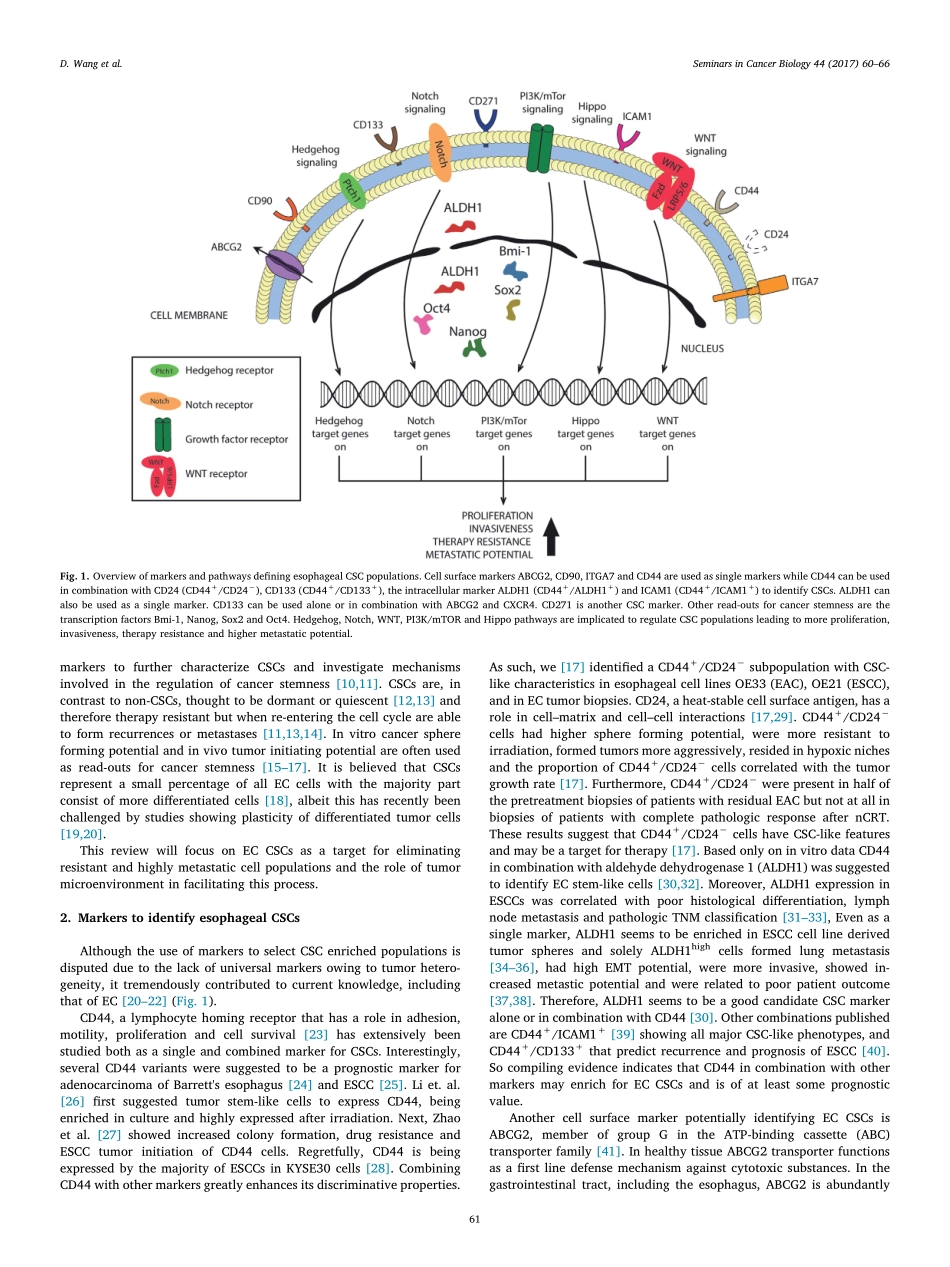
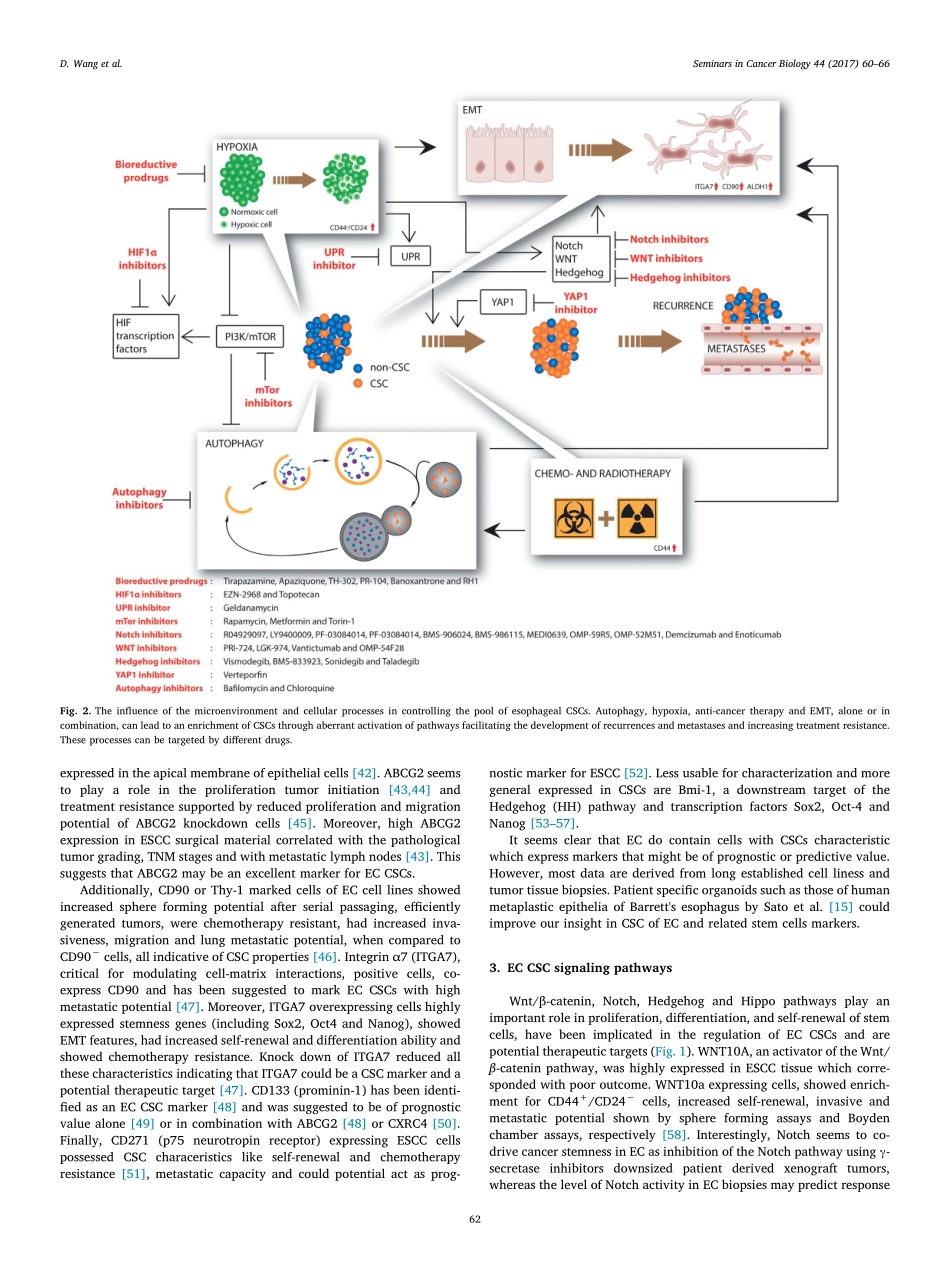
ContentslistsavailableatScienceDirectSeminarsinCancerBiologyjournalhomepage:www.elsevier.com/locate/semcancerReviewCancerstemcellswithincreasedmetastaticpotentialasatherapeutictargetforesophagealcancerD.Wanga,b,c,J.Th.M.Plukkerc,R.P.Coppesa,b,⁎aDepartmentofCellBiology,UniversityofGroningen,UniversityMedicalCenterGroningen,Groningen9700RB,TheNetherlandsbDepartmentofRadiationOncology,UniversityofGroningen,UniversityMedicalCenterGroningen,Groningen9700RB,TheNetherlandscDepartmentofSurgery,UniversityofGroningen,UniversityMedicalCenterGroningen,Groningen9700RB,TheNetherlandsARTICLEINFOKeywords:CancerstemcellsMetastasesandesophagealcancerABSTRACTEsophagealcancers(EC)arehighlyaggressivetumors,commonlypresentedinalocallyadvancedstagewithapoorprognosisandsurvival.Upto50%ofthepatientsareeligiblefortreatmentwithcurativeintentandreceivethestandardtreatmentwithneoadjuvantchemoradiotherapy(nCRT)andsurgery.Currently,pathologiccompleteresponsetonCRTis20–30%,withapartialornoresponseinabout50%and20%,respectively.ECrecurrencesoccurfrequentlyevenaftersuccessfulanti-cancertreatment,suggestinghighaggressivenesswithincreasedmetastaticpotential.Atumorsub-populationofso-calledcancerstemcells(CSCs),isknowntodisplayahighmetastaticpotentialandresistancetoconventionalanti-cancertherapy,herebybeingresponsiblefortheunbeneficialclinicalfeatures.Inthisreview,aconciseoverviewwillbegivenofthecurrentliteratureonesophagealCSCsandrelatedmetastases.EsophagealCSCmarkerswillbediscussedfollowedbythepathwaysthatinitiateandsustainthesecells.Inaddition,thecellularprocesses,epithelial-mesenchymaltransition(EMT),hypoxiaandautophagy,knowntocontributetocancerstemnessandmetastasiswillbeexplained.Finally,potentialoptionsfortreatmentalsorelatedtocancergenomeatlas(TCGA)dataonECwillbediscussed.1.IntroductionEsophagealcancer(EC)iscurrentlythe8thmostcommonmalig-nancyworldwideandthe6thleadingcauseofcancerrelateddeath,accountingformorethan490000newcasesand400000deathsin2014(worldcancerreport2014).The5-yearsurvivalofth...