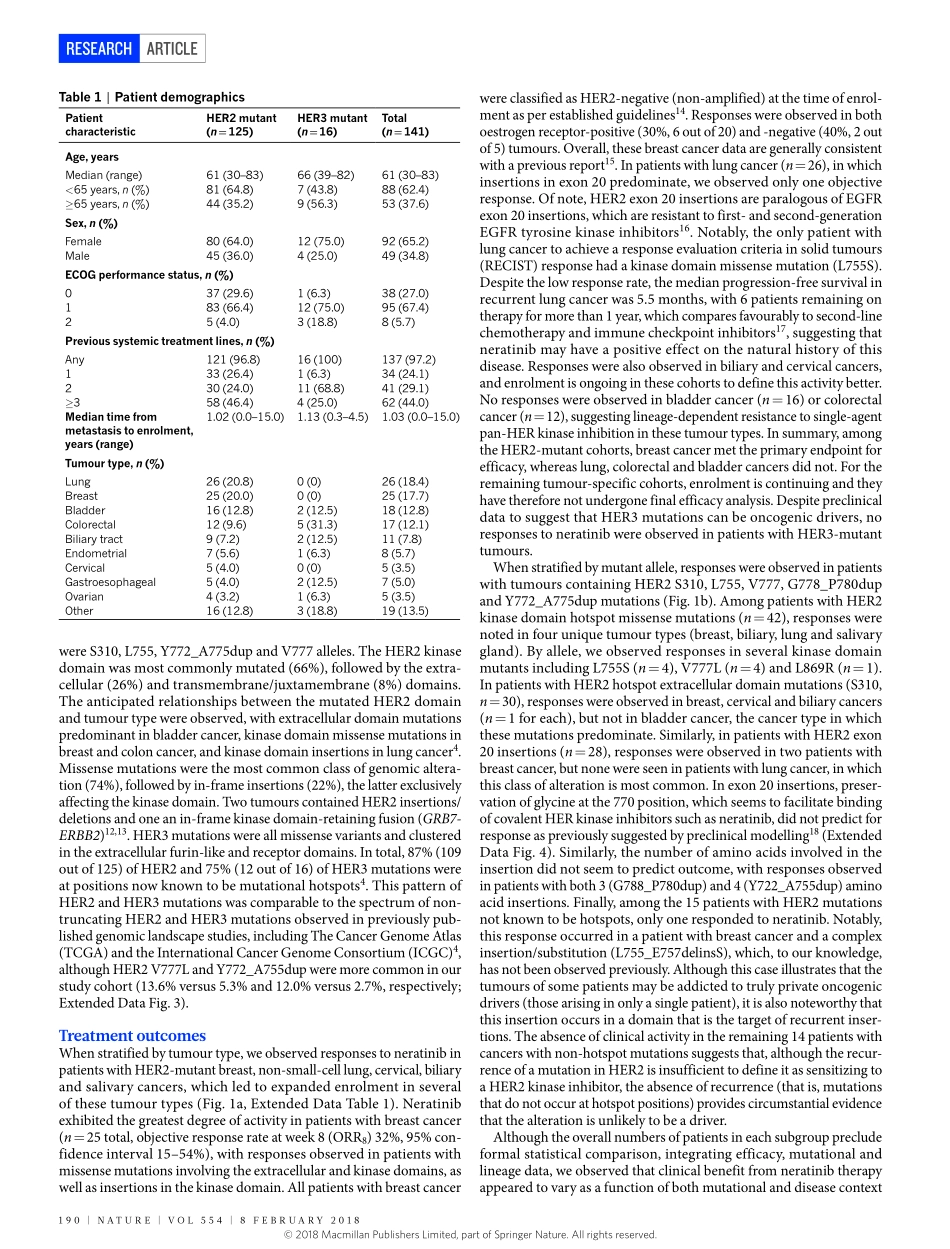
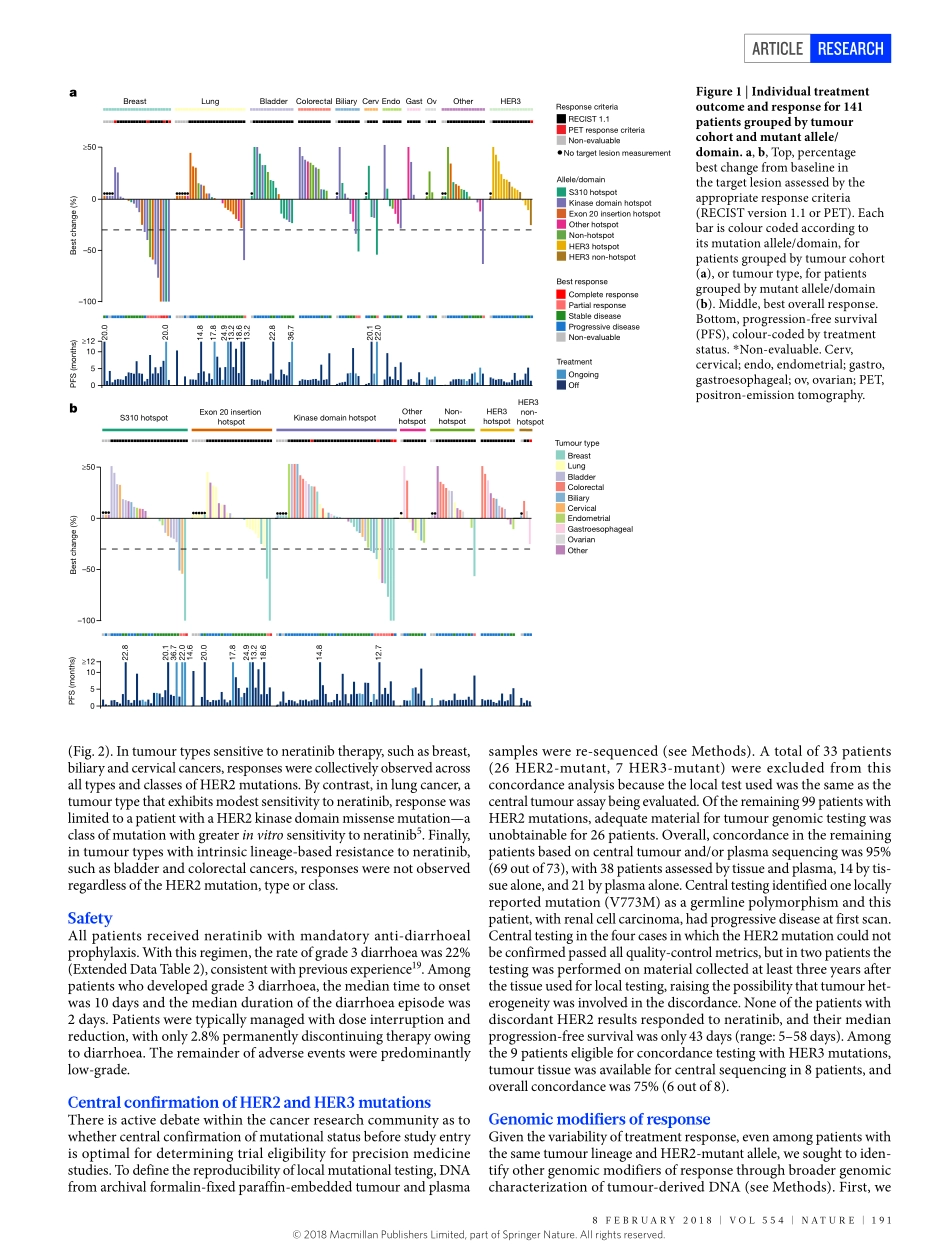
8february2018|VOL554|NaTure|189arTicLedoi:10.1038/nature25475HERkinaseinhibitioninpatientswithHER2-andHER3-mutantcancersDavidM.Hyman1,Sarinaa.Piha-Paul2,HelenWon1,Jordirodon3,cristinaSaura3,Geoffreyi.Shapiro4,DejanJuric5,Davidi.Quinn6,VictorMoreno7,bernardDoger7,ingrida.Mayer8,Valentinaboni9,emilianocalvo9,ShereneLoi10,albertc.Lockhart11,JosephP.erinjeri1,MaurizioScaltriti1,Garya.ulaner1,JuberPatel1,JiabinTang1,Hannahbeer1,S.DuyguSelcuklu1,aphrothitiJ.Hanrahan1,Nancybouvier1,MyraMelcer1,rajmohanMurali1,alisonM.Schram1,LillianM.Smyth1,KomalJhaveri1,bobT.Li1,alexanderDrilon1,JamesJ.Harding1,Gopaiyer1,barryS.Taylor1,Michaelf.berger1,richarde.cutlerJr12,fengXu12,annabutturini12,LisaD.eli12,GraceMann12,cynthiafarrell12,alshadS.Lalani12,richardP.bryce12,carlosL.arteaga8,fundaMeric-bernstam2,Josébaselga1&Davidb.Solit1GenomicprofilingofhumancancershasidentifiedrecurrentsomaticmutationsofHER2(encodedbyERBB2)andHER3(ERBB3),typicallyoccurringintheabsenceofgeneamplification1–3.MutationsinHER2areclusteredintheextracellular,transmembraneandkinasedomains.Unlikeothermutantoncogenes,suchasBRAForKRAS,nosinglemutantallelepredominatesandtheprecisedistributionofmutationsvariesbytumourtype4.Bycontrast,HER3mutationsclusterprimarilyintheextracellulardomainandtoalesserextentinthekinasedomain.AlthoughHER2andHER3mutationsarefoundinawidevarietyofcancers,theiroverallprevalencedoesnotexceed10%inanyindividualtumourtype,andtherateismoretypicallylessthan5%forHER2andlessthan1%forHER3.Biologicalmodellinghasyieldedconflictingfindingsastothefunc-tionalconsequencesofHER2andHER3mutations.Substantialdatasuggestthatasubsetofthesemutationsinduceligand-independentconstitutiveHER2receptorsignallingandpromoteoncogenesis5–7.Themechanismoftheseoncogeniceffectsseemstodifferbyvariant,withsomecausingenhancedHER2kinaseactivityandotherscausingreceptordimerization5,8.MutationsinHER3,whichinitswild-typeconfigurationhasimpairedkinasefunction,seemtorelyonwild-typeHER2toexertitsoncogeniceffects7.Mostpreclinicaldatat...