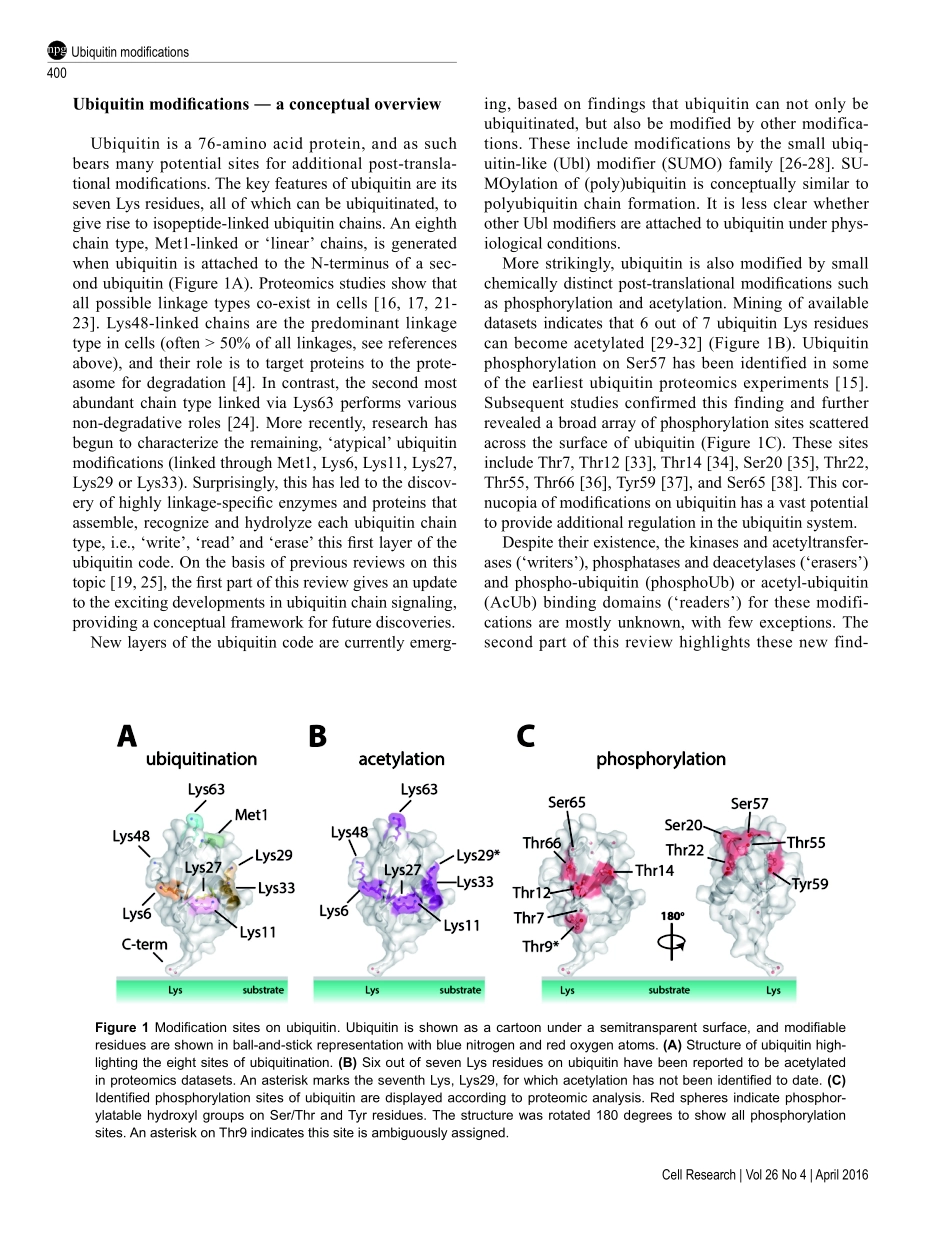
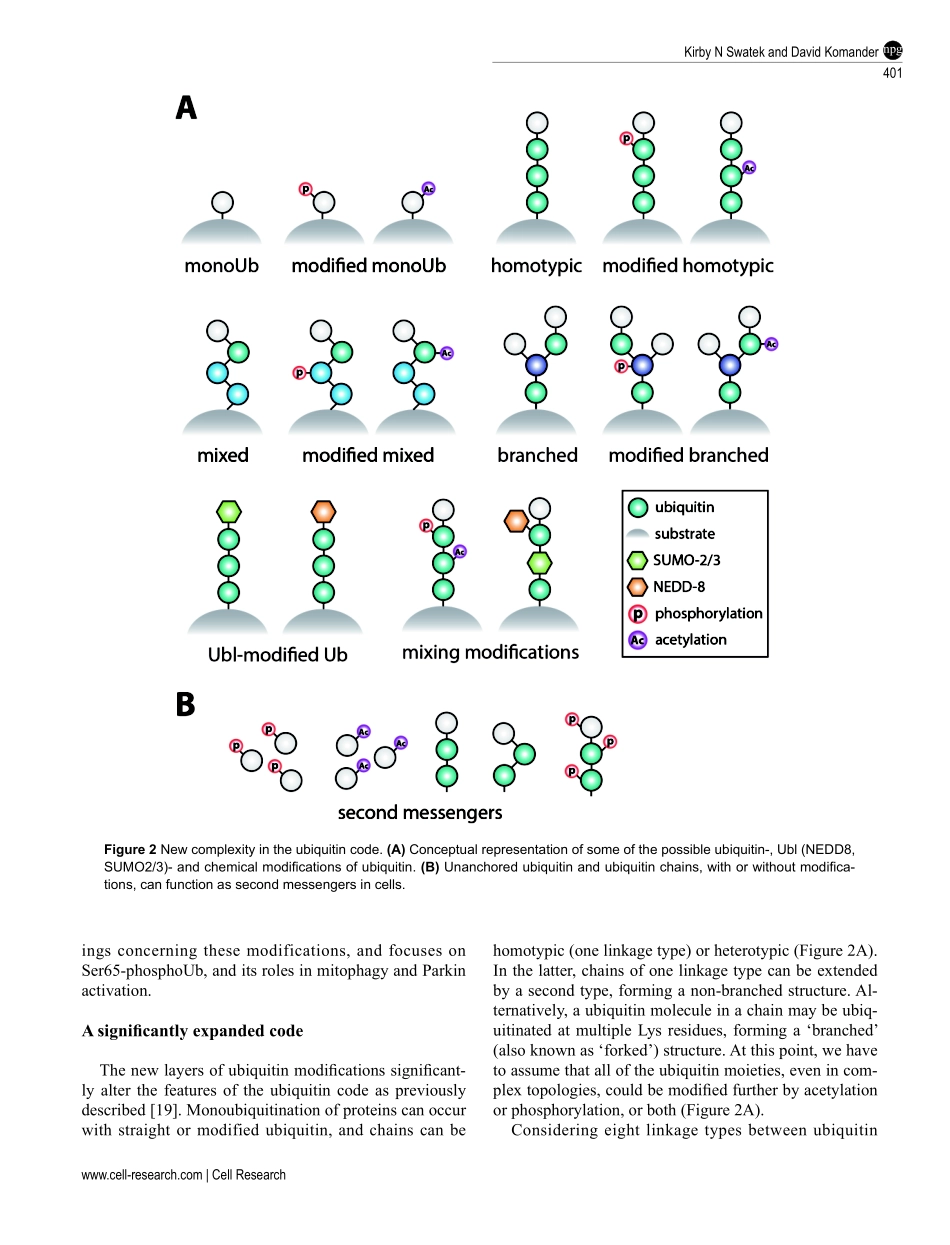
REVIEWnpgCellResearch(2016)26:399-422.www.nature.com/crUbiquitinmodificationsKirbyNSwatek1,DavidKomander11MedicalResearchCouncilLaboratoryofMolecularBiology,FrancisCrickAvenue,Cambridge,CB20QH,UKProteinubiquitinationisadynamicmultifacetedpost-translationalmodificationinvolvedinnearlyallaspectsofeukaryoticbiology.Onceattachedtoasubstrate,the76-aminoacidproteinubiquitinissubjectedtofurthermodi-fications,creatingamultitudeofdistinctsignalswithdistinctcellularoutcomes,referredtoasthe‘ubiquitincode’.Ubiquitincanbeubiquitinatedonsevenlysine(Lys)residuesorontheN-terminus,leadingtopolyubiquitinchainsthatcanencompasscomplextopologies.Alternativelyorinaddition,ubiquitinLysresiduescanbemodifiedbyubiq-uitin-likemolecules(suchasSUMOorNEDD8).Finally,ubiquitincanalsobeacetylatedonLys,orphosphorylatedonSer,ThrorTyrresidues,andeachmodificationhasthepotentialtodramaticallyalterthesignalingoutcome.Whilethenumberofdistinctlymodifiedubiquitinspeciesincellsismind-boggling,muchprogresshasbeenmadetocharacterizetherolesofdistinctubiquitinmodifications,andmanyenzymesandreceptorshavebeenidentifiedthatcreate,recognizeorremovetheseubiquitinmodifications.Wehereprovideanoverviewofthevariousubiquitinmodificationspresentincells,andhighlightrecentprogressonubiquitinchainbiology.Wethendiscusstherecentfindingsinthefieldofubiquitinacetylationandphosphorylation,withafocusonSer65-phosphorylationanditsroleinmitophagyandParkinactivation.Keywords:ubiquitin;proteasomaldegradation;phosphorylation;post-translationalmodification;ParkinCellResearch(2016)26:399-422.doi:10.1038/cr.2016.39;publishedonline25March2016IntroductionTherealizationbyGoldknopfetal.thathistonescanbemodifiedbytheproteinubiquitinthroughLys-linkedisopeptidebonds[1]markedanewerainpost-trans-lationalsignaling.Atthetime,smallchemicalmodifi-cationsofaminoacids,includingphosphorylationandacetylation,werealreadyknowntoregulateproteinfunction[2,3].Theprevalenceandimportanceofpro-tein-basedmodificationsemergedinthe1980s,whenlandmarkstudiesconnect...