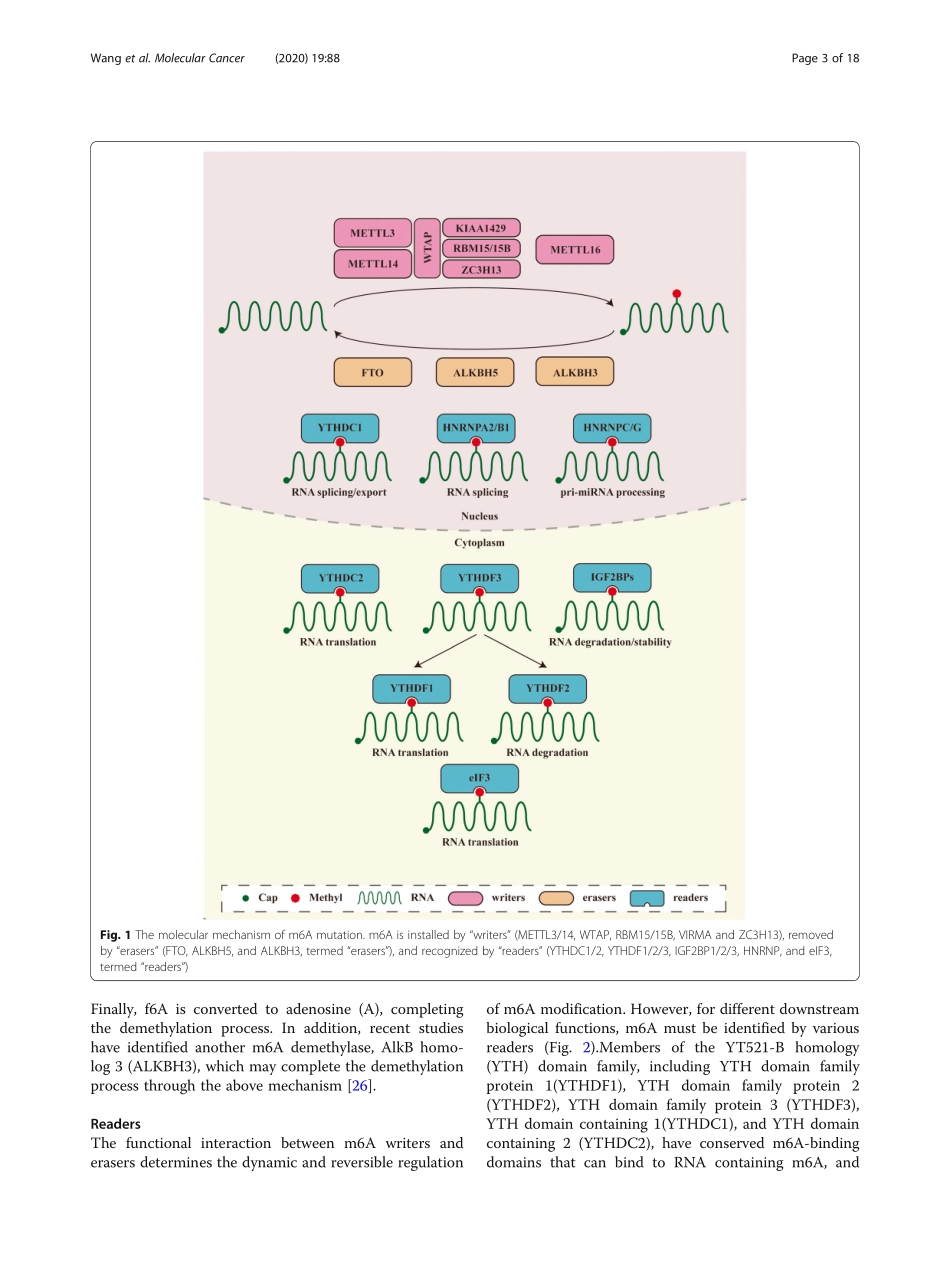
REVIEWOpenAccessThepotentialroleofRNAN6-methyladenosineinCancerprogressionTianyiWang1,2,ShanKong1,2,MeiTao1,2andShaoqingJu1,3*AbstractN6-methyladenosine(m6A)isconsideredthemostcommon,abundant,andconservedinternaltranscriptmodification,especiallyineukaryoticmessengerRNA(mRNA).m6Aisinstalledbym6Amethyltransferases(METTL3/14,WTAP,RBM15/15B,VIRMAandZC3H13,termed“writers”),removedbydemethylases(FTO,ALKBH5,andALKBH3,termed“erasers”),andrecognizedbym6A-bindingproteins(YTHDC1/2,YTHDF1/2/3,IGF2BP1/2/3,HNRNP,andeIF3,termed“readers”).Accumulatingevidencesuggeststhatm6ARNAmethylationgreatlyimpactsRNAmetabolismandisinvolvedinthepathogenesisofmanykindsofdiseases,includingcancers.Inthisreview,wefocusonthephysiologicalfunctionsofm6Amodificationanditsrelatedregulators,aswellasonthepotentialbiologicalrolesoftheseelementsinhumantumors.Keywords:N6-methyladenosine(m6A),Molecularmechanisms,CancerprogressionIntroductionMorethan160chemicallydistinctRNAmodificationshavebeenidentified,generatinganewfieldknownas“epitranscriptomics”[1].N6-methyladenosine(m6A)wasfirstdiscoveredineukaryoticmessengerRNA(mRNA)[2,3]andviralnuclearRNA[4,5]inthe1970sandhasbeenidentifiedasoneofthemostcommonandabundantRNAmodifications.However,researchonthismodificationhasbeenhindered,anditsbiologicalfunc-tionremainslargelyunknownduetothelackofmethodstodefineitslocationinRNA.Itwasnotuntil2011thatfatmassandobesity-associatedprotein(FTO)wasidentifiedasanm6AmRNAdemethylase,establish-ingtheviewofm6Aasareversiblemodification[6]andmakingitapopularresearchfocus.In2012,twogroupsindependentlyreportedhigh-throughputsequencingofm6Aatthewholetranscriptomelevel[7,8].Thedevel-opmentofm6Aantibodyaffinityenrichmentcombinedwithhigh-throughputm6AsequencingandmethylatedRNAm6Aimmunoprecipitationsequencing(MeRIP-m6A-seq)providedatechnicalfoundationforfurtherre-searchonm6A.Estimatessuggestthatmorethan7000codingand300noncodingRNAscontainm6Aandthat0.1–0.4%ofthetotaladeninenucleotidecontentismethylatedinmam-maliantranscripts[7–9].I...