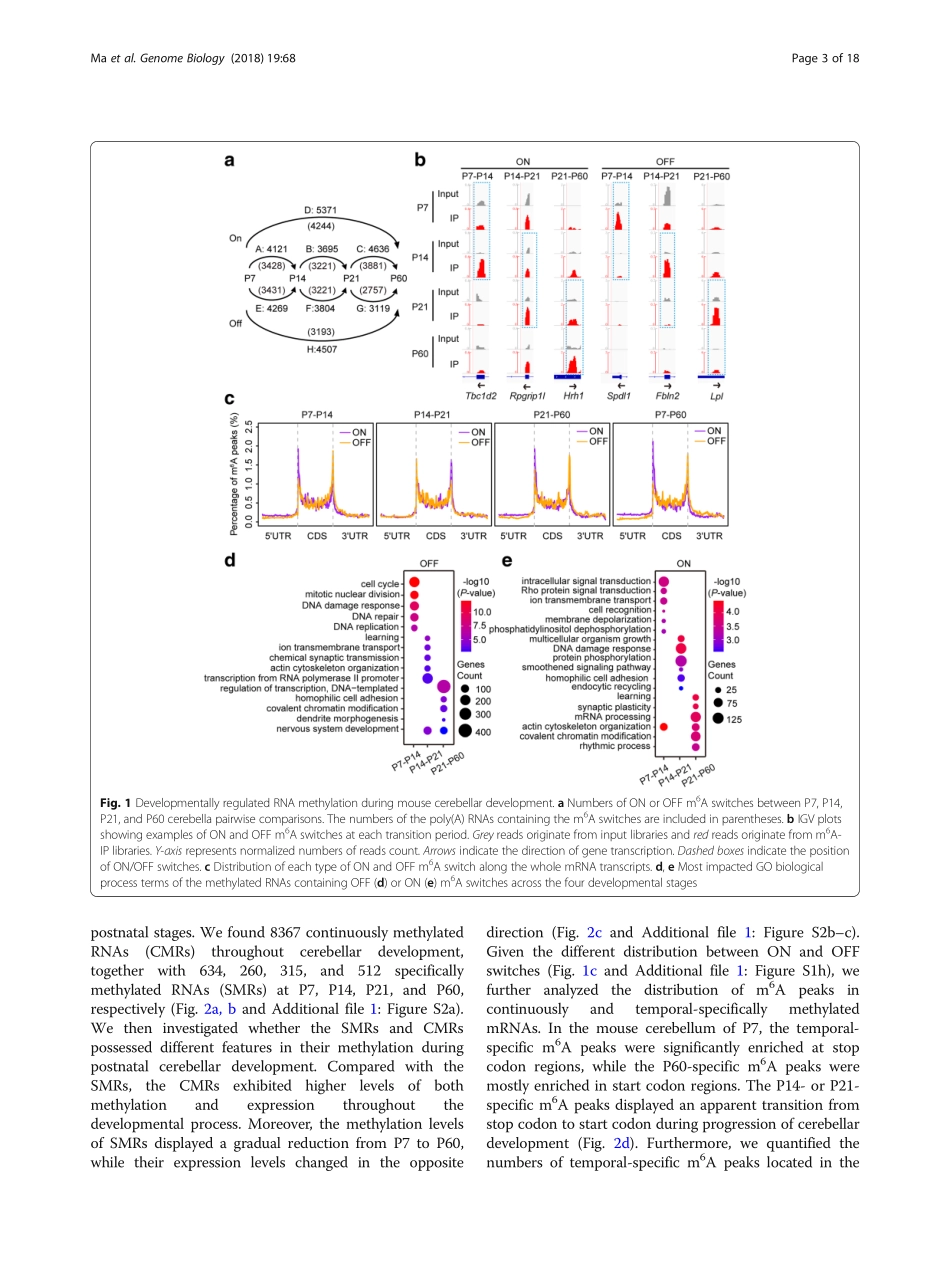
RESEARCHOpenAccessRNAm6AmethylationparticipatesinregulationofpostnataldevelopmentofthemousecerebellumChunhuiMa1†,MengqiChang1†,HongyiLv2,3†,Zhi-WeiZhang1,WeilongZhang4,XueHe1,GaolangWu1,ShunliZhao1,YaoZhang1,DiWang1,XufeiTeng2,3,ChunyingLiu1,QingLi1,ArneKlungland5,6,YameiNiu1*,ShuhuiSong2*andWei-MinTong1*AbstractBackground:N6-methyladenosine(m6A)isanimportantepitranscriptomicmarkwithhighabundanceinthebrain.Recently,ithasbeenfoundtobeinvolvedintheregulationofmemoryformationandmammaliancorticalneurogenesis.However,whileitisnowestablishedthatm6Amethylationoccursinaspatiallyrestrictedmanner,itsfunctionsinspecificbrainregionsstillawaitelucidation.Results:WeidentifywidespreadanddynamicRNAm6Amethylationinthedevelopingmousecerebellumandfurtheruncoverdistinctfeaturesofcontinuousandtemporal-specificm6Amethylationacrossthefourpostnataldevelopmentalprocesses.Temporal-specificm6ApeaksfromP7toP60exhibitremarkablechangesintheirdistributionpatternsalongthemRNAtranscripts.Wealsoshowspatiotemporal-specificexpressionofm6AwritersMETTL3,METTL14,andWTAPanderasersALKBH5andFTOinthemousecerebellum.EctopicexpressionofMETTL3mediatedbylentivirusinfectionleadstodisorganizedstructureofbothPurkinjeandglialcells.Inaddition,underhypobarichypoxiaexposure,Alkbh5-deletioncausesabnormalcellproliferationanddifferentiationinthecerebellumthroughdisturbingthebalanceofRNAm6Amethylationindifferentcellfatedeterminationgenes.Notably,nuclearexportofthehypermethylatedRNAsisenhancedinthecerebellumofAlkbh5-deficientmiceexposedtohypobarichypoxia.Conclusions:Together,ourfindingsprovidestrongevidencethatRNAm6Amethylationiscontrolledinaprecisespatiotemporalmannerandparticipatesintheregulationofpostnataldevelopmentofthemousecerebellum.Keywords:N6-methyladenosine,RNAmethylation,ALKBH5,METTL3,CerebellardevelopmentBackgroundEpigeneticregulation,includinghistonemodifications,DNAmodifications,andnon-codingRNAs,playscrucialrolesinbothembryonicandadultneurogenesis[1].Themostrecentlydiscoveredregulatorymodification,N6-me...