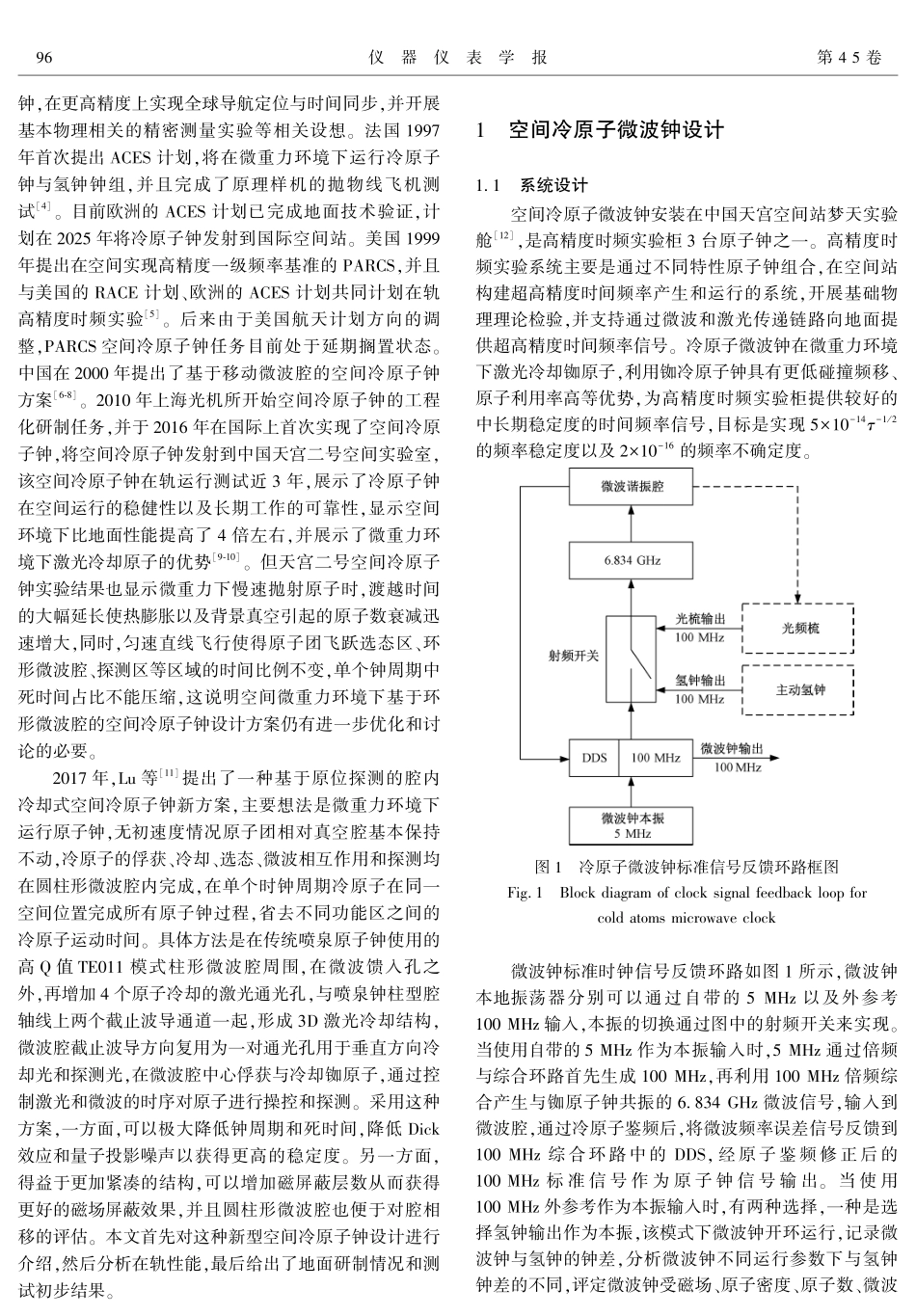
第45卷第2期2024年2月仪器仪表学报ChineseJournalofScientificInstrumentVol.45No.2Feb.2024DOI:10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2311838收稿日期:2023-08-27ReceivedDate:2023-08-27∗基金项目:国家自然科学基金(12304550,12004401)项目资助基于腔内原位探测的空间冷原子微波钟∗吕德胜,任伟,项静峰,赵剑波,邓思敏达(中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所空天激光技术与系统部上海201800)摘要:原子钟作为目前最精密的计时仪器,在国民经济和国家安全各领域发挥着重要作用。在地球轨道卫星上运行高精度原子钟,可以在地球大范围内开展高精度时间同步与比对。不同于以往通过抛射冷原子团两次经过微波腔实现Ramsey微波作用的空间冷原子钟,提出了一种新型的基于腔内原位探测的空间冷原子微波钟方案,在同一微波谐振腔内先后完成铷87原子的激光冷却、原子微波相互作用、冷原子探测等过程。该方案可以更好的利用微重力环境提高钟周期中原子与微波相互作用时间的占空比,从而有效减小Dick效应对原子钟性能的影响。介绍了冷原子微波钟系统设计与工作原理,给出了微重力环境下性能分析和预期指标,最后展示了冷原子微波钟地面测试中获得的大约为1.35×10-12τ-1/2的频率稳定度,初步展示了新型空间冷原子钟方案的可行性。关键词:原子钟;微重力;微波腔;空间站;频率稳定度中图分类号:TH7文献标识码:A国家标准学科分类代码:410.55Spacecoldatomsmicrowaveclockbasedonin-situdetectioninthecavityLyuDesheng,RenWei,XiangJingfeng,ZhaoJianbo,DengSiminda(ResearchCenterforAerospaceLaserandSystems,ShanghaiInstituteofOpticsandFineMechanics,ChineseAcademyofSciences,Shanghai201800,China)Abstract:Theatomicclock,asthemostprecisetiminginstrumentatpresent,isplayinganimportantroleinvariousfieldsofnationaleconomyandsecurity.Byoperatingatomicclocksonearthorbitsatellites,manyhigh-precisiontimesynchronizationandcomparison-relatedapplicationscanbeimplementedonalargescaleontheearth.Unlikepreviousspacecoldatomicclocksthatachievemicrowaveandatomsinteractionbylaunchingcoldatomscloudtotravelingtwomicrowavecavities,thisarticleproposesanewspacecoldatomicmicrowaveclockschemebasedoninsitudetectioninthecavity.Thisschemecompletesthelasercoolingofrubidium87atoms,atomsandmicrowaveinteraction,coldatomdetection,andotherclockprocessesint...