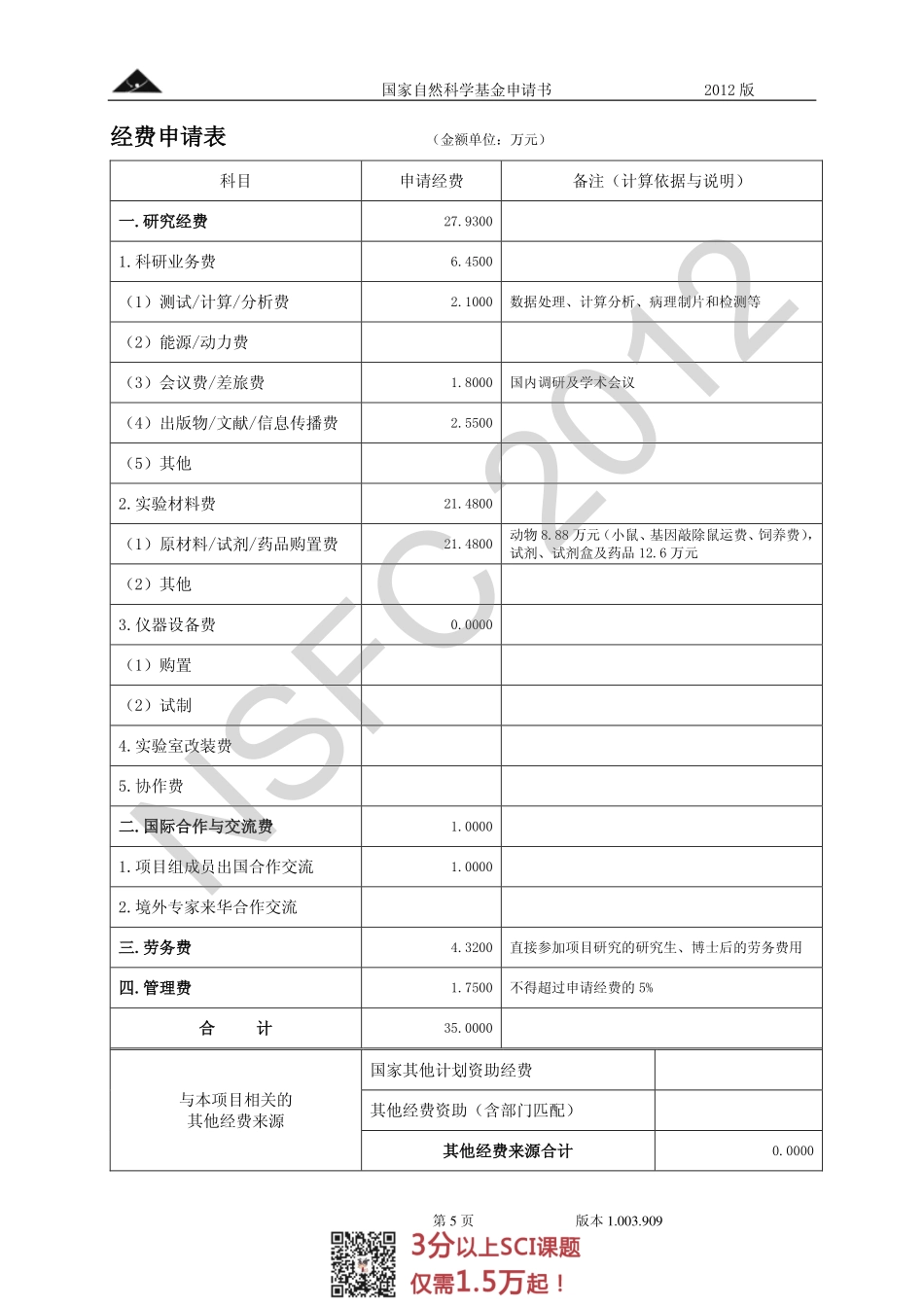
国家自然科学基金申请书2012版第3页版本1.003.909中文摘要(限400字):冠心病心肌缺血性损伤引起的左室收缩功能障碍及继发心室重构是临床心力衰竭最常见的原因。我们前期在国际上率先发现过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅激活因子1α(PGC-1α)的上调可改善线粒体呼吸功能,并显著逆转压力超负荷小鼠心室重构(BCVS一等奖,2010)。提示PGC-1α参与“能量饥饿”致心衰发生机制,但对PGC-1α在兼具压力负荷和容量负荷特性的心梗后心室重构中发生的改变和发挥的作用却远未明确。本项目拟运用基因干预和药理学方法,通过在体和离体实验,从不同时间(心梗早、中、晚期)和空间(梗死区、周边区、非缺血区)角度,观察PGC-1α与线粒体结构和能量代谢功能的变化及相关性,探明PGC-1α是否具有逆转或延缓心梗后心室重构的生物效应,而该生物效应是否通过提升与改善心肌线粒体能量代谢而实现的,再进而阐明其调控线粒体能量代谢的效应分子。为PGC-1α作为缺血性心肌病早期治疗靶标提供理论依据。英文摘要(限3000Characters):Leftventricularconractiledysfunctionandremodelingfollowingmyocardialischemiahavebeenidentifiedasamajorcontributingfactortoheartfailureinclinics.Reportsfromourlabfoundthatupregulationofperoxisomeproliferator-activatedreceptorγcoactivator1α(PGC-1α)reversedpressureoverload-inducedventricularremodelingbyimproveingmitochondrialfunction(FirstprizeinBCVSmeeting,2010).OurresultsindicateapivotalroleofPGC-1αintheonsetandprogressionofheartfailure.However,theroleofPGC-1αinpost-infarctremodelingwithconcurrentpressureandvolumeoverloadremainsunknown.WeaimtodemonstratewheatherPGC-1αretardorreversecardiacpost-infarctionremodeling(mal-adaptivehypertrophy,interstitialfibrosisanddilation)byimprovingandamelioratingmitochondrialenergymetabolismandfurtherexplortheeffectormoleculeforregulatingmitochondrionusinginvivoandinvitroexperiment.Thestudywilldemonstratedininfarcted,ischemicandnonischemicareaatdifferenttimepoints.WetrytofindthepathwayforPGC-1αtoregulatingmitochondrioninischemicmyocardium.NSFC2012国家自然科学基金申请书2012版第5页版本1.003.909经费申请表(金额单位:万元)科目申请经费备注(计算依据与说明)一.研究经费27.93001.科研业务费6.4500...