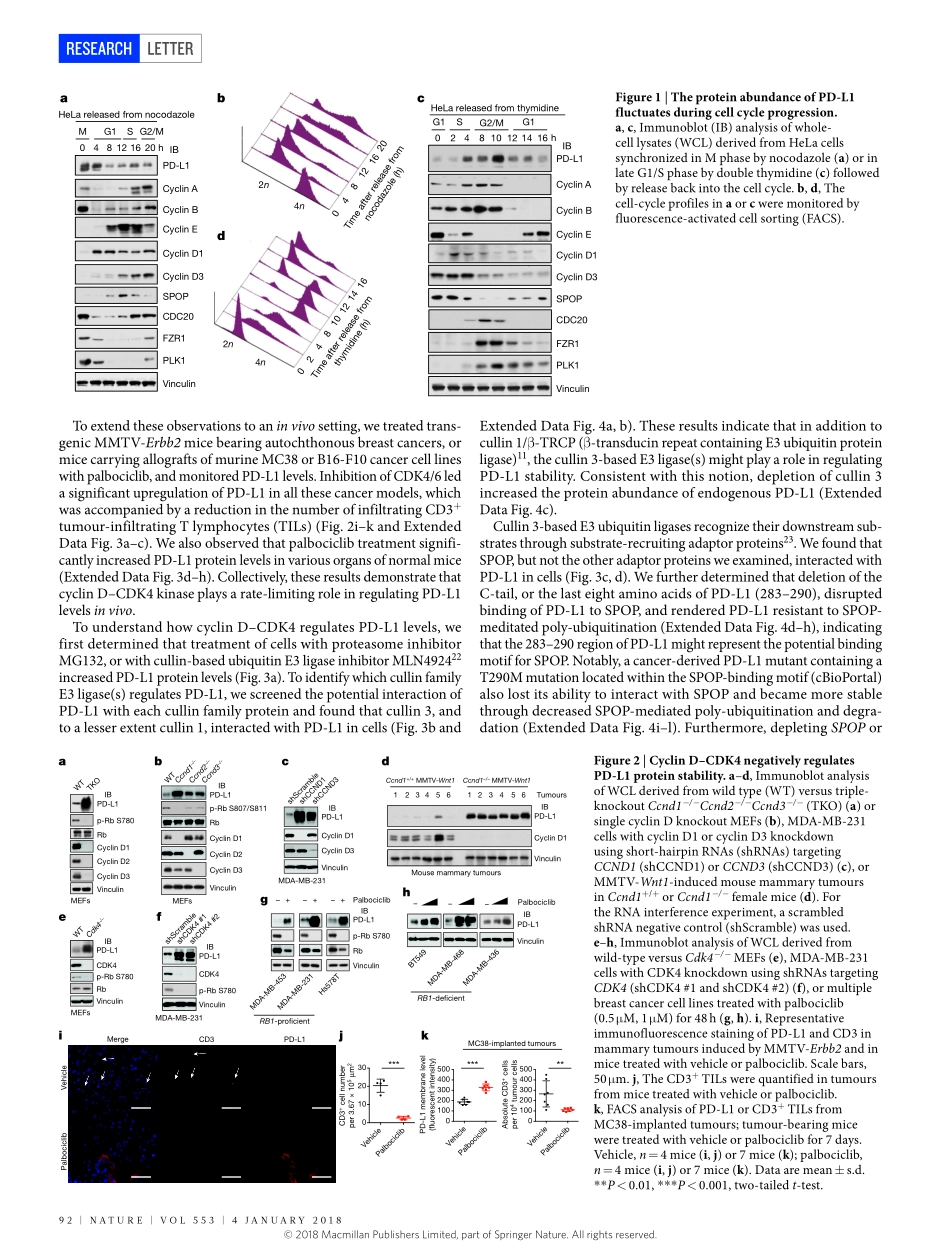
4january2018|VOL553|naTurE|91LETTErdoi:10.1038/nature25015CyclinD–CDK4kinasedestabilizesPD-L1viacullin3–SPOPtocontrolcancerimmunesurveillancejinfangZhang1*,XiaBu2*,HaizhenWang3*,yashengZhu4,yanGeng3,naoeTairanihira1,yuyongTan1,5,yanpengCi1,6,FeiWu1,7,XiangpengDai1,jianpingGuo1,yu-HanHuang1,CaoqiFan3,8,Shanchengren4,yinghaoSun4,Gordonj.Freeman2§*,PiotrSicinski3§*&WenyiWei1§*Treatmentsthattargetimmunecheckpoints,suchastheonemediatedbyprogrammedcelldeathprotein1(PD-1)anditsligandPD-L1,havebeenapprovedfortreatinghumancancerswithdurableclinicalbenefit1,2.However,manypatientswithcancerfailtorespondtocompoundsthattargetthePD-1andPD-L1interaction,andtheunderlyingmechanism(s)isnotwellunderstood3–5.RecentstudiesrevealedthatresponsetoPD-1–PD-L1blockademightcorrelatewithPD-L1expressionlevelsintumourcells6,7.Hence,itisimportanttounderstandthemechanisticpathwaysthatcontrolPD-L1proteinexpressionandstability,whichcanofferamolecularbasistoimprovetheclinicalresponserateandefficacyofPD-1–PD-L1blockadeinpatientswithcancer.HereweshowthatPD-L1proteinabundanceisregulatedbycyclinD–CDK4andthecullin3–SPOPE3ligaseviaproteasome-mediateddegradation.InhibitionofCDK4andCDK6(hereafterCDK4/6)invivoincreasesPD-L1proteinlevelsbyimpedingcyclinD–CDK4-mediatedphosphorylationofspeckle-typePOZprotein(SPOP)andtherebypromotingSPOPdegradationbytheanaphase-promotingcomplexactivatorFZR1.Loss-of-functionmutationsinSPOPcompromiseubiquitination-mediatedPD-L1degradation,leadingtoincreasedPD-L1levelsandreducednumbersoftumour-infiltratinglymphocytesinmousetumoursandinprimaryhumanprostatecancerspecimens.Notably,combiningCDK4/6inhibitortreatmentwithanti-PD-1immunotherapyenhancestumourregressionandmarkedlyimprovesoverallsurvivalratesinmousetumourmodels.OurstudyuncoversanovelmolecularmechanismforregulatingPD-L1proteinstabilitybyacellcyclekinaseandrevealsthepotentialforusingcombinationtreatmentwithCDK4/6inhibitorsandPD-1–PD-L1immunecheckpointblockadetoenhancetherapeuticefficacyforhumancancers.Deregulatedce...