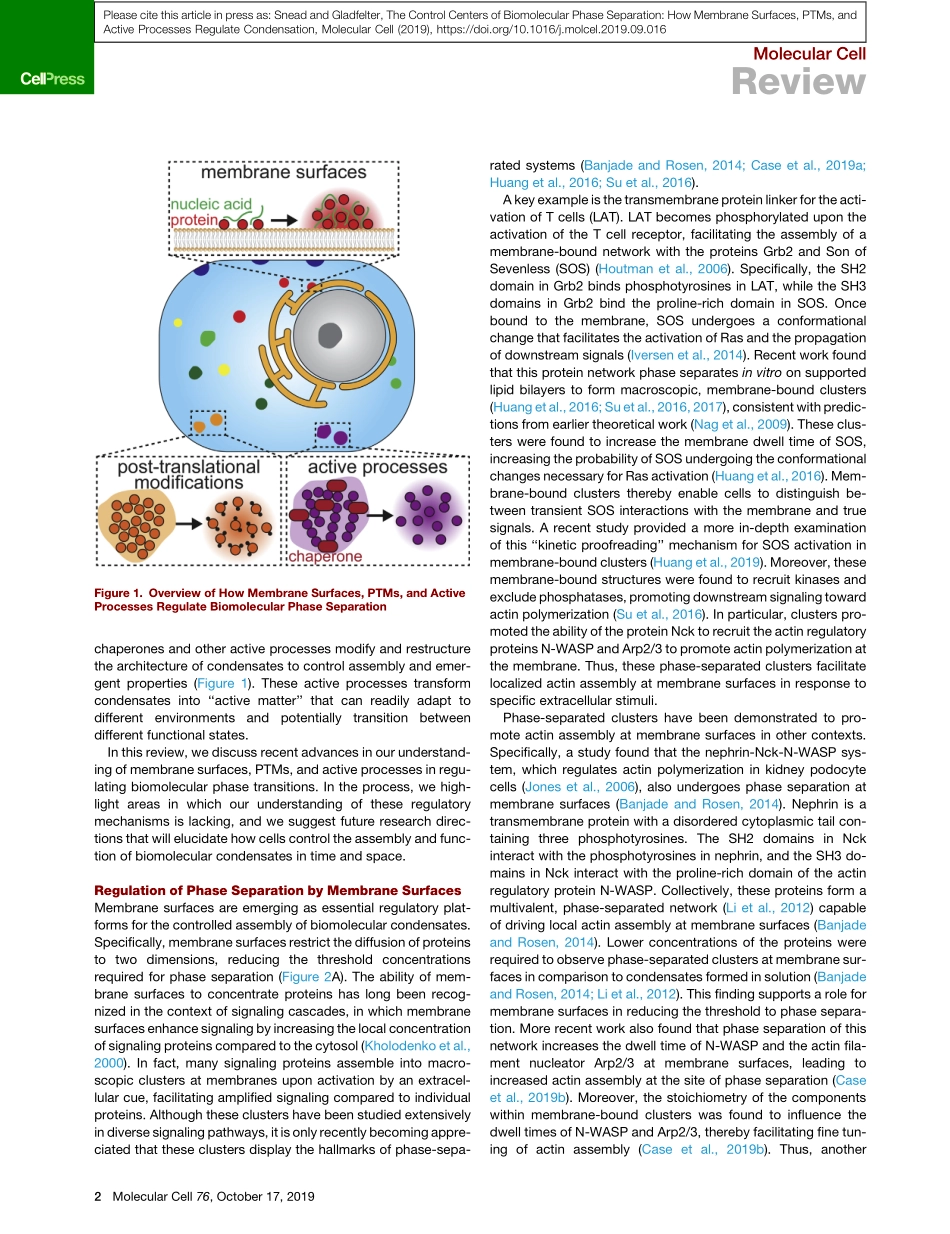
MolecularCellReviewTheControlCentersofBiomolecularPhaseSeparation:HowMembraneSurfaces,PTMs,andActiveProcessesRegulateCondensationWiltonT.Snead1andAmyS.Gladfelter1,2,*1DepartmentofBiology,TheUniversityofNorthCarolinaatChapelHill,ChapelHill,NC27599,USA2MarineBiologicalLaboratory,WoodsHole,MA02543,USA*Correspondence:amyglad@unc.eduhttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.016Biomolecularcondensationisemergingasanessentialprocessforcellularcompartmentalization.Thefor-mationofbiomolecularcondensatescanbedrivenbyliquid-liquidphaseseparation,whicharisesfromweak,multivalentinteractionsamongproteinsandnucleicacids.Asubstantialbodyofrecentworkhasre-vealedthatdiversecellularprocessesrelyonbiomolecularcondensationandthataberrantphaseseparationmaycausedisease.Manyproteinsdisplayanintrinsicpropensitytoundergophaseseparation.However,themechanismsbywhichcellsregulatephaseseparationtobuildfunctionalcondensatesattheappropriatetimeandlocationareonlybeginningtobeunderstood.Here,wereviewthreekeycellularmechanismsthatenablethecontrolofbiomolecularphaseseparation:membranesurfaces,post-translationalmodifica-tions,andactiveprocesses.Wediscusshowthesemechanismsmayfunctioninconcerttoproviderobustcontroloverbiomolecularcondensatesandsuggestnewresearchavenuesthatwillelucidatehowcellsbuildandmaintainthesekeycentersofcellularcompartmentalization.Thecompartmentalizationofcellsintodistinct,functionalvolumesisessentialforlife.Allcellsrequirethepartitioningofmoleculesintoseparatecompartmentstocarryoutdiverseprocesses.Biomole-cularcondensates,composedofphase-separatedproteinandnucleicacid,areemergingascriticalcentersofcellularcompart-mentalization(Bananietal.,2017).Thesestructuresoftenbehaveasliquid-likedroplets,inwhichcomponentmoleculesaremobileandexchangewiththesurroundingmedium(Brangwynneetal.,2015).Inthisreview,werefertotheseentitiesasbiomolecularcon-densates,phase-separatedstructuresornetworks,droplets,orclusters.Phase-separatedstructurescanbefoundinphysiolog-icalcontextsthroughoutthecell,inclu...