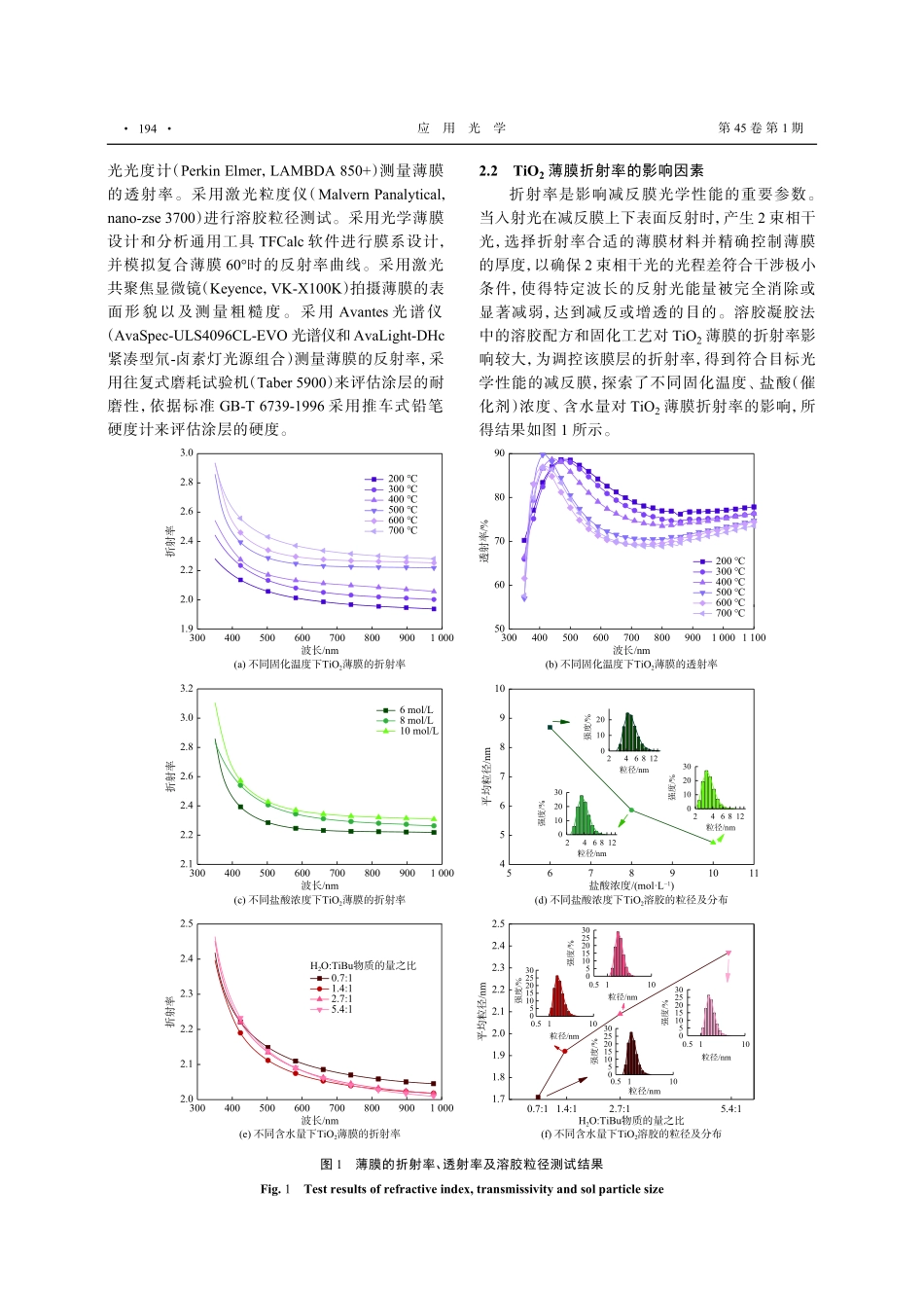
文章编号:1002-2082(2024)01-0192-07近红外车载激光雷达高耐磨双层减反膜斯宇晗1,叶晓军1,王晓亮2,李红波1(1.华东理工大学材料科学与工程学院,上海200237;2.宸光(上海)新材料科技发展有限公司,上海201100)摘要:工作波长为905nm的激光雷达在汽车自动驾驶领域具有强大的应用前景,但工业常用的磁控溅射减反膜,作为其光学窗口表面涂层之一,存在耐磨性不足问题,难以适应恶劣户外环境。采用溶胶凝胶法结合高温固化工艺,为工作波长为905nm的车载激光雷达减反膜提供高耐磨、低成本的解决方案,并研究了固化温度、盐酸浓度、络合剂存在且低酸浓度下的含水量对TiO2折射率的影响。从反射率、粗糙度、硬度、耐磨性等方面对采用不同底层固化方式的双层减反膜的光学性能和机械性能进行评估,结果表明:当入射光波长为905nm时,薄膜表现出优良的减反性能,入射角为15°时反射率小于1%,入射角为60°时反射率小于5%,粗糙度最低为0.005μm,基本满足水平视角120°的激光雷达的光学需求。薄膜铅笔硬度达8H,最多能够承受8000次往复摩擦且无明显损伤,具有优良的适应恶劣环境的能力。关键词:激光雷达;溶胶凝胶;减反膜;折射率;TFCalc中图分类号:TN205文献标志码:ADOI:10.5768/JAO202445.0105003Highwearresistantdouble-layerantireflectioncoatingsfornear-infraredvehicularlidarSIYuhan1,YEXiaojun1,WANGXiaoliang2,LIHongbo1(1.SchoolofMaterialsScienceandEngineering,EastChinaUniversityofScienceandTechnology,Shanghai200237,China;2.ChenGuang(Shanghai)NewMaterialTechnologyDevelopmentCo.,Ltd.,Shanghai201100,China)Abstract:Thelidaroperatesat905nmisconsideredtohaveessentialapplicationvaluesinautomotiveautonomousdriving.Theantireflectioncoatingsmadebymagnetronsputteringcommonlyusedinindustryhavetheproblemofinsufficientwearresistance,whichisdifficulttoadapttotheharshoutdoorenvironment.Thesol-gelmethodcombinedwithhigh-temperaturecuringprocesswasusedtoprovideasolutionofhighwearresistanceandlowcostforantireflectioncoatingsappliedtovehicularlidarwhichoperatedat905nm,andtheinfluencesofcuringtemperature,concentrationofhydrochloricacid(HCl),watercontentinweakacidenvironmentonrefractiveindexofTiO2werestudied.Theopticalandmechanicalpropertiesofthecoatingswithdifferent...