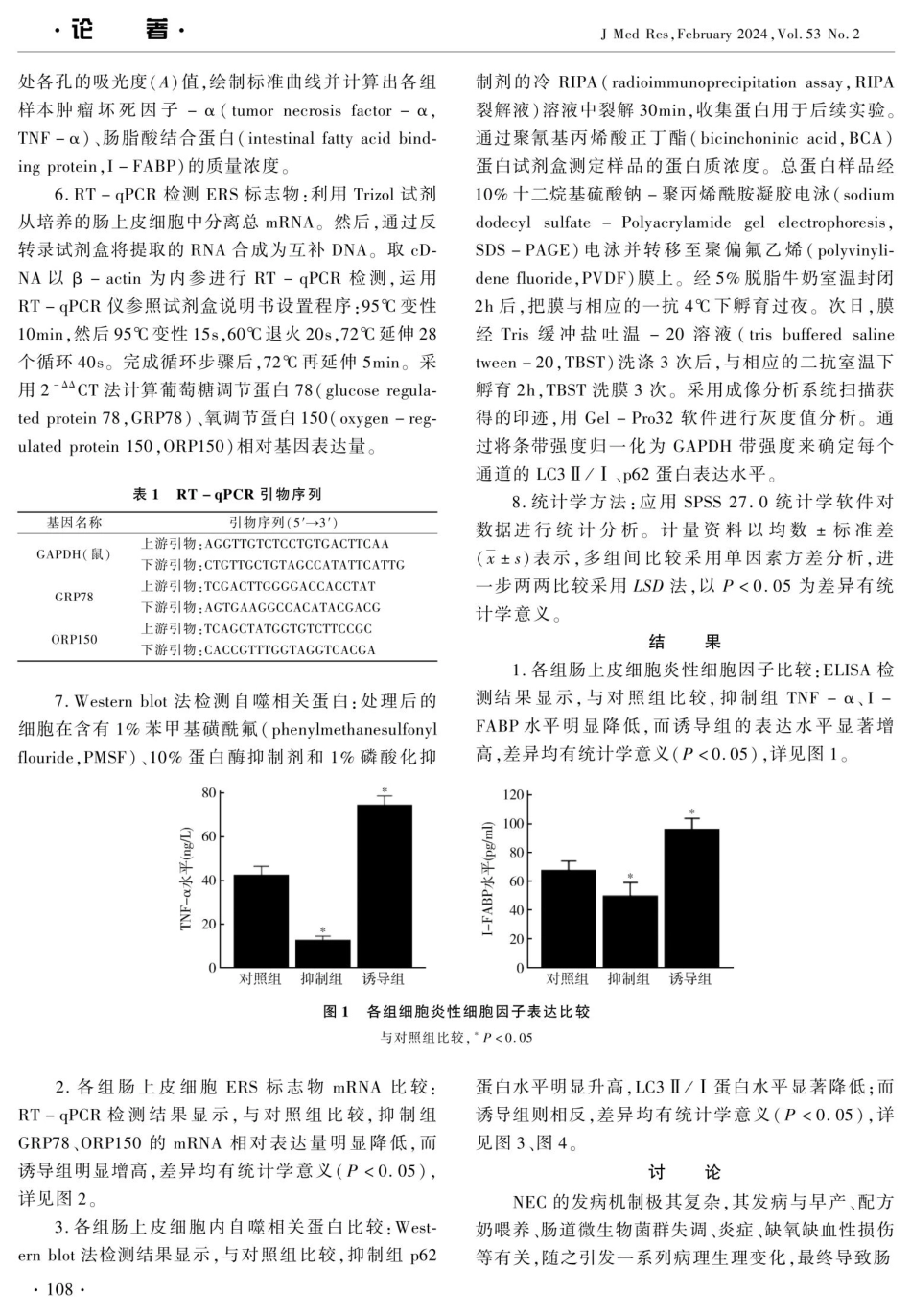
·论着·JMedRes,February2024,Vol.53No.2内质网应激诱导的自噬对新生大鼠坏死性小肠结肠炎的影响王丽红杨晓丽有李静摘要目的探讨抑制内质网应激(endoplasmicreticulumstress,ERS)诱导的自噬对新生大鼠坏死性小肠结肠炎(necrotiz-ingenterocolitis,NEC)的影响。方法首先建立新生大鼠NEC模型,然后从中分离提取出肠上皮细胞,分为对照组、抑制组、诱导组。对照组正常培养,抑制组加4-苯基丁酸,诱导组加衣霉素处理24h。采用酶联免疫吸附试验(enzyme-linkedimmunosorbentassay,ELISA)检测各组细胞炎性细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumornecrosisfactor-α,TNF-α)、肠脂酸结合蛋白(intestinalfattyacidbindingprotein,I-FABP)的表达水平;实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(real-timequantitativepolymerasechainreaction,RT-qPCR)检测各组细胞ERS标志物葡萄糖调节蛋白78(glucoseregulatedprotein78,GRP78)、氧调节蛋白150(oxygen-regulatedpro-tein150,ORP150)的mRNA表达水平;Westernblot法检测各组细胞自噬相关蛋白LC3IⅡ/I、p62的表达水平。结果与对照组比较,抑制组p62表达明显增高,TNF-α、I-FABP、CRP78、ORP150、LC3IⅡ/I表达显著降低,而诱导组p62表达明显降低,TNF-α、I-FABP、CRP78、ORP150、LC3I/I表达显著增高,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论抑制ERS诱导的自噬激活可减轻NEC新生大鼠肠黏膜损伤和炎性反应,改善肠道屏障功能。关键词内质网应激自噬坏死性小肠结肠炎肠上皮细胞作用机制中图分类号R722EffectofEndoplasmicReticulumStress-inducedAutophagyonNecrotizingEnterocolitisinNeonatalRats.WANGLihong,YANGXiaoli,LIJing.ShanxiPeople'sHospital,Shanxi030000,ChinaAbstractObjectiveToinvestigatetheeffectofinhibitingautophagyinducedbyendoplasmicreticulumstress(ERS)onnecrotiz-ingenterocolitis(NEC)inneonatalrats.MethodsFirst,theNECmodelofneonatalratswasestablished.Then,theintestinalepitheli-alcellswereisolatedanddividedintothreegroups:controlgroup,inhibitiongroupandinductiongroup.Thecontrolgroupwasculturednormally,theinhibitiongroupwasaddedwith4-phenylbutyricacid,andtheinductiongroupwasaddedwithtunicamycinfor24hours.Enzyme-linkedimmunosorbentassay(ELISA)wasusedtodetecttheexpressionofthecellularinflammatorycytokinestumornecrosisfactor-α(TNF-α)andintestinalfattya...