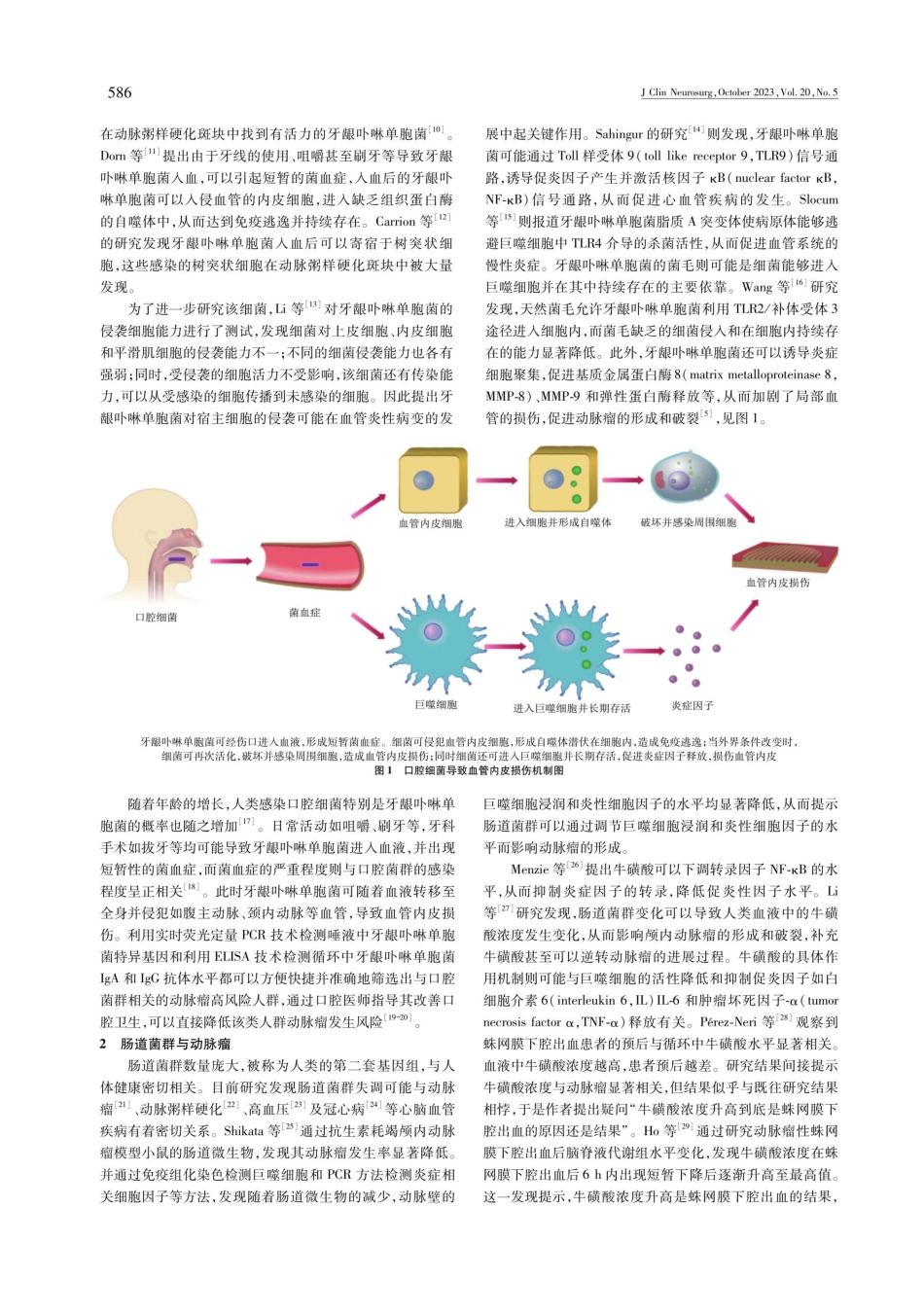
临床神经外科杂志2023年第20卷第5期585D0I:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7770.2023.05.021·综述·口腔菌群和肠道菌群对颅内动脉瘤的影响雷霆,石祥恩【摘要】动脉瘤是一种常见的脑血管病,成年人群发病率约3%左右。动脉瘤有一定的破裂风险,而一旦发生破裂,可能严重影响患者的生活质量,甚至导致患者死亡。动脉瘤形成原因较多且复杂,目前研究表明,口腔细菌可以通过免疫逃逸等机制,定植并直接参与血管炎症反应,还可以通过多种途径促进巨噬细胞M1极化,导致基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)活化,细胞外基质重塑,激活核因子kB(nuclearfactorkB,NF-kB)途径,释放大量炎症因子,破坏动脉壁,促进动脉瘤形成和破裂。肠道细菌则可通过人体内代谢物影响炎症细胞如巨噬细胞介导的炎症反应和巨噬细胞M1/M2比率,从而影响脑动脉瘤的发生发展过程。本综述回顾了人体微生物在颅内动脉瘤成因和破裂中的影响及其潜在机制。【关键词】动脉瘤;口腔菌群;肠道菌群;巨噬细胞【中图分类号】R654.3;R651EffectsoforalandintestinalmicrobiotaonintracranialaneurysmsLEITing,SHIXiang'en.DepartmentofNeurosurgery,FuxingHospital,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100038,ChinaCorrespondingauthor:SHIXiang'enAbstract:Aneurysmisacommoncerebrovasculardisease,withanincidenceof3%inadults.Oncetheaneurysmisruptured,itmayseriouslyaffectthepatient'squalityoflifeandevenleadtodeath.Therearemanyandcomplexreasonsfortheformationofaneurysms.Currentstudieshaveshownthatperiodontalpathogenscancolonizeanddirectlyparticipateinvascularinflammationthroughimmuneescape,andtheycanalsopromotethepolarizationofmacrophageMl,resultinginmatrixmetalloproteinase(MMP)activation,extracellularmatrixremodeling,activationofthenuclearfactorkB(NF-kB)pathway,releaseofinflammatorycytokines,destructionofarterialwall,andpromotionofaneurysmformationandrupture.Thegutmicrobiomecanaffectinflammatorycellssuchasthemacrophage-mediatedinflammatoryresponseandthemacrophageM1/M2ratiothroughhumanmetabolites,thusaffectingtheoccurrenceanddevelopmentofcerebralaneurysms.Wereviewtheinfluenceandpotentialofhumanmicroorganismsinthecauseandruptureofintracranialaneurysms.Keywords:aneurysm;periodontalpathogens;gutmicrobiome;macrophages颅内动脉瘤是...