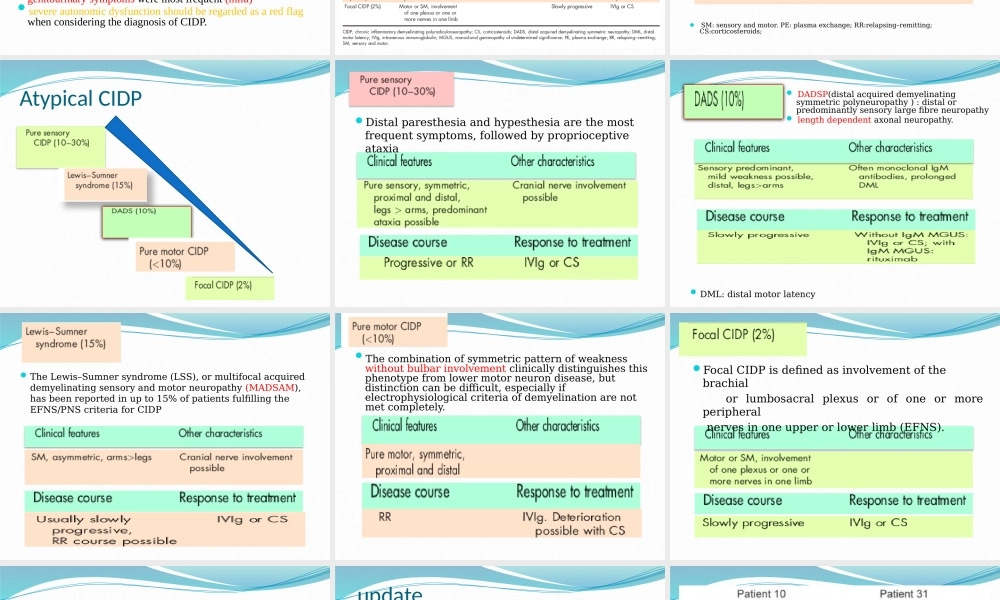
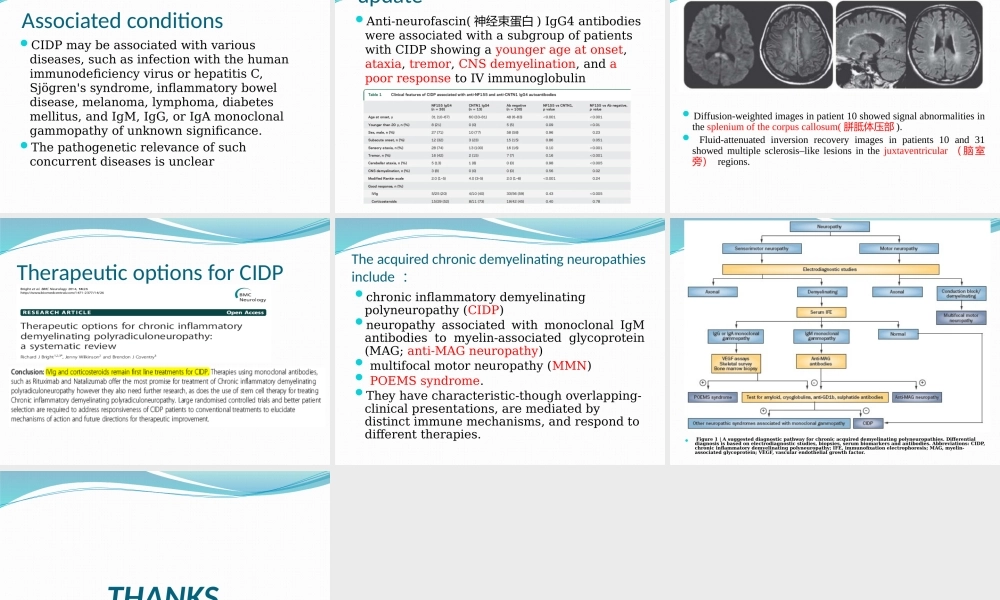
ChronicInflammatoryDemyelinatinPolyradiculoneuropathy:updateonclinicalfeatures,phenotypesandtreatmentoptionsDepartmentofNeurology,FujianProvincialHospitalXingyongChenIntroductionTraditionally,chronicinflammatorydemyelinatingpolyradiculoneuropathy(CIDP)hasbeenconsideredaheterogeneousdisorderincludingabroadspectrumofclinicalphenotypes.TheEuropeanFederationofNeurologicalSocieties/PeripheralNerveSociety(EFNS/PNS)CIDPtreatmentguidelinehasdefinedseveralclinicalpicturesasatypicalCIDPphenotypes,additionaltotheclassical(typical)pictureofCIDPprevalenceofaround6casesper100,000predominantlyaffectmales,andtypicallyoccurinmiddletooldageCIDPcanalsooccurinchildren.TheincidenceofCIDPincreaseswithage,risingto1.5timestheoverallaverageinpeopleover65yearsofageClinicalpresentationClassicCIDPischaracterizedbytheoccurrenceofsymmetricalweaknessinbothproximalanddistalmuscles,impairedsensationandparasthesiaandabsentordiminishedtendonreflexesThediseaseevolvesovermorethan8weeks,thusdistinguishingtheconditionfromGBSwhichhasanacuteonset.Thetimecoursemayberelapsing,chronicprogressive,monophasicorGBSlikeonset.NewlyrecognisedclinicalfeaturesinCIDPAcuteonsetofCIDPmayoccurinupto18%ofCIDPpatients,resemblingtheGBSdiagnosiswaschangedtoCIDPin5%ofGBSpatientsFatiguecanbethemaincomplaintinCIDPpatients(75%)Activity-inducedweaknessSeverepainispresentinonlyaminorityofCIDPpatients;TremorcanbeadisablingsymptominCIDP(50%)ahigherincidenceofalmost40%ofrestlesslegssyndromeinpatientswithCIDPAutonomicsymptoms:23%,ofwhichgastrointestinalandgenitourinarysymptomsweremostfrequent(mild)severeautonomicdysfunctionshouldberegardedasaredflagwhenconsideringthediagnosisofCIDP.CIDPPHENOTYPESTheclinicalpresentationofCIDPisvariabledeterminedbythenumberanddistributionofthedemyelinatingperipheralnervelesionsSM:sensoryandmotor.PE:plasmaexchange;RR:relapsing–remitting;CS:corticosteroids;AtypicalCIDPDistalparesthesiaandhypesthesiaarethemostfrequentsymptoms,followedbyproprioceptiveataxiaDA...