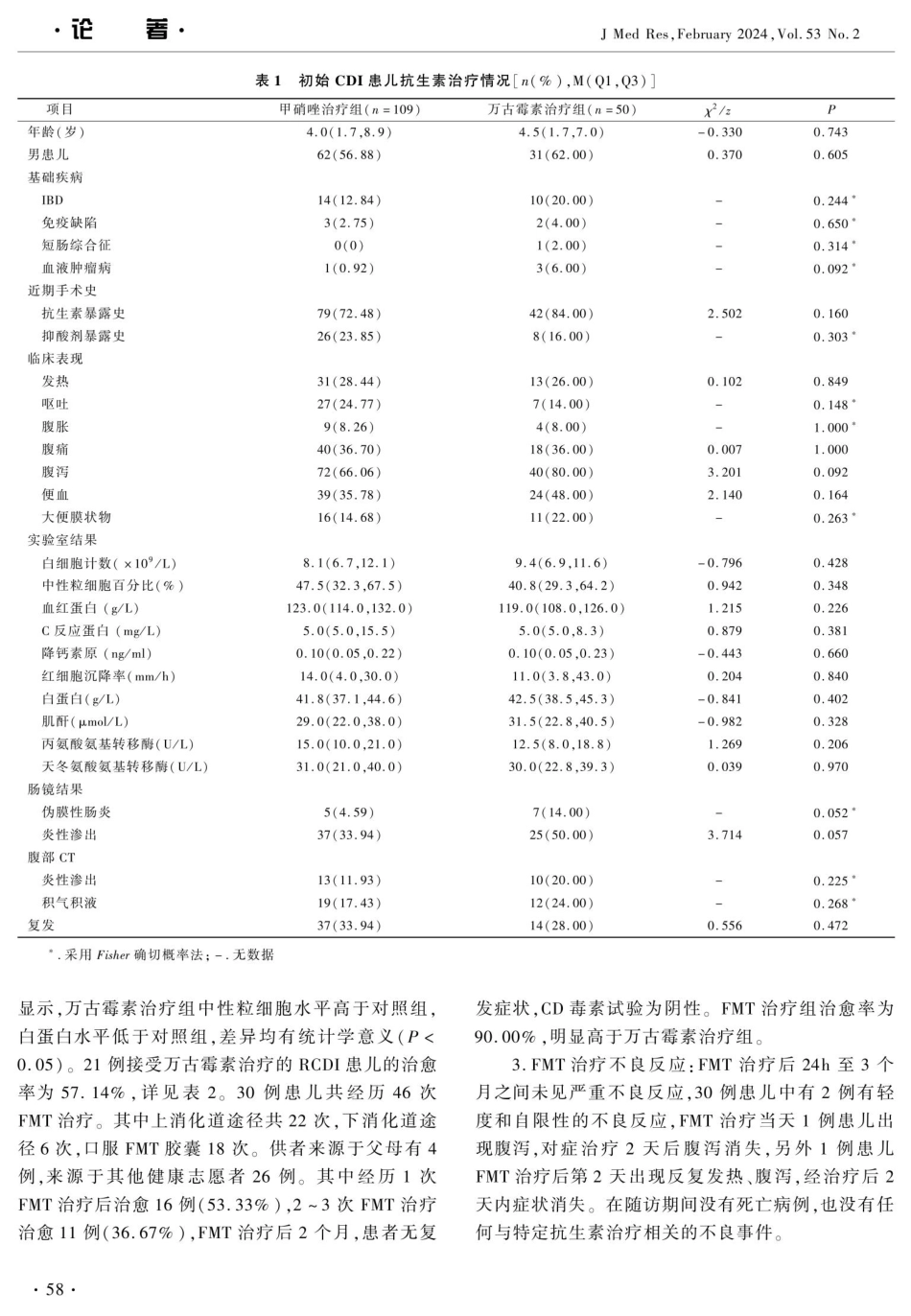
·论着·JMedRes,February2024,Vol.53No.2儿童艰难梭菌感染临床疗效分析曹荣李小露王怡仲张婷摘要目的分析儿童艰难梭菌感染(clostridiumdifficileinfection,CDI)的临床特征及治疗情况。方法回顾性分析2014年9月~2022年10月于上海交通大学医学院附属儿童医院消化感染科住院收治的159例CDI患儿的临床资料,根据治疗方法的不同将初始CDI患儿分为万古霉素治疗组和甲硝唑治疗组,复发后根据万古霉素或肠菌移植(fecalmicrobiotatransplanta-tion,FMT)治疗将复发性CDI(recurrentCDI,RCDI)患儿分为RCDI万古霉素治疗组和FMT治疗组。结果共纳人159例初发CDI患儿,其中男患儿93例,女患儿66例;患儿年龄为4.3(1.7,8.0)岁。初次发作CDI后,109例(68.55%)患儿经甲硝唑治疗,50例(31.45%)患儿经万古霉素治疗。初次发作CDI患儿经抗生素治疗后共有51例复发,其中甲硝唑治疗组37例,复发率为33.94%,万古霉素治疗组14例,复发率为28.00%,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。RCDI患儿中,万古霉素治疗21例,FMT治疗30例,FMT治愈率为90.00%,万古霉素治愈率为57.14%,FMT治愈率明显高于万古霉素。FMT治疗2个月后无严重不良事件报告。结论甲硝唑可作为儿童初始CDI的首选用药,FMT治疗RCDI优于常规抗生素治疗。关键词艰难梭菌感染复发甲硝唑万古霉素肠菌移植治疗中图分类号R516文献标识码AD0110.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2024.02.012ClinicalEfficacyofClostridiumDifficileInfectioninChildren.CAORong,LIXiaolu,WANGYizhong,etal.DepartmentofGastroenter-ologyandHepatology,ShanghaiChildren'sHospital,SchoolofMedicine,ShanghaiJiaoTongUniversity,Shanghai200062,ChinaAbstractObjectiveToanalyzetheclinicalcharacteristicsandtreatmentofclostridiumdifficileinfection(CDI)inchildren.MethodsTheclinicaldataof159childrenwithCDIadmittedtotheDepartmentofGastroenterologyandHepatology,ShanghaiChildren'sHospital,SchoolofMedicine,ShanghaiJiaoTongUniversityfromSeptember2014toOctober2022wereretrospectivelyanalyzed.Allini-tialCDIpatientsweredividedintovancomycintreatmentgroupandmetronidazoletreatmentgroupaccordingtodiferenttreatmentmeth-ods,ChildrenwithrecurrentCDI(RCDI)weredividedintotwogroupsaccordingtovancomycinorFMTtreatment.ResultsAtotalof159childrenwithinitialCDIwereincluded,including93malesand66females,theageofthese...