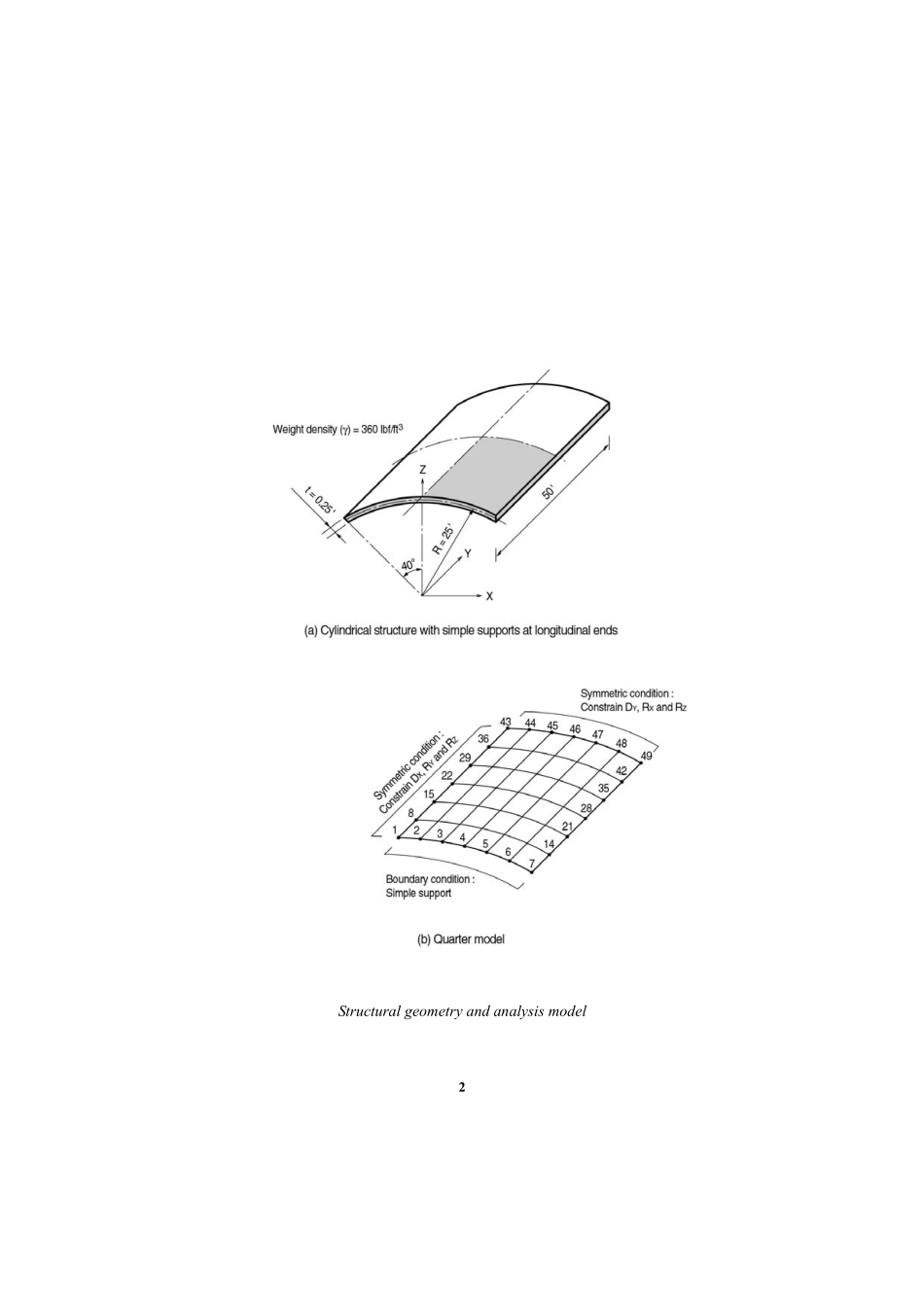
1Example22TitleSimplysupportedcylindricalshellDescriptionComputetheaxialdeformationsandverticaldisplacementsofashellstructureunderitsselfweight.Onlyaquartermodelmaybeanalyzedduetosymmetry.2StructuralgeometryandanalysismodelExample603MODELAnalysisType3-DstaticanalysisUnitSystemft,lbfDimensionLength25ftRadius25ftCentralangle40˚ElementPlateelement(Thicktype)MaterialModulusofelasticityE=4.32×108lbf/ft2Weightdensityγ=360lbf/ft3ElementPropertyElementsizea×b=[25/6ft×40×(π/180)]×[25/6ft]Thicknesst=0.25ftBoundaryConditionNodes1~7;ConstrainDx,DzandRy.(Simplesupports)Nodes1~43;ConstrainDx,RyandRz.(SymmetricaboutY-Zplane)(atanincrementof7)Nodes43~49;ConstrainDy,RxandRz.(SymmetricaboutX-ZplaneatY=25ft)LoadCaseSelfweightisimposedinthe-Zdirection.4ResultsAxialdisplacementsofthestructureVerticaldisplacementsofthestructureExample605Displacements6ComparisonofResultsUnit:ftAxialdeformation(δY)Verticaldisplacement(δZ)NodeTheoreticalSAP2000MIDAS/GenNodeTheoreticalSAP2000MIDAS/Gen10.00040.00.0430.0450.0460.04620.00090.00050.0005440.0270.0310.03130.00200.00180.001845-0.018-0.013-0.01340.00300.00290.002946-0.082-0.078-0.07850.00210.00240.002447-0.155-0.155-0.1556-0.0016-0.0017-0.001748-0.241-0.234-0.2347-0.0120-0.0118-0.011849-0.309-0.307-0.307ReferencesMacNeal,R.H.andHarder,R.L.,“AProposedStandardSetofProblemstoTestFiniteElementAccuracy”,FiniteElementsinAnalysisandDesign1,1985,pp.3-20,North-Holland.Zienkiewicz,O.C.,“TheFiniteElementMethod”,McGraw-Hill,1977.Scordelis,A.C.,andLo,K.S.,“ComputerAnalysisofCylindricalShells”,JournaloftheAmericanConcreteInstitute,Vol.61,May1964.