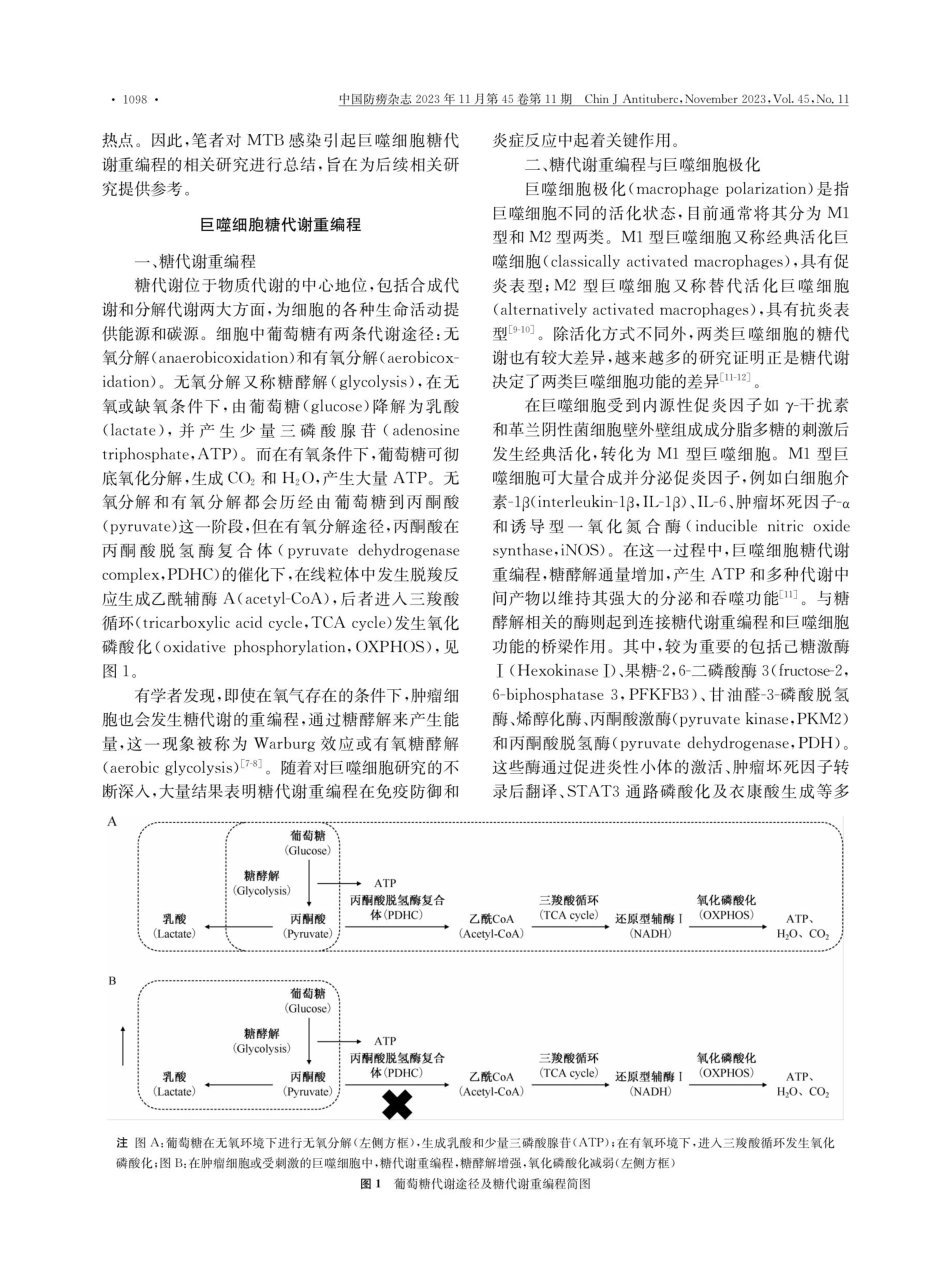
中国防痨杂志2023年11月第45卷第11期ChinJAntituberc,November2023,Vol.45,No.11·1097·综述·巨噬细胞糖代谢重编程在结核分枝杆菌感染中的研究进展南岳龙美贞董玉慧慧王元智周向梅【摘要】巨噬细胞是参与先天性免疫的重要细胞,也是结核分枝杆菌感染的主要目标。研究发现,免疫细胞代谢重编程与其功能密切相关。在感染的早期阶段,巨噬细胞以M1极化为主,糖代谢方式从线粒体氧化磷酸化转变为有氧糖酵解(Warburg效应),促进炎性因子的分泌;在感染后期,巨噬细胞从有氧糖酵解转变为线粒体氧化磷酸化,从而抑制巨噬细胞促炎和抗菌反应。全面认识结核分枝杆菌感染期间巨噬细胞代谢与功能的关系有助于宿主导向疗法的发展。本文中,笔者对结核分枝杆菌感染期间巨噬细胞糖代谢重编程的相关研究进行了总结,以期为结核病的防治提供新思路。【关键词】分枝杆菌,结核;巨噬细胞;免疫,细胞;代谢;糖酵解;综述文献(主题)【中图分类号】R392.12;R52ResearchprogressonmacrophageglucosemetabolismreprogramminginMycobacteriumtuberculosisinfectionNanYue,LongMeizhen,DongYuhui,WangYuanzhi,ZhouXiangmei.NationalKeyLaboratoryofVeterinaryPublicHealthandSafety,CollegeofVeterinaryMedicine,ChineseAgriculturalUniversity,Beijing100193,ChinaCorrespondingauthor:ZhouXiangmei,Email:zhouxm@cau.edu.cn[Abstract]MacrophagesareimportantcellsinvolvedininnateimmunityandalsothemaintargetofMycobacteriumtuberculosisinfection.Itwasfoundthatmetabolicreprogrammingofimmunecellsiscloselyrelatedtotheirfunctions.Intheearlystageofinfection,themainchangeofmacrophagesisM1polarized,andthemodeofglucosemetabolismchangesfrommitochondrialoxidativephosphatetoaerobicglycolysis(Warburgeffect),whichpromotesthesecretionofinflammatoryfactors;whileinthelatestagesofinfection,themodeofglucosemetabolismofmacrophageschangesfromaerobicglycolysistomitochondrialoxidativephosphorylation,whichinhibitsmacrophageproinflammatoryandantimicrobialresponses.AcomprehensiveunderstandingoftherelationshipbetweenmacrophagemetabolismandfunctionduringMycobacteriumtuberculosisinfectionishelptothedevelopmentofhostdirectedtherapy.Inthisarticle,theauthorsummarizedtherelatedresearchonmacrophageglycometabolismreprogram...