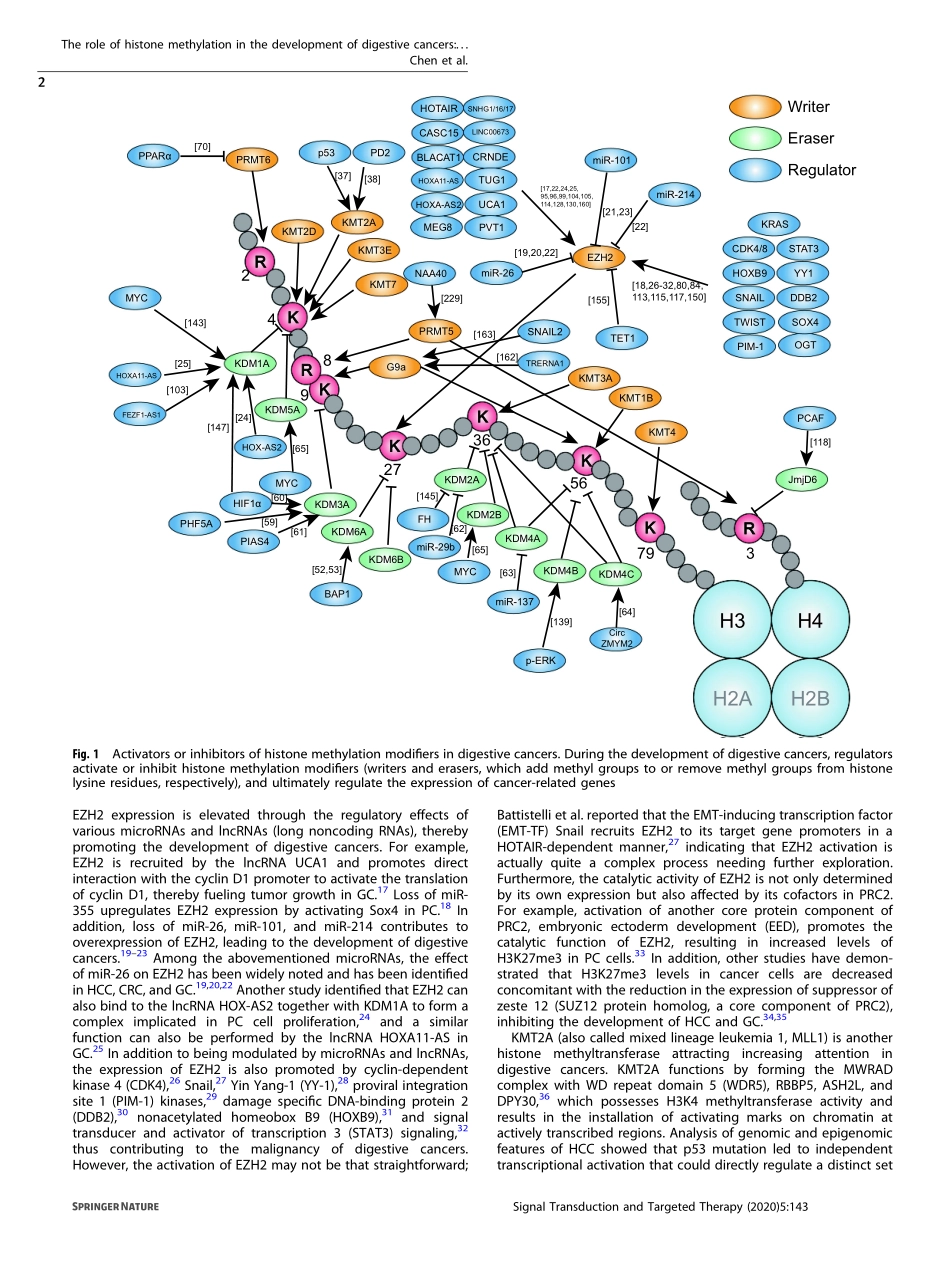
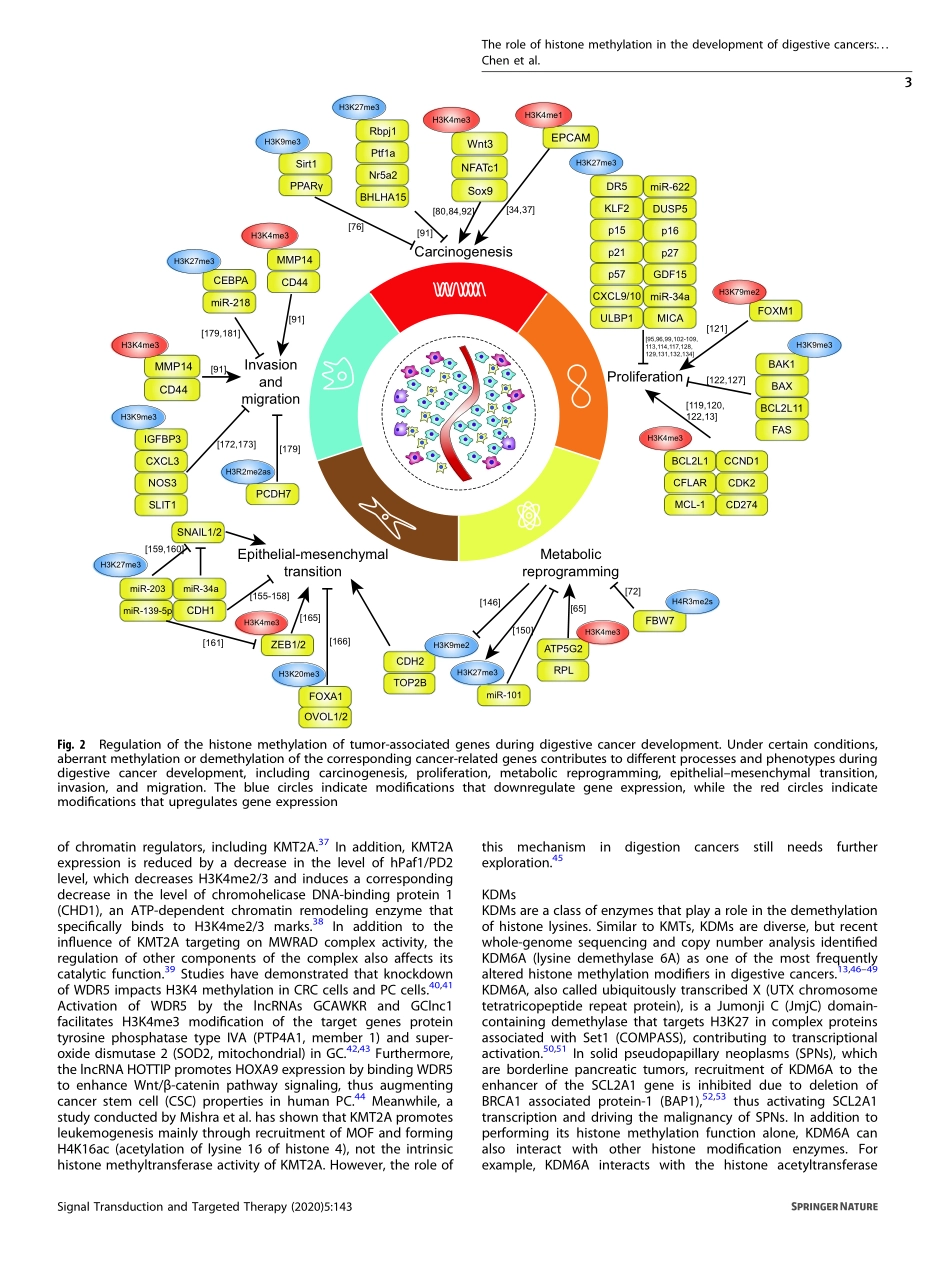
REVIEWARTICLEOPENTheroleofhistonemethylationinthedevelopmentofdigestivecancers:apotentialdirectionforcancermanagementYuanChen1,BoRen1,JinshouYang1,HuanyuWang1,GangYang1,RuiyuanXu1,LeiYou1andYupeiZhao1Digestivecancersaretheleadingcauseofcancer-relateddeathworldwideandhavehighrisksofmorbidityandmortality.Histonemethylation,whichismediatedmainlybylysinemethyltransferases,lysinedemethylases,andproteinargininemethyltransferases,hasemergedasanessentialmechanismregulatingpathologicalprocessesindigestivecancers.Undercertainconditions,aberrantexpressionofthesemodifiersleadstoabnormalhistonemethylationordemethylationinthecorrespondingcancer-relatedgenes,whichcontributestodifferentprocessesandphenotypes,suchascarcinogenesis,proliferation,metabolicreprogramming,epithelial–mesenchymaltransition,invasion,andmigration,duringdigestivecancerdevelopment.Inthisreview,wefocusontheassociationbetweenhistonemethylationregulationandthedevelopmentofdigestivecancers,includinggastriccancer,livercancer,pancreaticcancer,andcolorectalcancer,aswellasonitsclinicalapplicationprospects,aimingtoprovideanewperspectiveonthemanagementofdigestivecancers.SignalTransductionandTargetedTherapy(2020)5:143;https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00252-1INTRODUCTIONDigestivecancers,includinggastriccancer(GC),livercancer,pancreaticcancer(PC),colorectalcancer(CRC),etc.,arecommonlyobservedmalignanciesinclinicalpractice.Thelatestepidemiolo-gicaldataindicatethatanestimated333,680peoplewillbediagnosedwithdigestivecancersintheUnitedStatesin2020andthat~167,790willdieofthesediseases;bothoftheseestimatesrankfirstamongallcancers.1Althoughprogresshasrecentlybeenmadeinthemanagementofdigestivecancers,the5-yearsurvivalrateofsomecancersremainsunsatisfactory—forexample,18%forlivercancerandonly9%forPC.1Therefore,furtherstudyofthemolecularmechanismunderlyingdigestivecancersisurgentlyneeded.Theinterestinepigeneticshasincreased.Histonemodifications,includingacetylation,methylation,phosphorylation,andubiquitylation,areapivotalformof...