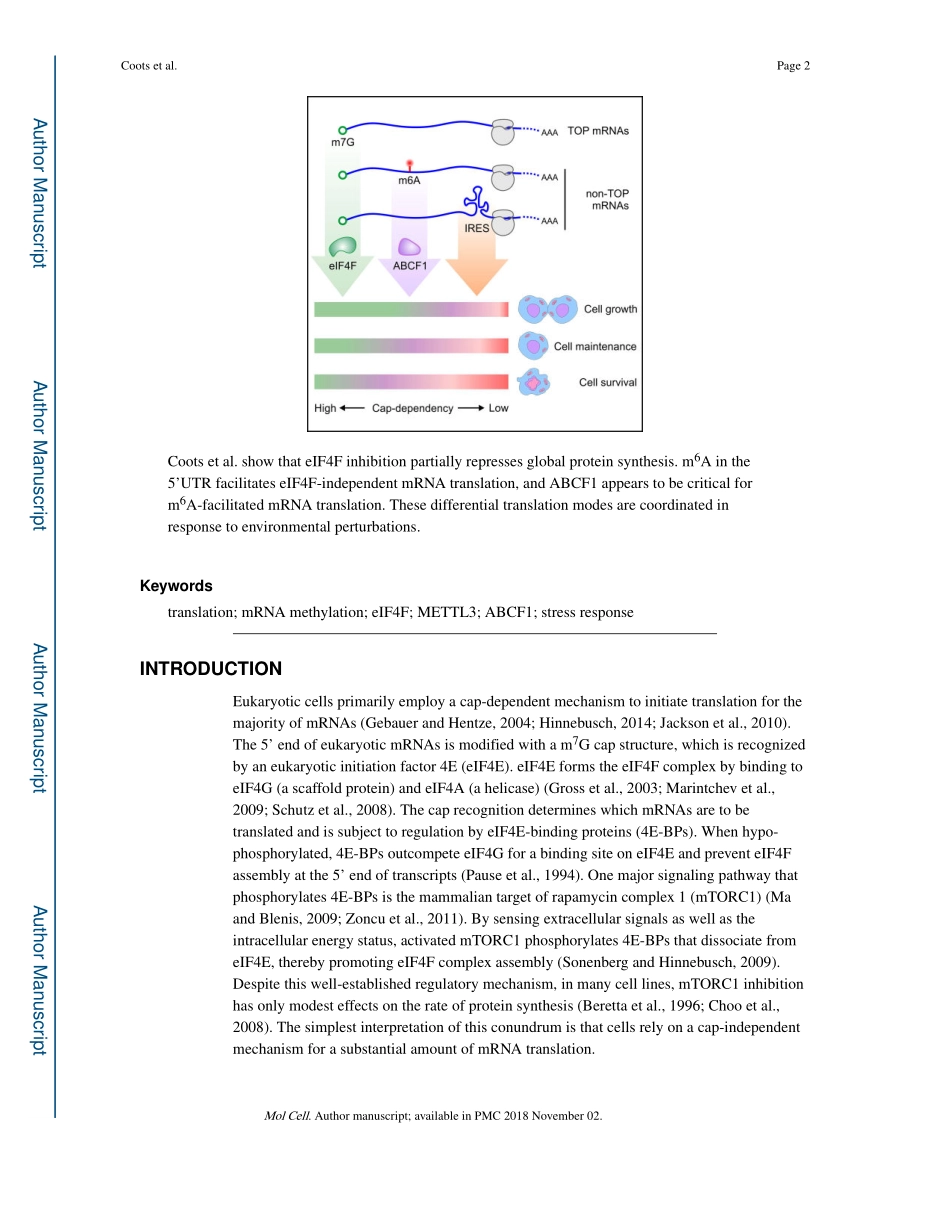
m6AFacilitateseIF4F-IndependentmRNATranslationRyanA.Coots1,2,3,Xiao-MinLiu1,3,YuanhuiMao1,LeimingDong1,JunZhou1,JiWan1,XingqianZhang1,andShu-BingQian1,2,4,*1DivisionofNutritionalSciences,CornellUniversity,Ithaca,NY14853,USA2GraduateFieldofNutritionalSciences,CornellUniversity,Ithaca,NY14853USASUMMARYIneukaryoticcells,proteinsynthesistypicallybeginswiththebindingofeIF4Ftothe7-methylguanylate(m7G)capfoundonthe5’endofthemajorityofmRNAs.Surprisingly,overalltranslationaloutputremainsrobustundereIF4Finhibition.ThebroadspectrumofeIF4F-resistanttranslatomesisincompatiblewithcap-independenttranslationmediatedbyinternalribosomeentrysites(IRES).Here,wereportthatN6-methyladenosine(m6A)facilitatesmRNAtranslationthatisresistanttoeIF4Finactivation.DepletionofthemethyltransferaseMETTL3selectivelyinhibitstranslationofmRNAsbearing5’UTRmethylation,butnotmRNAswith5’terminaloligopyrimidine(TOP)elements.WeidentifyABCF1asacriticalmediatorofm6A-promotedtranslationunderbothstressandphysiologicalconditions.SupportingtheroleofABCF1inm6A-facilitatedmRNAtranslation,ABCF1-sensitivetranscriptslargelyoverlapwithMETTL3-dependentmRNAtargets.ByillustratingthescopeandmechanismofeIF4F-independentmRNAtranslation,thesefindingsreshapeourcurrentperceptionsofcellulartranslationalpathways.InBrief*Correspondence:sq38@cornell.edu(S.-B.Q).3Theseauthorscontributedequally4LeadContactPublisher'sDisclaimer:ThisisaPDFfileofanuneditedmanuscriptthathasbeenacceptedforpublication.Asaservicetoourcustomersweareprovidingthisearlyversionofthemanuscript.Themanuscriptwillundergocopyediting,typesetting,andreviewoftheresultingproofbeforeitispublishedinitsfinalcitableform.Pleasenotethatduringtheproductionprocesserrorsmaybediscoveredwhichcouldaffectthecontent,andalllegaldisclaimersthatapplytothejournalpertain.AUTHORCONTRIBUTIONSR.A.C.andS.-B.Q.conceivedtheprojectanddesignedthestudy.R.A.C.performedmostoftheexperiments.X.-M.L.performedcapbindingandproteininteractionassaysaswellasRibo-seqandRNA-seq.Y.M.andJ.W.analyzedthesequen...