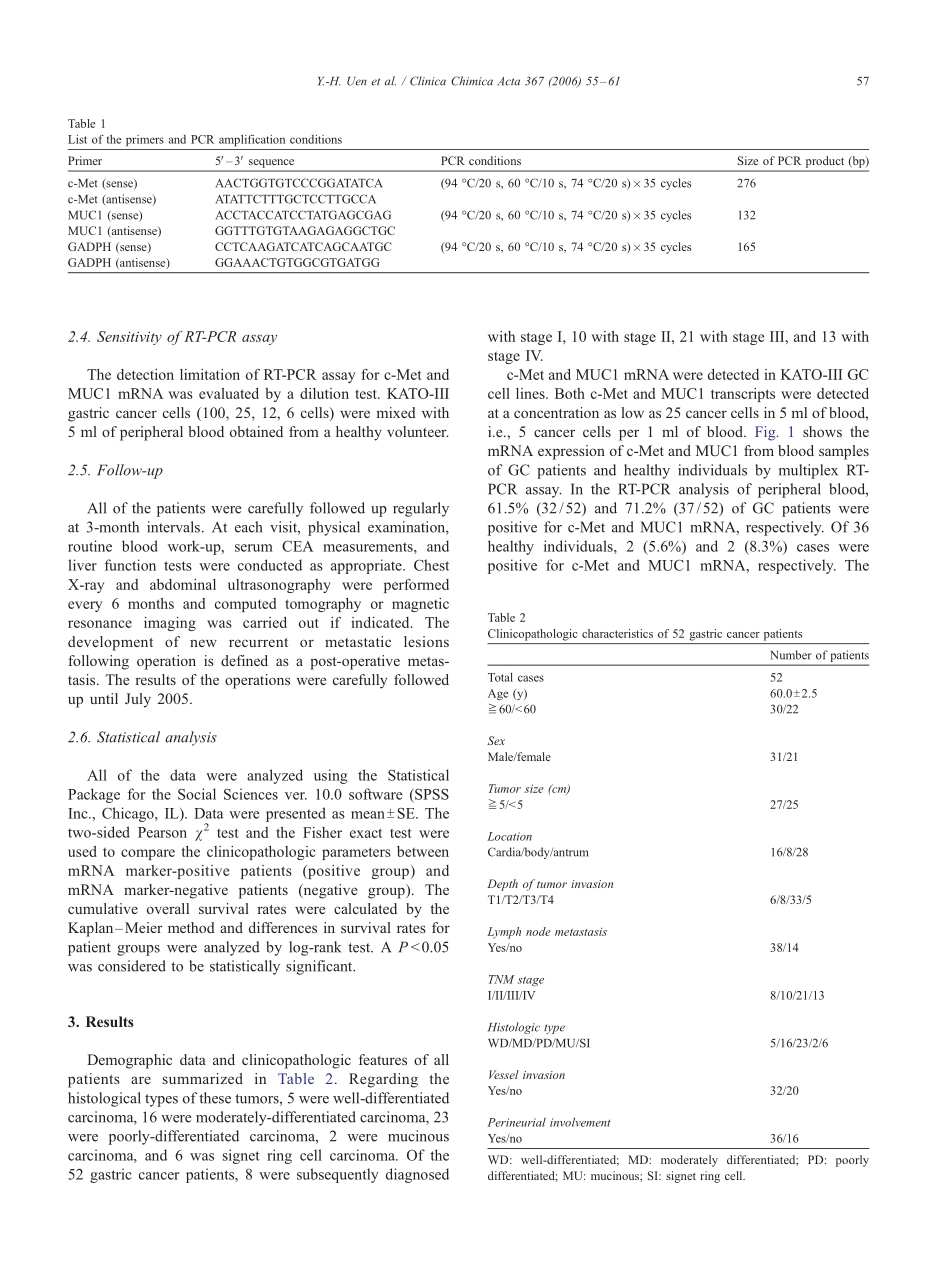
ClinicalsignificanceofMUC1andc-MetRT-PCRdetectionofcirculatingtumorcellsinpatientswithgastriccarcinomaYih-HueiUena,Shiu-RuLinb,Chan-HanWub,Jan-SingHsiehc,Chien-YuLud,Fang-JungYud,Tsung-JenHuangc,Jaw-YuanWangb,c,*aDepartmentofSurgery,Chi-MeiHospital,Tainan,TaiwanbMedicoGenomicCenterandDepartmentofClinicalLaboratory,Chung-HoMemorialHospital,KaohsiungMedicalUniversity,TaiwancDepartmentofSurgery,FacultyofMedicine,CollegeofMedicineandDivisionofGastrointestinalandGeneralsurgery,Chung-HoMemorialHospital,KaohsiungMedicalUniversity,TaiwandDivisionofGastrointestinalMedicine,DepartmentofInternalMedicine,Chung-HoMemorialHospital,KaohsiungMedicalUniversity,Kaohsiung,TaiwanReceived20August2005;receivedinrevisedform17November2005;accepted18November2005Availableonline5January2006AbstractBackground:Recently,severalreversetranscription-polymerasechainreaction(RT-PCR)techniqueshavebeenproventobeusefulinthedetectionofcirculatingtumorcells(CTCs)incancerpatients.WeattemptedtodetectCTCsinpatientswithgastriccancer(GC)usingaRT-PCRassayforc-MetandMUC1andtoevaluatetheirclinicalvalue.Methods:UsingaRT-PCRassay,c-MetandMUC1mRNAswereamplifiedin52GCpatientsand36healthyindividuals.Analyseswerecarriedoutfortheircorrelationwiththepatients’clinicopathologicfeatures,theoccurrenceofnewpost-operativemetastasis,aswellastheoverallsurvivalrates.Results:IntheRT-PCRanalysisofperipheralblood,61.5%(32/52)and71.2%(37/52)ofGCpatientswerepositiveforc-MetandMUC1mRNA,respectively.ThesensitivityandspecificityofeithermRNAdetectedinperipheralbloodis82.7%and86.1%,respectively,withanaccuracyof84.1%.Thedetectionofc-MetorMUC1mRNAwassignificantlycorrelatedwiththedepthoftumorinvasion,lymphnodemetastases,TNMstage,vesselinvasion,perineuralinvolvement,andpost-operativemetastasis(allP<0.05).Kaplan–Meieranalysisdemonstratedthattheoverallsurvivalrateofpatientswithpositivec-MetorMUC1mRNAexpressionintheperipheralbloodwassignificantlyshorterthaninpatientsnegativeforc-MetorMUC1mRNAexpression(bothP<0.05).Conclusions:Ourfindingssug...