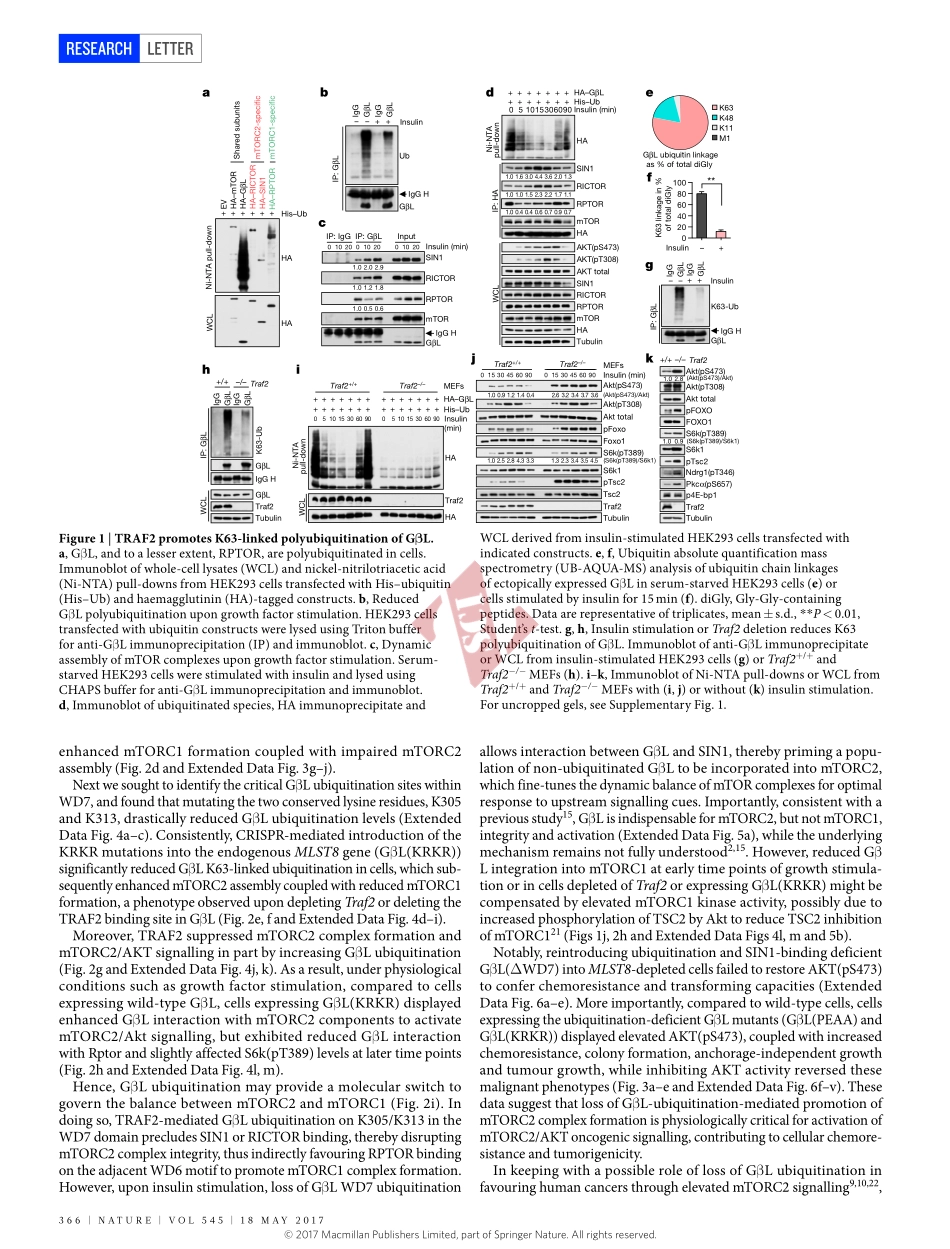
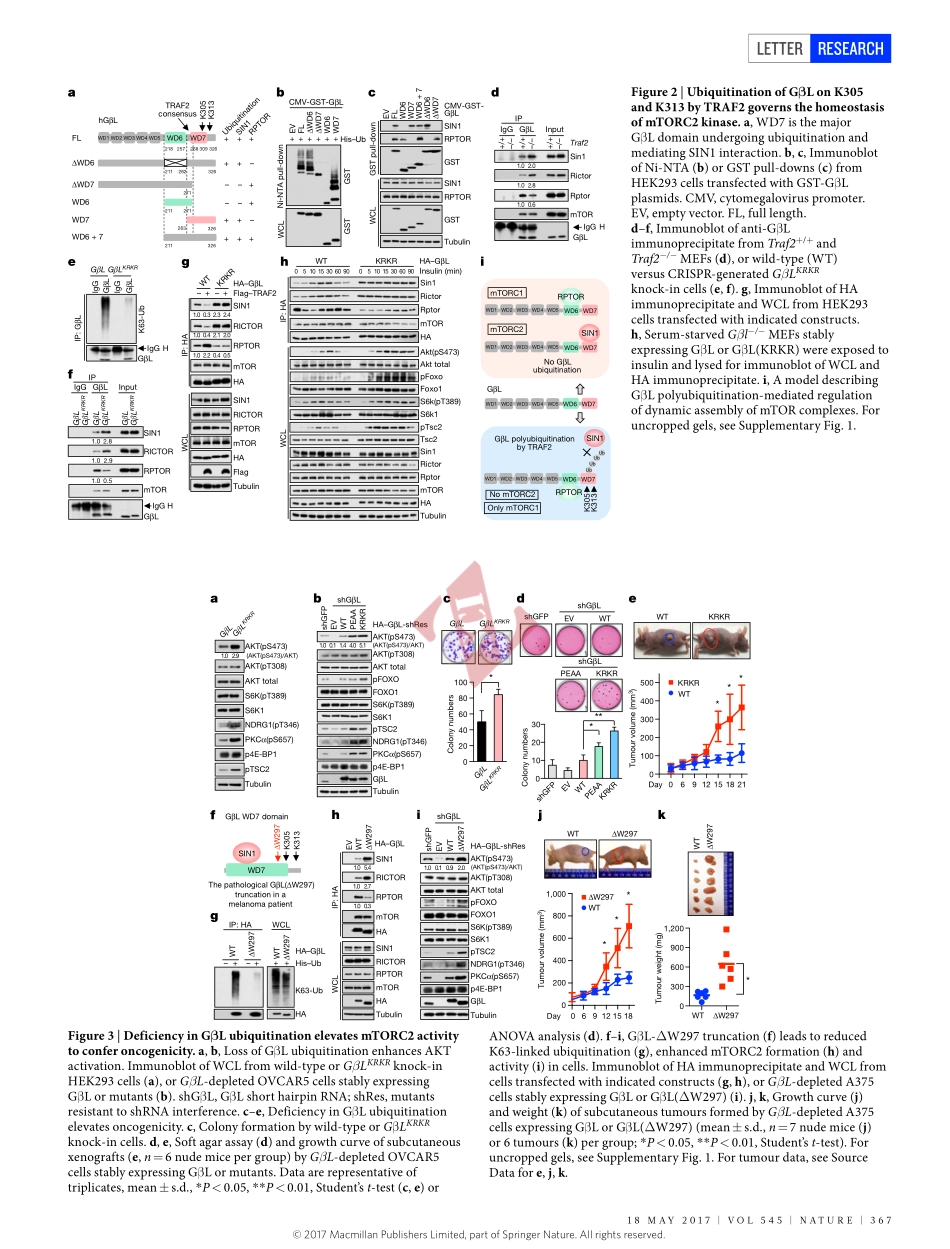
18may2017|VOL545|NaTURE|365LETTERdoi:10.1038/nature22344TRAF2andOTUD7Bgovernaubiquitin-dependentswitchthatregulatesmTORC2signallingBinWang1,2*,ZuliangJie3*,DonghyunJoo3,albanOrdureau4,PengdaLiu2,WenjianGan2,JianpingGuo2,JinfangZhang2,BrianJ.North2,XiangpengDai2,XuhongCheng3,XiuwuBian5,LingqiangZhang6,J.WadeHarper4,Shao-CongSun3&WenyiWei2Themechanistictargetofrapamycin(mTOR)hasakeyroleintheintegrationofvariousphysiologicalstimulitoregulateseveralcellgrowthandmetabolicpathways1.mTORprimarilyfunctionsasacatalyticsubunitintwostructurallyrelatedbutfunctionallydistinctmulti-componentkinasecomplexes,mTORcomplex1(mTORC1)andmTORC2(refs1,2).DysregulationofmTORsignallingisassociatedwithavarietyofhumandiseases,includingmetabolicdisordersandcancer1.Thus,bothmTORC1andmTORC2kinaseactivityistightlycontrolledincells.mTORC1isactivatedbybothnutrients3–6andgrowthfactors7,whereasmTORC2respondsprimarilytoextracellularcuessuchasgrowth-factor-triggeredactivationofPI3Ksignalling8–10.AlthoughbothmTORandGβL(alsoknownasMLST8)assembleintomTORC1andmTORC2(refs11–15),itremainslargelyunclearwhatdrivesthedynamicassemblyofthesetwofunctionallydistinctcomplexes.Hereweshow,inhumansandmice,thattheK63-linkedpolyubiquitinationstatusofGβLdictatesthehomeostasisofmTORC2formationandactivation.Mechanistically,theTRAF2E3ubiquitinligasepromotesK63-linkedpolyubiquitinationofGβL,whichdisruptsitsinteractionwiththeuniquemTORC2componentSIN1(refs12–14)tofavourmTORC1formation.Bycontrast,theOTUD7BdeubiquitinaseremovespolyubiquitinchainsfromGβLtopromoteGβLinteractionwithSIN1,facilitatingmTORC2formationinresponsetovariousgrowthsignals.Moreover,lossofcriticalubiquitinationresiduesinGβL,byeitherK305R/K313Rmutationsoramelanoma-associatedGβL(ΔW297)truncation,leadstoelevatedmTORC2formation,whichfacilitatestumorigenesis,inpartbyactivatingAKToncogenicsignalling.InsupportofaphysiologicallypivotalroleforOTUD7BintheactivationofmTORC2/AKTsignalling,geneticdeletionofOtud7binmicesuppressesAktactivationandKras-drivenlungt...