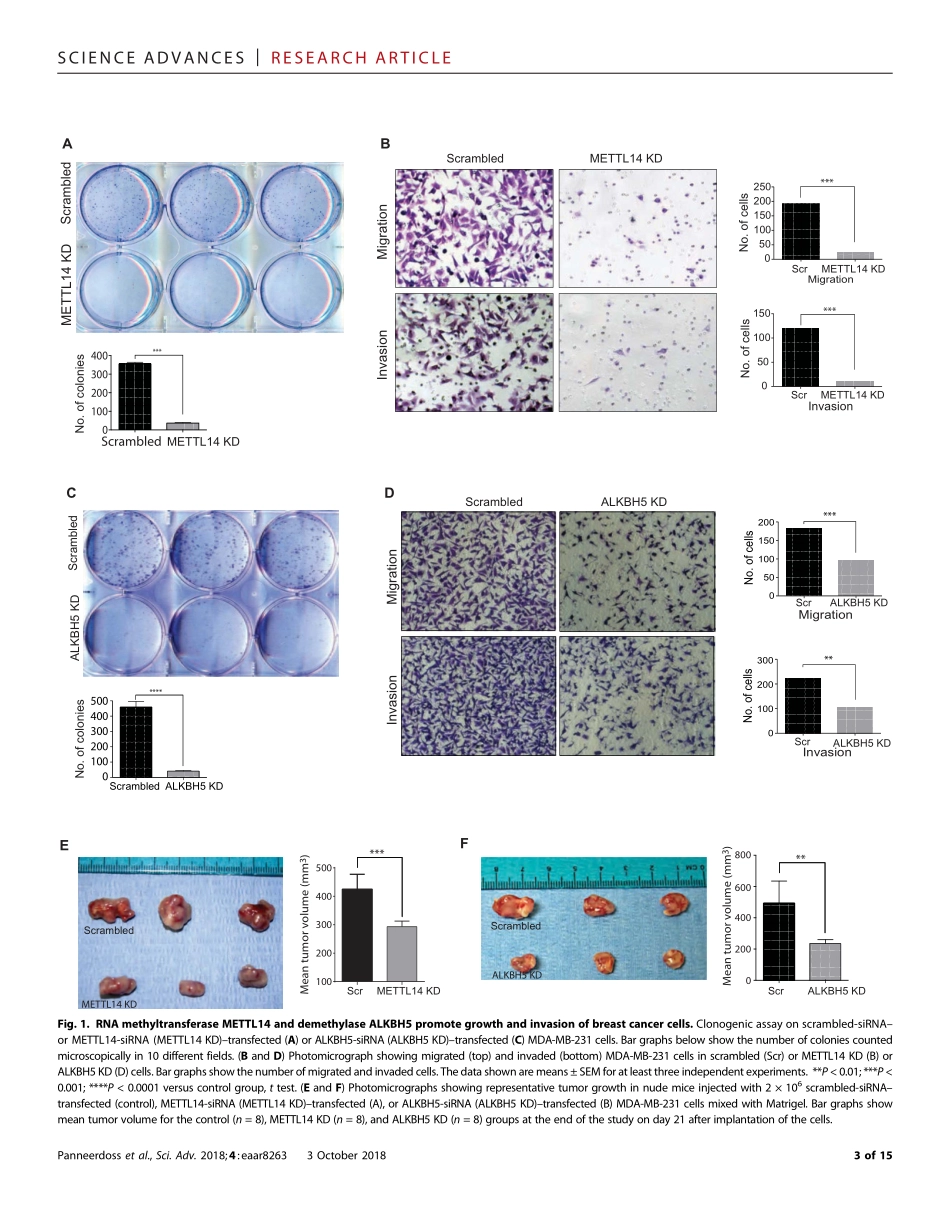
CANCERCopyright©2018TheAuthors,somerightsreserved;exclusivelicenseeAmericanAssociationfortheAdvancementofScience.NoclaimtooriginalU.S.GovernmentWorks.DistributedunderaCreativeCommonsAttributionNonCommercialLicense4.0(CCBY-NC).Cross-talkamongwriters,readers,anderasersofm6AregulatescancergrowthandprogressionSubbarayaluPanneerdoss1,2*,VijayK.Eedunuri1,2*,PoojaYadav1,2,SantoshTimilsina1,2,SubapriyaRajamanickam2,3,SuryavathiViswanadhapalli4,NourhanAbdelfattah1,2,BenjaminC.Onyeagucha1,2,XiadongCui5,ZhaoLai2,TabrezA.Mohammad2,YogeshK.Gupta2,6,TimHui-MingHuang3,YufeiHuang5†,YidongChen2,7†,ManjeetK.Rao1,2†TheimportanceofRNAmethylationinbiologicalprocessesisanemergingfocusofinvestigation.Wereportthatalteringm6AlevelsbysilencingeitherN6-adenosinemethyltransferaseMETTL14(methyltransferase-like14)orde-methylaseALKBH5(ALKBhomolog5)inhibitscancergrowthandinvasion.METTL14/ALKBH5mediatetheirprotumori-genicfunctionbyregulatingm6Alevelsofkeyepithelial-mesenchymaltransitionandangiogenesis-associatedtranscripts,includingtransforminggrowthfactor–bsignalingpathwaygenes.UsingMeRIP-seq(methylatedRNAimmunoprecipitationsequencing)analysisandfunctionalstudies,wefindthatthesetargetgenesareparticularlysensitivetochangesinm6Amodifications,asalteredm6Astatusleadstoaberrantexpressionofthesegenes,result-ingininappropriatecellcycleprogressionandevasionofapoptosis.OurresultsrevealthatMETTL14andALKBH5determinethem6Astatusoftargetgenesbycontrollingeachother’sexpressionandbyinhibitingm6AreaderYTHDF3(YTHN6-methyladenosineRNAbindingprotein3),whichblocksRNAdemethylaseactivity.Furthermore,weshowthatALKBH5/METTL14constituteapositivefeedbackloopwithRNAstabilityfactorHuRtoregulatethestabilityoftargettranscripts.Wediscoverthathypoxiaaltersthelevel/activityofwriters,erasers,andreaders,leadingtodecreasedm6Aandconsequentlyincreasedexpressionoftargettranscriptsincancercells.Thisstudyunveilsapreviouslyundefinedroleform6Aincancerandshowsthatthecollaborationamongwriters-erasers-readerssetsupthem6Athresholdtoen...