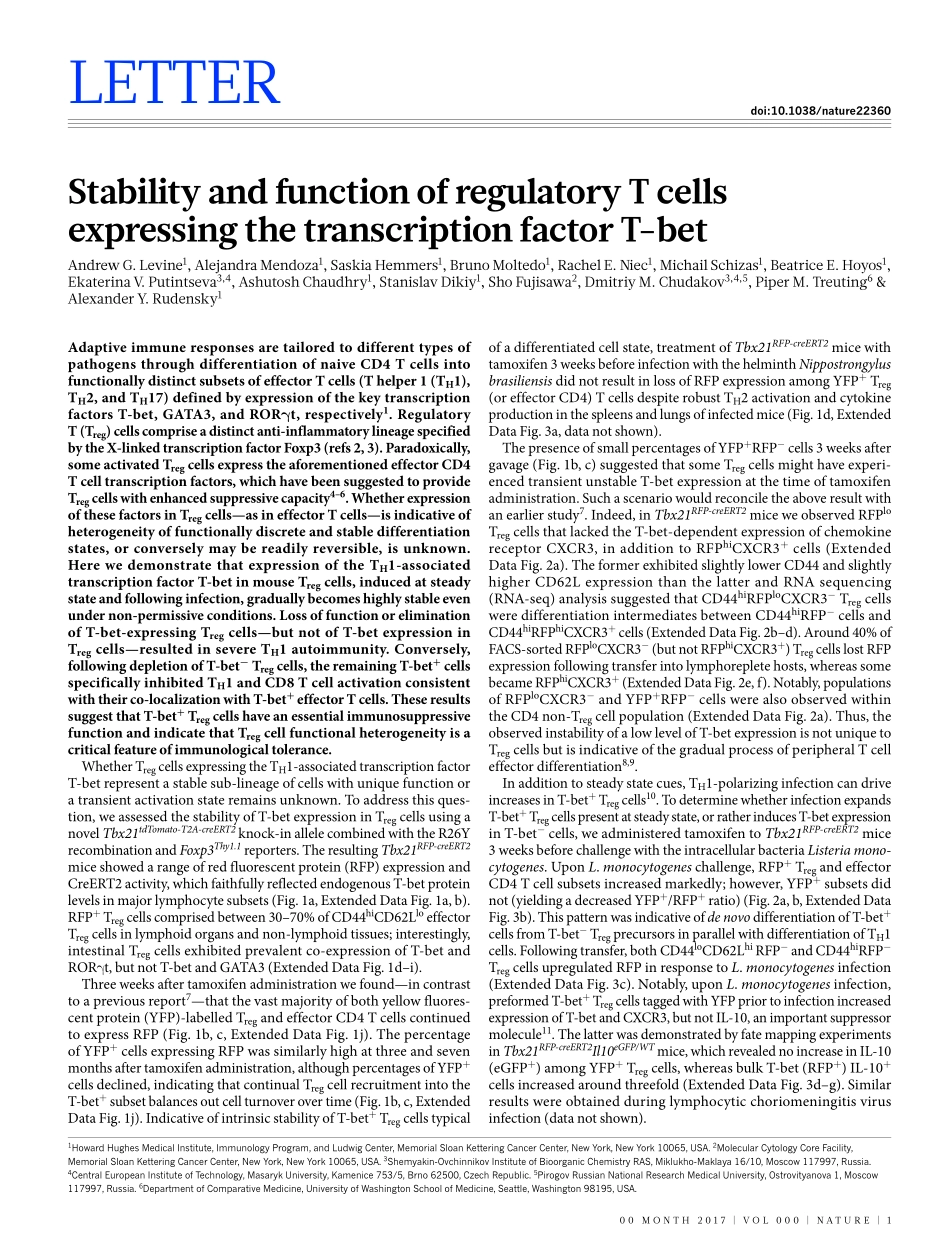
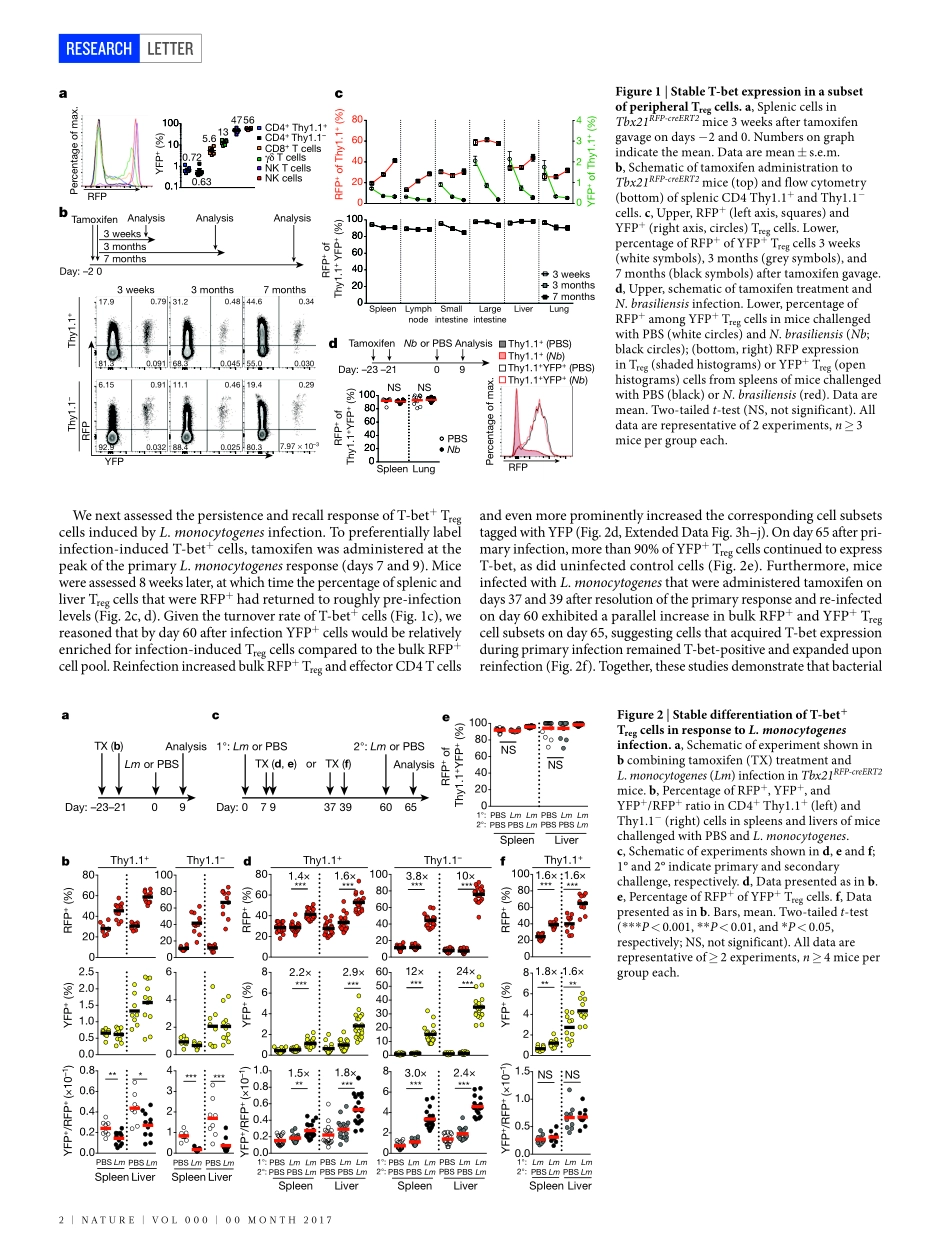
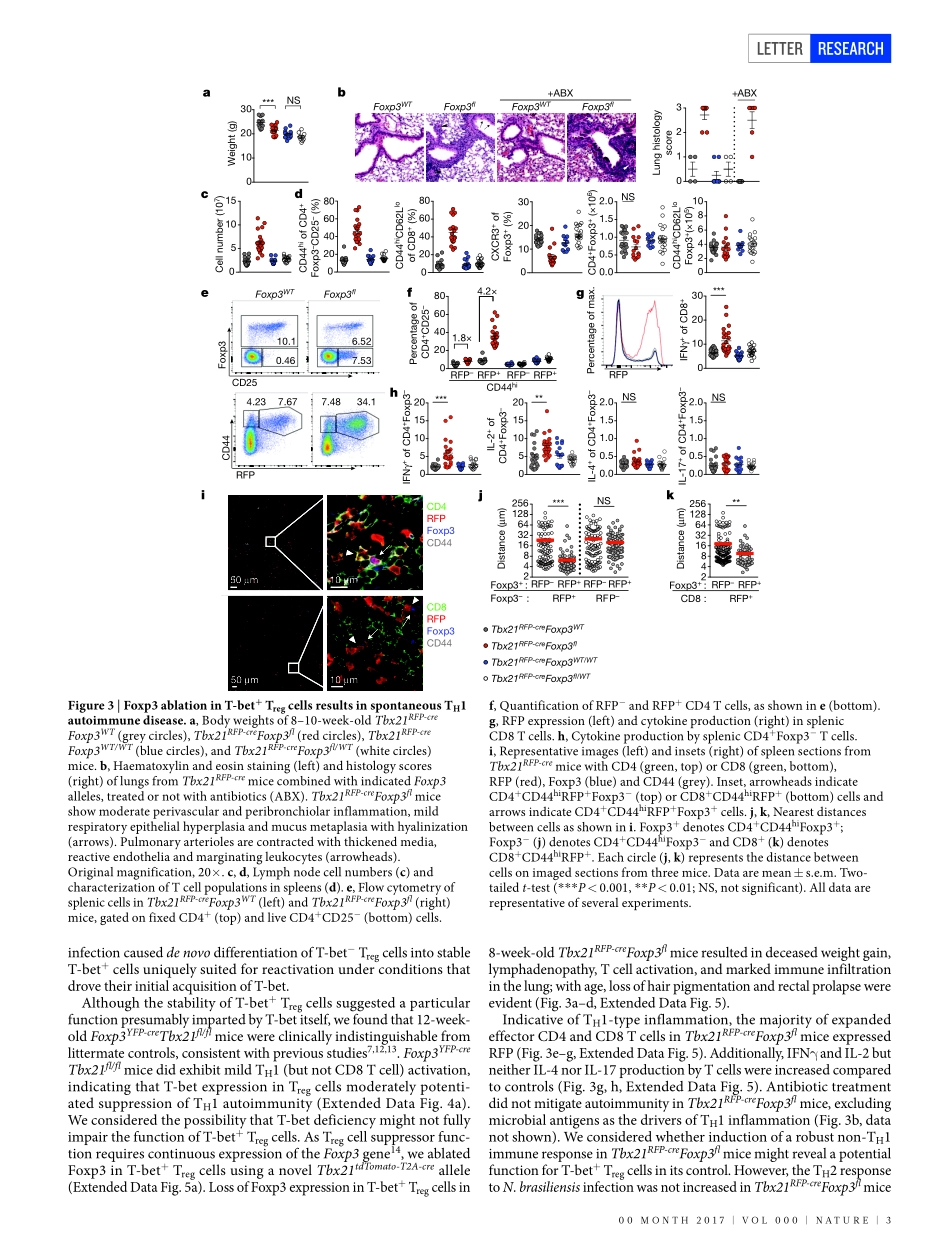
00Month2017|VoL000|nAtURE|1LEttERdoi:10.1038/nature22360StabilityandfunctionofregulatoryTcellsexpressingthetranscriptionfactorT-betAndrewG.Levine1,AlejandraMendoza1,Saskiahemmers1,BrunoMoltedo1,RachelE.niec1,MichailSchizas1,BeatriceE.hoyos1,EkaterinaV.Putintseva3,4,AshutoshChaudhry1,StanislavDikiy1,ShoFujisawa2,DmitriyM.Chudakov3,4,5,PiperM.treuting6&AlexanderY.Rudensky1AdaptiveimmuneresponsesaretailoredtodifferenttypesofpathogensthroughdifferentiationofnaiveCD4TcellsintofunctionallydistinctsubsetsofeffectorTcells(Thelper1(TH1),TH2,andTH17)definedbyexpressionofthekeytranscriptionfactorsT-bet,GATA3,andRORγt,respectively1.RegulatoryT(Treg)cellscompriseadistinctanti-inflammatorylineagespecifiedbytheX-linkedtranscriptionfactorFoxp3(refs2,3).Paradoxically,someactivatedTregcellsexpresstheaforementionedeffectorCD4Tcelltranscriptionfactors,whichhavebeensuggestedtoprovideTregcellswithenhancedsuppressivecapacity4–6.WhetherexpressionofthesefactorsinTregcells—asineffectorTcells—isindicativeofheterogeneityoffunctionallydiscreteandstabledifferentiationstates,orconverselymaybereadilyreversible,isunknown.HerewedemonstratethatexpressionoftheTH1-associatedtranscriptionfactorT-betinmouseTregcells,inducedatsteadystateandfollowinginfection,graduallybecomeshighlystableevenundernon-permissiveconditions.LossoffunctionoreliminationofT-bet-expressingTregcells—butnotofT-betexpressioninTregcells—resultedinsevereTH1autoimmunity.Conversely,followingdepletionofT-bet−Tregcells,theremainingT-bet+cellsspecificallyinhibitedTH1andCD8Tcellactivationconsistentwiththeirco-localizationwithT-bet+effectorTcells.TheseresultssuggestthatT-bet+TregcellshaveanessentialimmunosuppressivefunctionandindicatethatTregcellfunctionalheterogeneityisacriticalfeatureofimmunologicaltolerance.WhetherTregcellsexpressingtheTH1-associatedtranscriptionfactorT-betrepresentastablesub-lineageofcellswithuniquefunctionoratransientactivationstateremainsunknown.Toaddressthisques-tion,weassessedthestabilityofT-betexpressioninT...