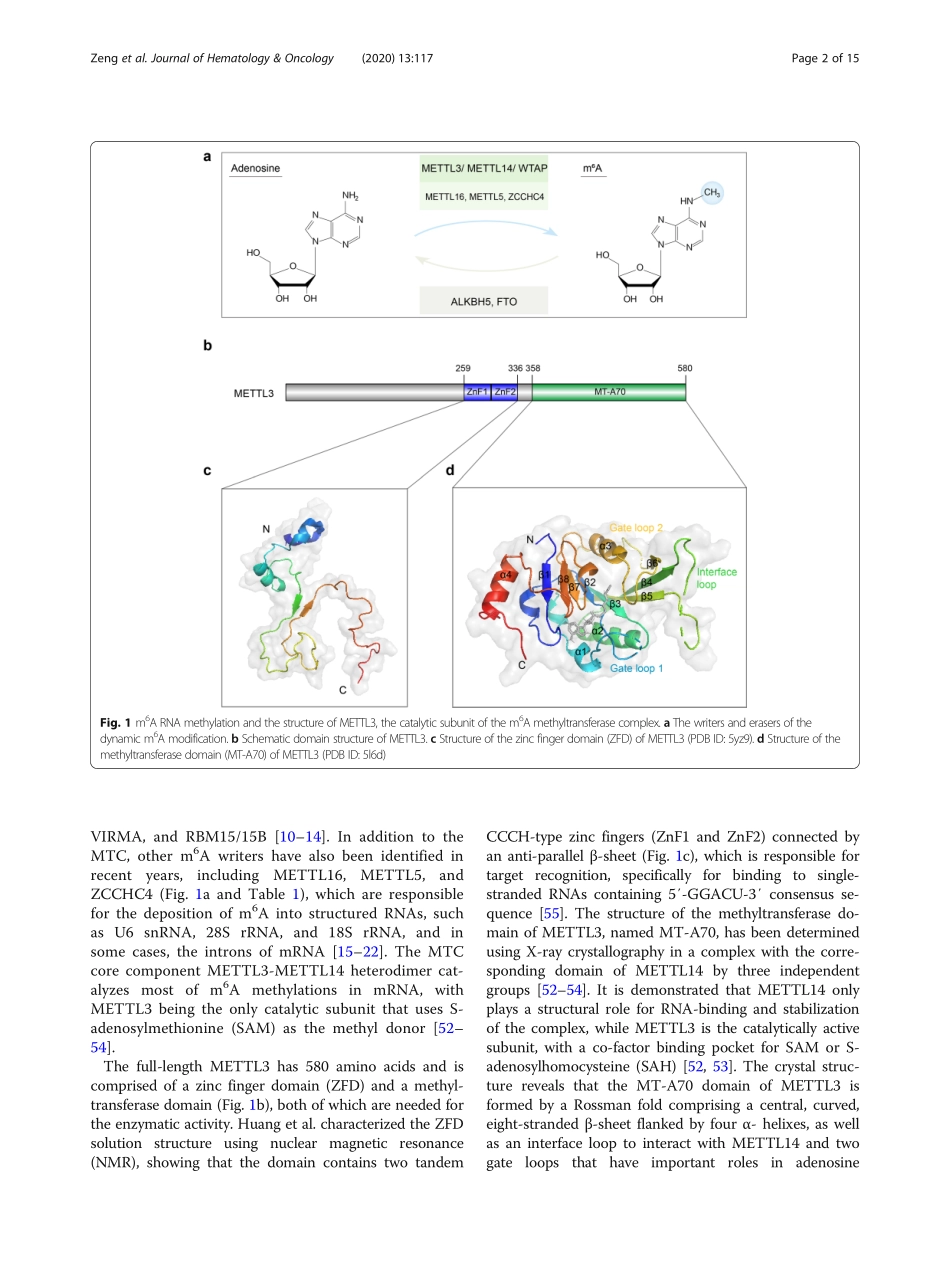
REVIEWOpenAccessRolesofMETTL3incancer:mechanismsandtherapeutictargetingChengwuZeng1,2†,WanxuHuang1,3†,YangqiuLi2*andHengyouWeng1,4*AbstractN6-methyladenosine(m6A)isthemostabundantmRNAmodificationandiscatalyzedbythemethyltransferasecomplex,inwhichmethyltransferase-like3(METTL3)isthesolecatalyticsubunit.AccumulatingevidenceinrecentyearsrevealsthatMETTL3playskeyrolesinavarietyofcancertypes,eitherdependentorindependentonitsm6ARNAmethyltransferaseactivity.Whiletherolesofm6Amodificationsincancerhavebeenextensivelyreviewedelsewhere,thecriticalfunctionsofMETTL3invarioustypesofcancer,aswellasthepotentialtargetingofMETTL3ascancertreatment,havenotyetbeenhighlighted.Herewesummarizeourcurrentunderstandingbothontheoncogenicandtumor-suppressivefunctionsofMETTL3,aswellastheunderlyingmolecularmechanisms.Thewell-documentedproteinstructureoftheMETTL3/METTL14heterodimerprovidesthebasisforpotentialtherapeutictargeting,whichisalsodiscussedinthisreview.Keywords:RNAmodification,METTL3,m6A,Cancer,Non-codingRNA,DrugdiscoveryIntroductionTherearemorethan170modificationsinRNA,amongwhichN6-methyladenosine(m6A)isthemostprevalentinternalmodificationinmessengerRNA(mRNA)[1–4].Over7000humantranscriptsharboratleastonem6Asite,whichisfoundwithintheconsensusmotifRRACH(whereR=A/G,H=A/C/U),andmostofthem6Asitesareenrichedinthecodingsequence(CDS)andthe3′un-translatedregion(3′UTR)ofmRNA,especiallyaroundthestopcodons[5,6].Althoughm6Awasdiscoveredmorethan40yearsago[7],itfailedtosparkenthusiasminthisfielduntiltheidentificationofFTOasanm6Ademethylasein2011[8],whichrevealsthatm6Acanbedynamicallyregulatedandmightplayvitalrolesindevel-opmentanddiseases.Sincethen,FTOandALKBH5,bothbelongingtotheAlkBfamilyofFe(II)/a-ketoglutarate(a-KG)-dependentdioxygenases[9],wereclassifiedasm6A“eraser”proteinsthatremovem6AmodificationsfromRNA(Fig.1aandTable1).Incontrasttobeingremovedby“eraser”proteins,m6AcanberecognizedbyasetofRNA-bindingproteinscalledm6A“reader”proteinsthatcanspecificallyrecognizeandbindtom6A-modifiedt...