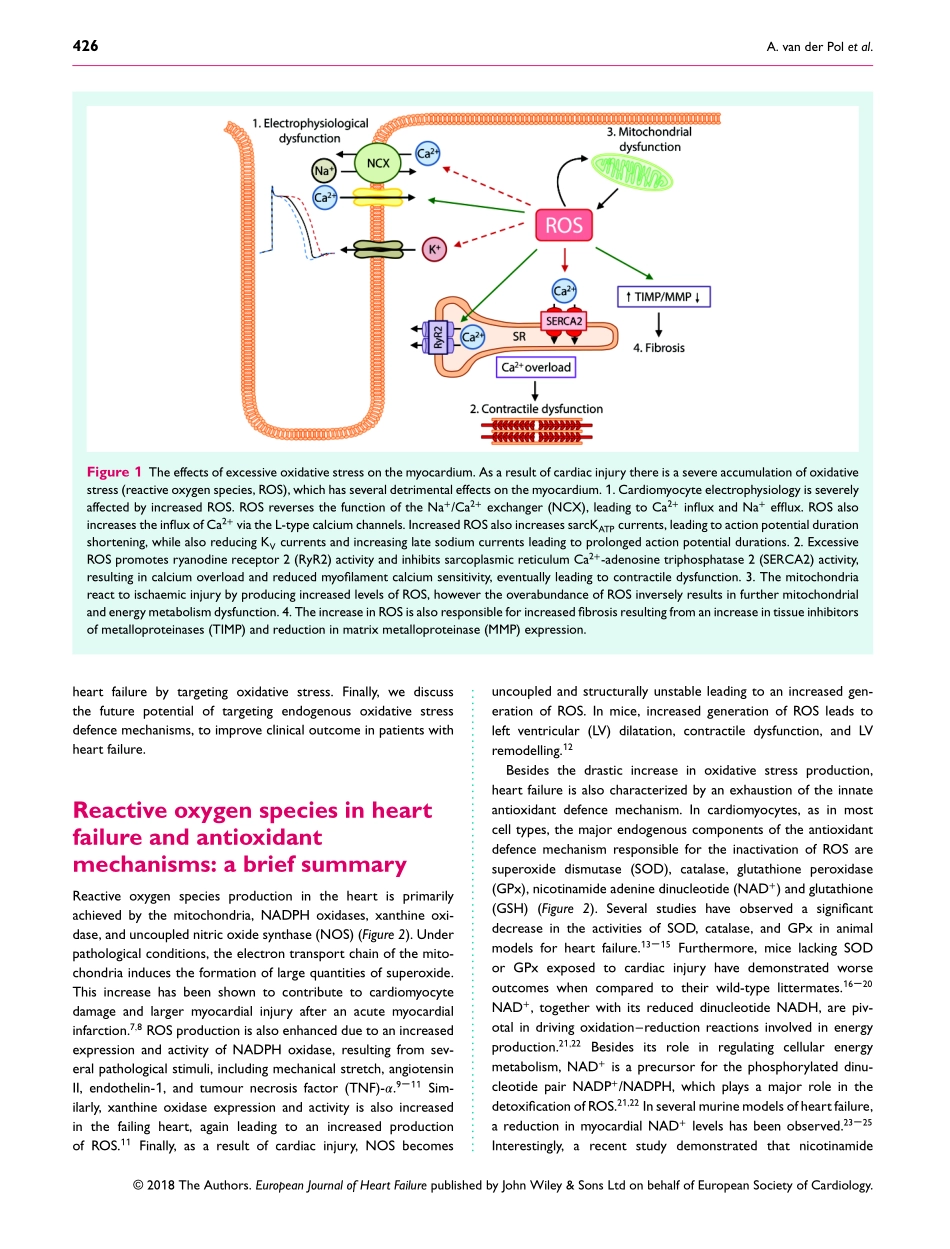
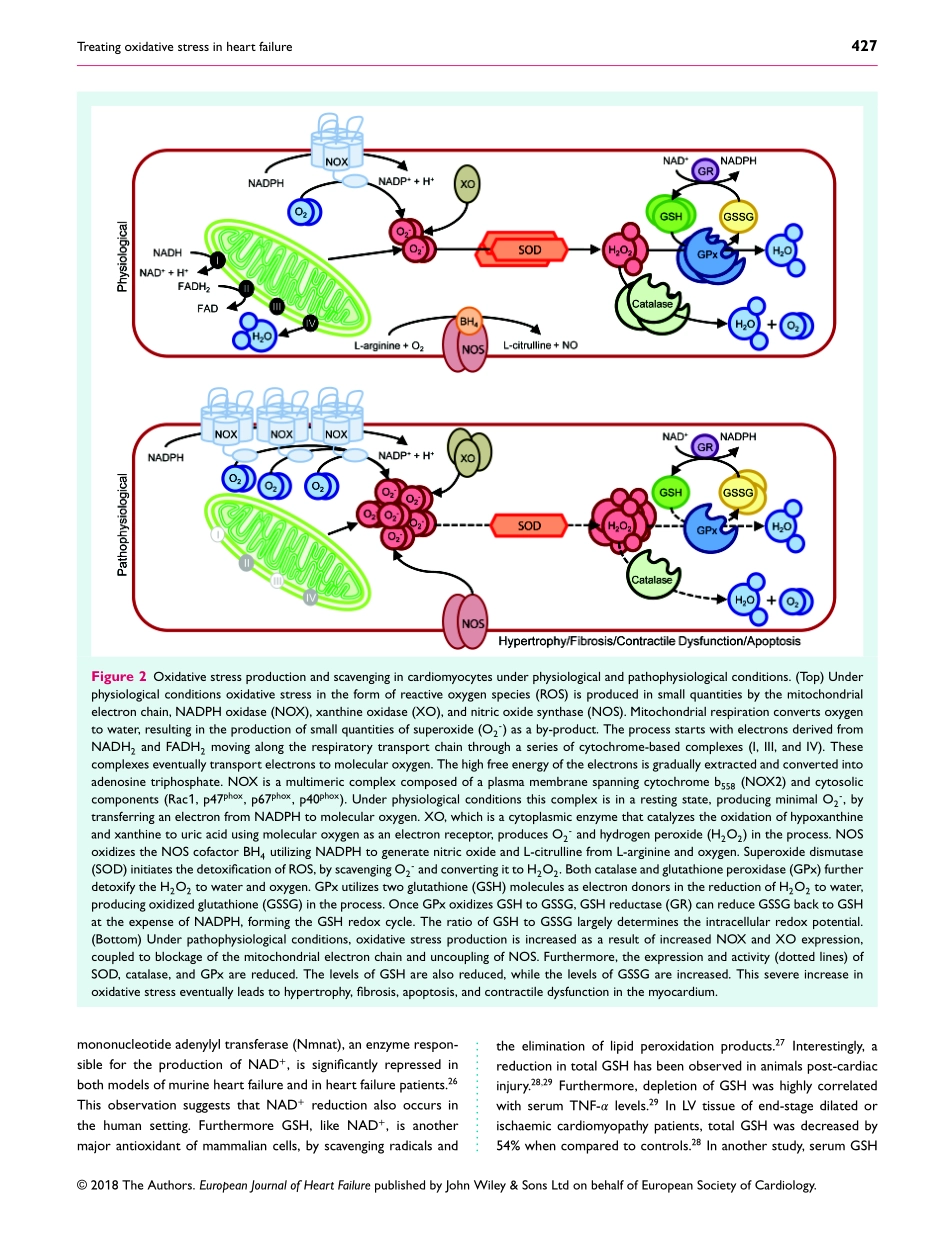
EuropeanJournalofHeartFailure(2019)21,425–435REVIEWdoi:10.1002/ejhf.1320Treatingoxidativestressinheartfailure:past,presentandfutureAtzevanderPol1,2,WiekH.vanGilst1,AdriaanA.Voors1,andPetervanderMeer1*1DepartmentofCardiology,UniversityMedicalCenterGroningen,UniversityofGroningen,Groningen,TheNetherlands;and2PerioperativeInflammationandInfectionGroup,DepartmentofMedicine,FacultyofMedicineandHealthSciences,UniversityofOldenburg,Oldenburg,GermanyReceived17April2018;revised20July2018;accepted23August2018;onlinepublish-ahead-of-print19October2018Advancesincardiovascularresearchhaveidentifiedoxidativestressasanimportantpathophysiologicalpathwayinthedevelopmentandprogressionofheartfailure.Oxidativestressisdefinedastheimbalancebetweentheproductionofreactiveoxygenspecies(ROS)andtheendogenousantioxidantdefencesystem.Underphysiologicalconditions,smallquantitiesofROSareproducedintracellularly,whichfunctionincellsignalling,andcanbereadilyreducedbytheantioxidantdefencesystem.However,underpathophysiologicalconditions,theproductionofROSexceedsthebufferingcapacityoftheantioxidantdefencesystem,resultingincelldamageanddeath.Overthelastdecadesseveralstudieshavetriedtotargetoxidativestresswiththeaimtoimproveoutcomeinpatientswithheartfailure,withverylimitedsuccess.Thereasonsastowhythesestudiesfailedtodemonstrateanybeneficialeffectsremainunclear.However,oneplausibleexplanationmightbethatcurrentlyemployedstrategies,whichtargetoxidativestressbyexogenousinhibitionofROSproductionorsupplementationofexogenousantioxidants,arenoteffectiveenough,whilebolsteringtheendogenousantioxidantcapacitymightbeafarmorepotentavenuefortherapeuticintervention.Inthisreview,weprovideanoverviewofoxidativestressinthepathophysiologyofheartfailureandthestrategiesutilizedtodatetotargetthispathway.Weprovidenovelinsightsintomodulationofendogenousantioxidants,whichmayleadtonoveltherapeuticstrategiestoimproveoutcomeinpatientswithheartfailure...................................................................................