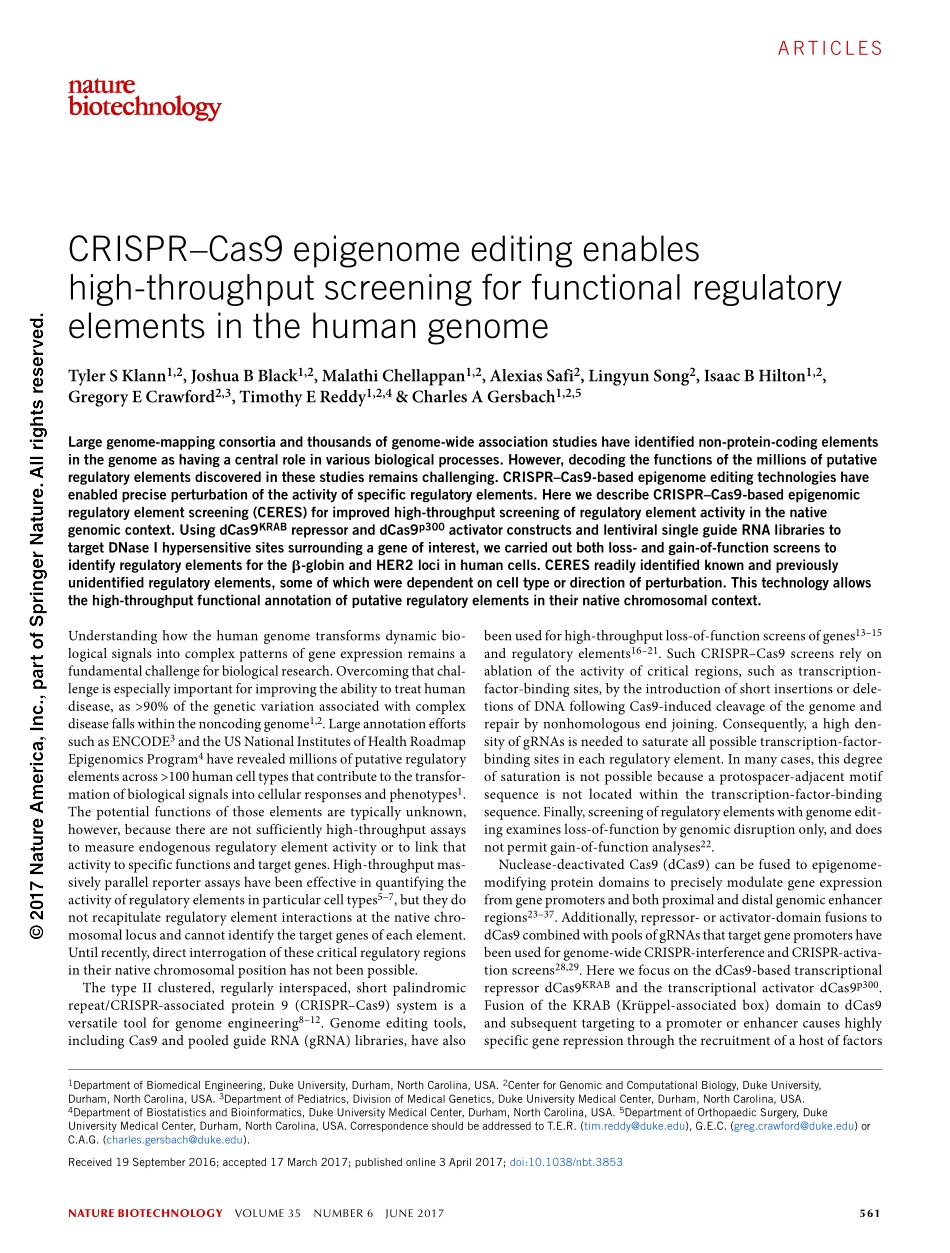
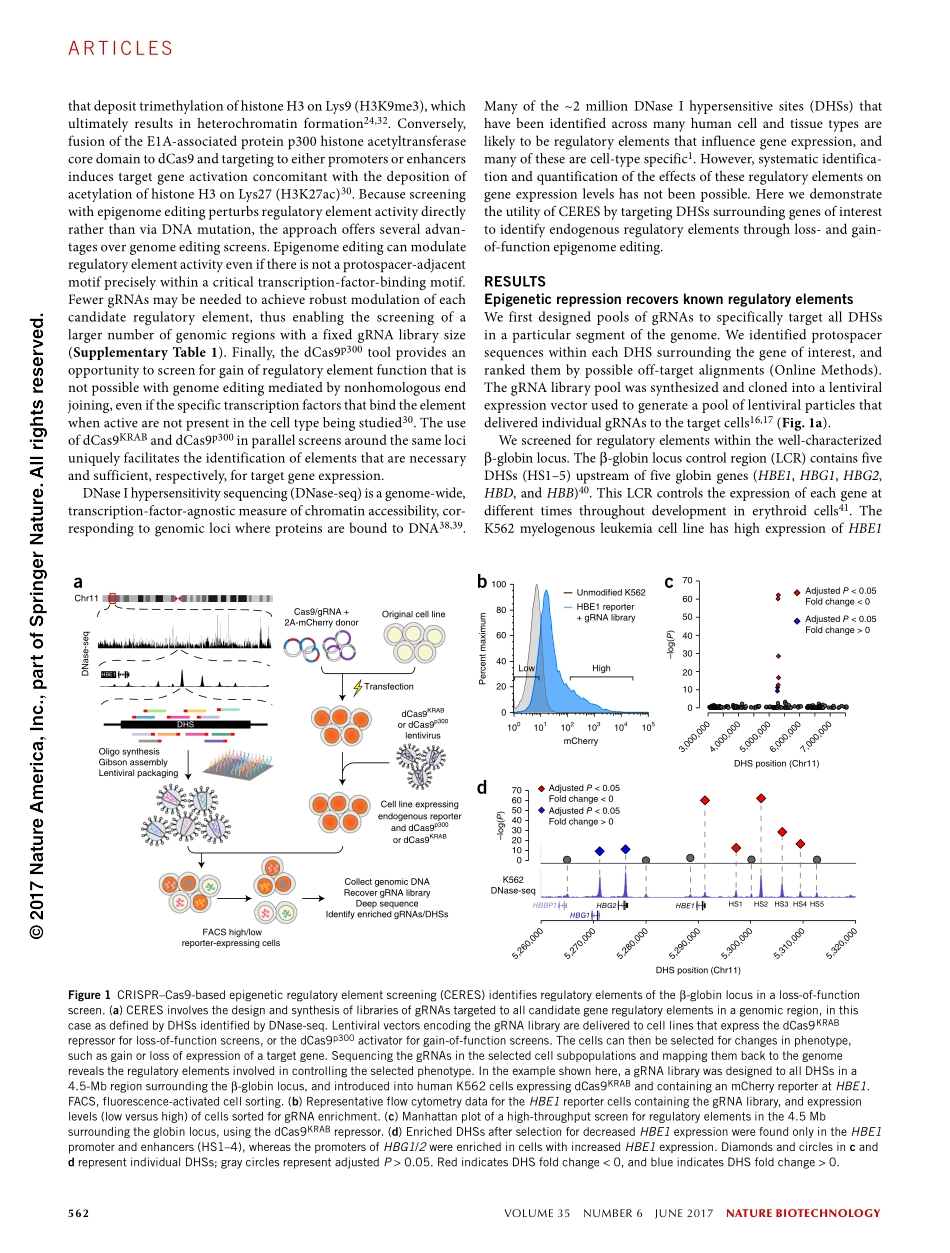
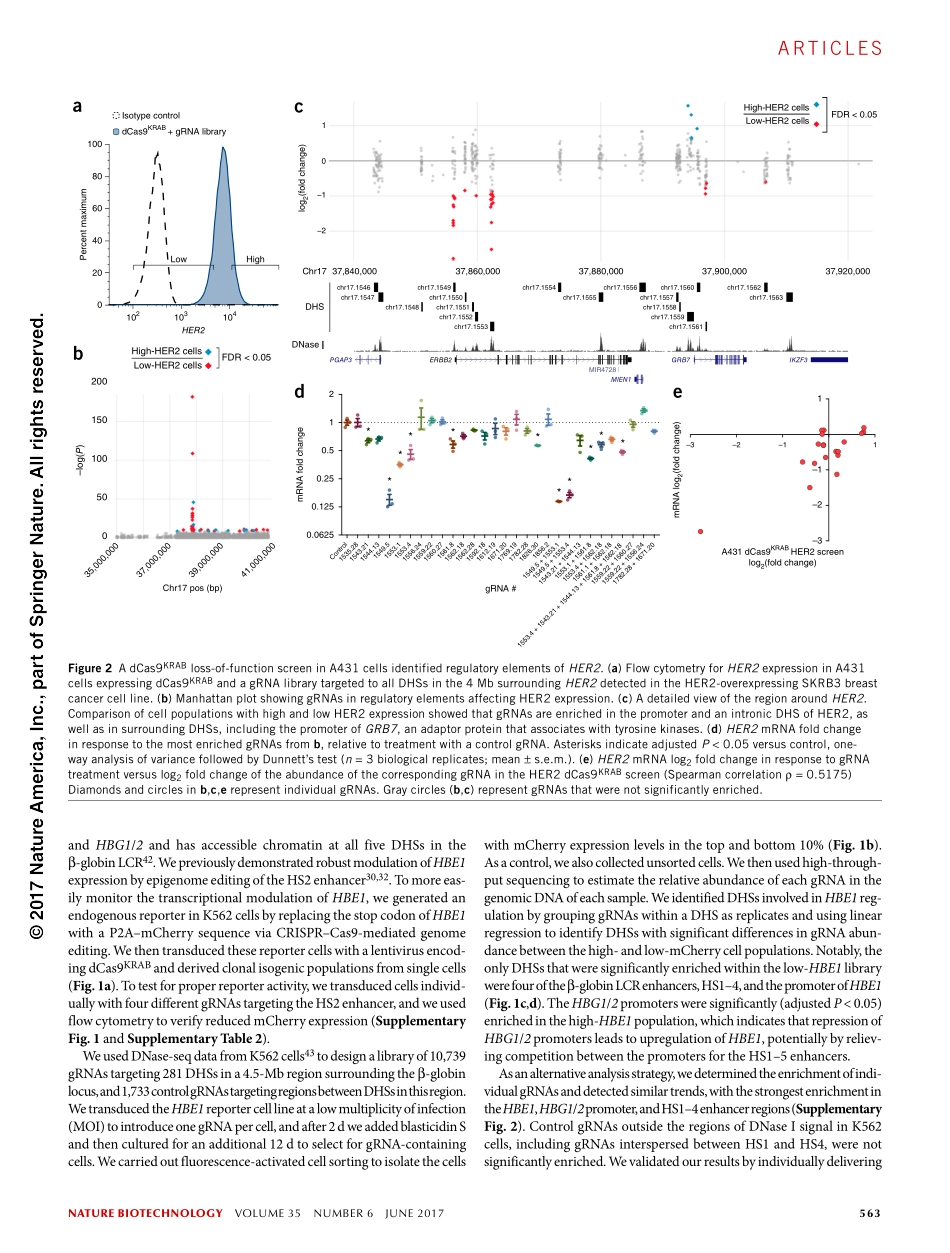
naturebiotechnologyVOLUME35NUMBER6JUNE2017561ArticlesUnderstandinghowthehumangenometransformsdynamicbio-logicalsignalsintocomplexpatternsofgeneexpressionremainsafundamentalchallengeforbiologicalresearch.Overcomingthatchal-lengeisespeciallyimportantforimprovingtheabilitytotreathumandisease,as>90%ofthegeneticvariationassociatedwithcomplexdiseasefallswithinthenoncodinggenome1,2.LargeannotationeffortssuchasENCODE3andtheUSNationalInstitutesofHealthRoadmapEpigenomicsProgram4haverevealedmillionsofputativeregulatoryelementsacross>100humancelltypesthatcontributetothetransfor-mationofbiologicalsignalsintocellularresponsesandphenotypes1.Thepotentialfunctionsofthoseelementsaretypicallyunknown,however,becausetherearenotsufficientlyhigh-throughputassaystomeasureendogenousregulatoryelementactivityortolinkthatactivitytospecificfunctionsandtargetgenes.High-throughputmas-sivelyparallelreporterassayshavebeeneffectiveinquantifyingtheactivityofregulatoryelementsinparticularcelltypes5–7,buttheydonotrecapitulateregulatoryelementinteractionsatthenativechro-mosomallocusandcannotidentifythetargetgenesofeachelement.Untilrecently,directinterrogationofthesecriticalregulatoryregionsintheirnativechromosomalpositionhasnotbeenpossible.ThetypeIIclustered,regularlyinterspaced,shortpalindromicrepeat/CRISPR-associatedprotein9(CRISPR–Cas9)systemisaversatiletoolforgenomeengineering8–12.Genomeeditingtools,includingCas9andpooledguideRNA(gRNA)libraries,havealsobeenusedforhigh-throughputloss-of-functionscreensofgenes13–15andregulatoryelements16–21.SuchCRISPR–Cas9screensrelyonablationoftheactivityofcriticalregions,suchastranscription-factor-bindingsites,bytheintroductionofshortinsertionsordele-tionsofDNAfollowingCas9-inducedcleavageofthegenomeandrepairbynonhomologousendjoining.Consequently,ahighden-sityofgRNAsisneededtosaturateallpossibletranscription-factor-bindingsitesineachregulatoryelement.Inmanycases,thisdegreeofsaturationisnotpossiblebecauseaprotospacer-adjacentmotifsequenceisnotlocatedwithinth...