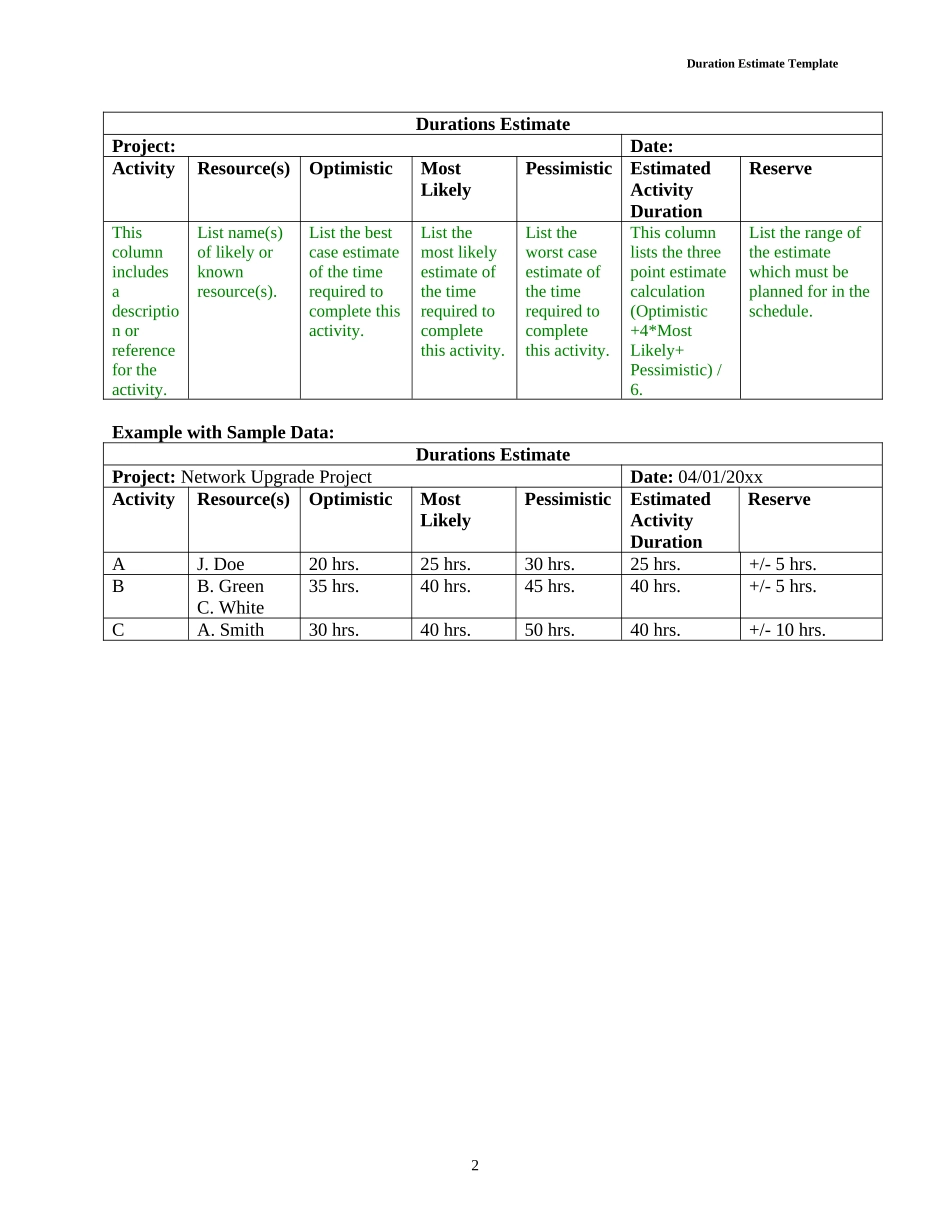
DURATIONESTIMATECOMPANYNAMESTREETADDRESSCITY,STATEZIPCODEDATEDurationEstimateTemplateTheEstimateActivityDurationprocessisusedtoapproximatetheamountoftimeorworkperiodsneededtocompleteprojectactivitieswiththeassignedresources.Therearemanyinputsandconsiderationsrequiredforestimatingactivitydurations.Theseinclude:scopeoftheactivity;resourcetypesandquantities;resourcesavailable;resourcecalendars;projectscopestatement;andotherorganizationalandenvironmentalfactors.Thisprocessestimatestheamountofworkrequiredtocompleteanactivityaswellasthenumberofresourcesneededtocompletethework.Theseestimatesarethenusedtodeterminethenumberofworkperiodsrequiredforanactivitytobecompleted.Anyassumptionsandsupportingdatamustalsobedocumentedtosupporttheestimates.Thereareseveraltoolsandtechniquesthatcanbeusedtoestimateactivitydurations.Thefollowingisalistofthesetoolsandtechniques,abriefdescription,andwhentheyaretypicallyused:a.ExpertJudgment–useshistoricalinformationorinformationfrompastprojectstodevelopestimates.Dependingonsizeandcomplexityoftheprojectthismethodmaynotbeextremelyaccurate.Sometimesusedearlyintheprojectlifecyclewhenthereislimitedinformationavailable.b.AnalogousEstimating–usesinformationandparameters/specificationsfrompreviousprojectstoestimateactivitydurations.Thismayincludeadjustingtheestimatesbasedonthecomplexityoftheproject.Thismethodisalsousedwhenthereislimitedinformationavailablefortheprojectandmayalsorelyonexpertjudgmentasapartoftheestimate.c.ParametricEstimating–usesastatisticalorquantitativerelationshipbetweenplannedprojectactivitiesandhistoricalorknowndatatodevelopestimates.Ifittakes2daystopourandset600squarefeetofconcreteandourprojectcallsfor1,200squarefeetofconcretethenwecanestimatetheactivityat4days.Thismethodmayachievebetteraccuracythanexpertjudgmentoranalogousestimatingbutreliesonknowndata.d.Three-PointEstimating–usesaweightedaverageofoutcomesandaccountsforsomeuncertaintyindeterminingtheestimate.Thismethodaccountsforthemostlikelyoutcome,bestcase,andworstcasesce...