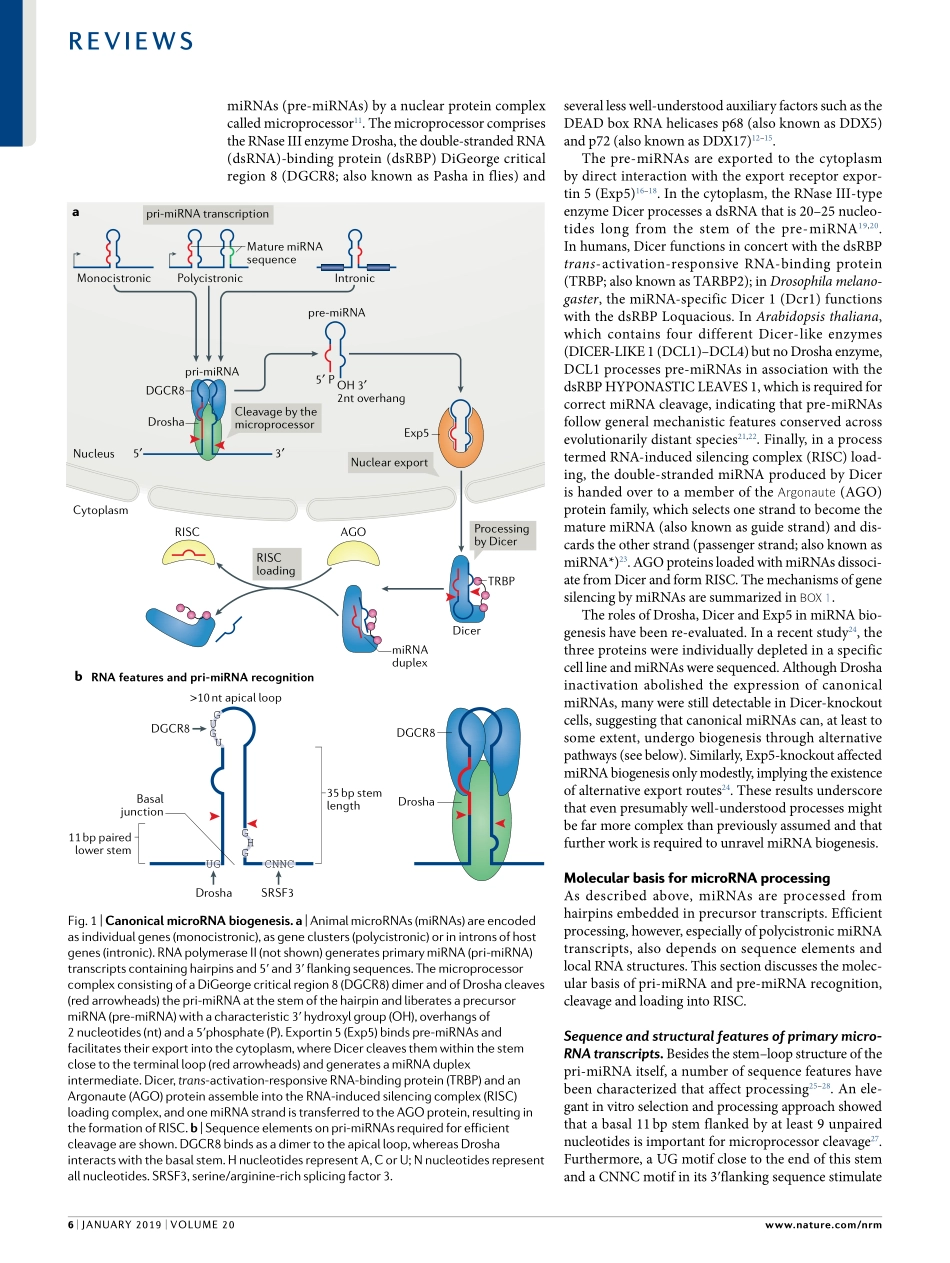
MicroRNAs(miRNAs)wereidentifiedintheearly1990s(refs1,2),butittookalmost10yearsuntiltheirfun-damentalrolesingeneregulationwererecognized3–5.Today,weknowthatmiRNAsareexpressedinalmostalleukaryotesandthatevenseveralvirusesencodemiRNAs,highlightingtheregulatorypowerofthesesmallRNAs,becausevirusescannotaffordtowastepreciousspaceintheirlimitedgenomes.Numerousstudiesoverthepastdecadehaveelucidatedthemolec-ulardetailsofmiRNAfunctionandbiogenesis,whicharetightlyregulatedatmultiplelevels.AberrantmiRNAexpressionhasbeenassociatedwithmanydifferentdis-eases,includingcancerandneurologicaldisorders,andmiRNAinhibitorsaredevelopedtowardstherapyatanincrediblepace6.AlthoughweunderstandreasonablywellthebasicprinciplesofmiRNAbiogenesisandfunction,novelandunexpectedaspectsoftheseprocessesarereportedonaregularbasis,andmanyexcitingissuesremaintobeexplored.InthisReview,wesummarizethecurrentknowledgeofmiRNAbiogenesisandhighlightnoveldevelopmentsaswellasopenquestions.WefocusonmiRNAsequencefeaturesthatareimportantforefficientmiRNAprocessingandonrecentstructuralinsightsintothemechanismsofthemajormiRNA-generatingmolecularmachines.Wethendiscussregulatorypost-translationalmodifications(PTMs)ofmiRNAbiogenesisfactors,whichlinkcellsignallingpathwayswithmiRNAexpression.WethendiscusstheinterplaybetweenRNA-bindingproteins(RBPs)andmiRNAprocessingintermediates,whichconstitutesabroadlayerofpost-transcriptionalregulationofmiRNAbiogenesisinmanytissues.Finally,wepresentrecentfindingsonnon-canonicalmiRNAbiogenesispathwaysaswellasexamplesofdiseasesassociatedwithgenomicmutationsinmiRNAprocessingfactors.OverviewofcanonicalmicroRNAbiogenesisCanonicalanimalmiRNAsareencodedinthegenomeasindividualgenesorasclusterscontainingafewtoseveralhundreddifferentmiRNAs.ClusteredmiRNAsaretranscribedtogetheraspolycistronictranscripts,whichareprocessedtotheindividualmaturemiRNAs.ManymiRNAsareembeddedinintronsofprotein-codinggenes7–9.FunctionallinksbetweenthehostgeneandthemiRNA,however,arerare.Generally,miRNAsaretranscribedbyRN...