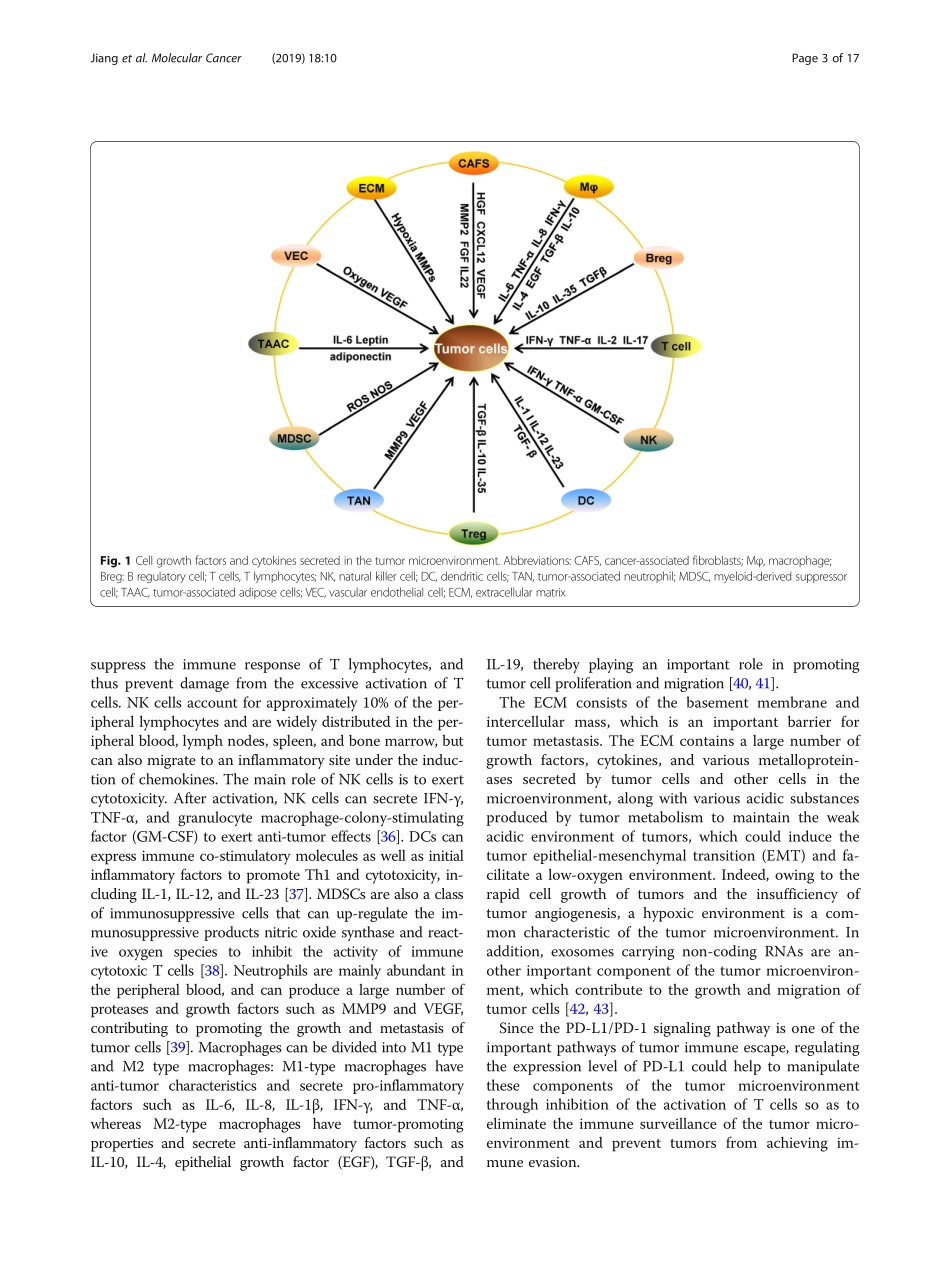
REVIEWOpenAccessRoleofthetumormicroenvironmentinPD-L1/PD-1-mediatedtumorimmuneescapeXianjieJiang1,2,3,JieWang2,XiangyingDeng2,FangXiong2,JunshangGe1,2,BoXiang1,2,3,XuWu2,4,JianMa1,2,3,MingZhou1,2,3,XiaolingLi1,2,3,YongLi2,5,GuiyuanLi1,2,3,WeiXiong1,2,3,CanGuo1,2,3*andZhaoyangZeng1,2,3*AbstractTumorimmuneescapeisanimportantstrategyoftumorsurvival.Therearemanymechanismsoftumorimmuneescape,includingimmunosuppression,whichhasbecomearesearchhotspotinrecentyears.Theprogrammeddeathligand-1/programmeddeath-1(PD-L1/PD-1)signalingpathwayisanimportantcomponentoftumorimmunosuppression,whichcaninhibittheactivationofTlymphocytesandenhancetheimmunetoleranceoftumorcells,therebyachievingtumorimmuneescape.Therefore,targetingthePD-L1/PD-1pathwayisanattractivestrategyforcancertreatment;however,thetherapeuticeffectivenessofPD-L1/PD-1remainspoor.ThissituationrequiresgainingadeeperunderstandingofthecomplexandvariedmolecularmechanismsandfactorsdrivingtheexpressionandactivationofthePD-L1/PD-1signalingpathway.Inthisreview,wesummarizetheregulationmechanismsofthePD-L1/PD-1signalingpathwayinthetumormicroenvironmentandtheirrolesinmediatingtumorescape.Overall,theevidenceaccumulatedtodatesuggeststhatinductionofPD-L1byinflammatoryfactorsinthetumormicroenvironmentmaybeoneofthemostimportantfactorsaffectingthetherapeuticefficiencyofPD-L1/PD-1blocking.Keywords:Tumorimmuneescape,PD-L1,PD-1,Tumormicroenvironment,InflammatoryfactorBackgroundTumorimmuneescapereferstothephenomenonbywhichtumorcellscangrowandmetastasizebyavoidingrecognitionandattackbytheimmunesystemthroughvariousmechanisms,whichisanimportantstrategyfortumorsurvivalanddevelopment[1].Thearemanyindu-ciblefactorsoftumorimmuneescape,includingthelowimmunogenicityoftumorcells,recognitionoftumor-specificantibodiesasautoantigens,tumorsurfaceanti-genmodulation,tumor-inducedexemptionregions,andtumor-inducedimmunosuppression,thelatterofwhichhasbeenthemostextensivelystudiedmechanismtodate.Tumor-inducedimmunosuppressionoperatesintwomainways.Thefirstoccu...