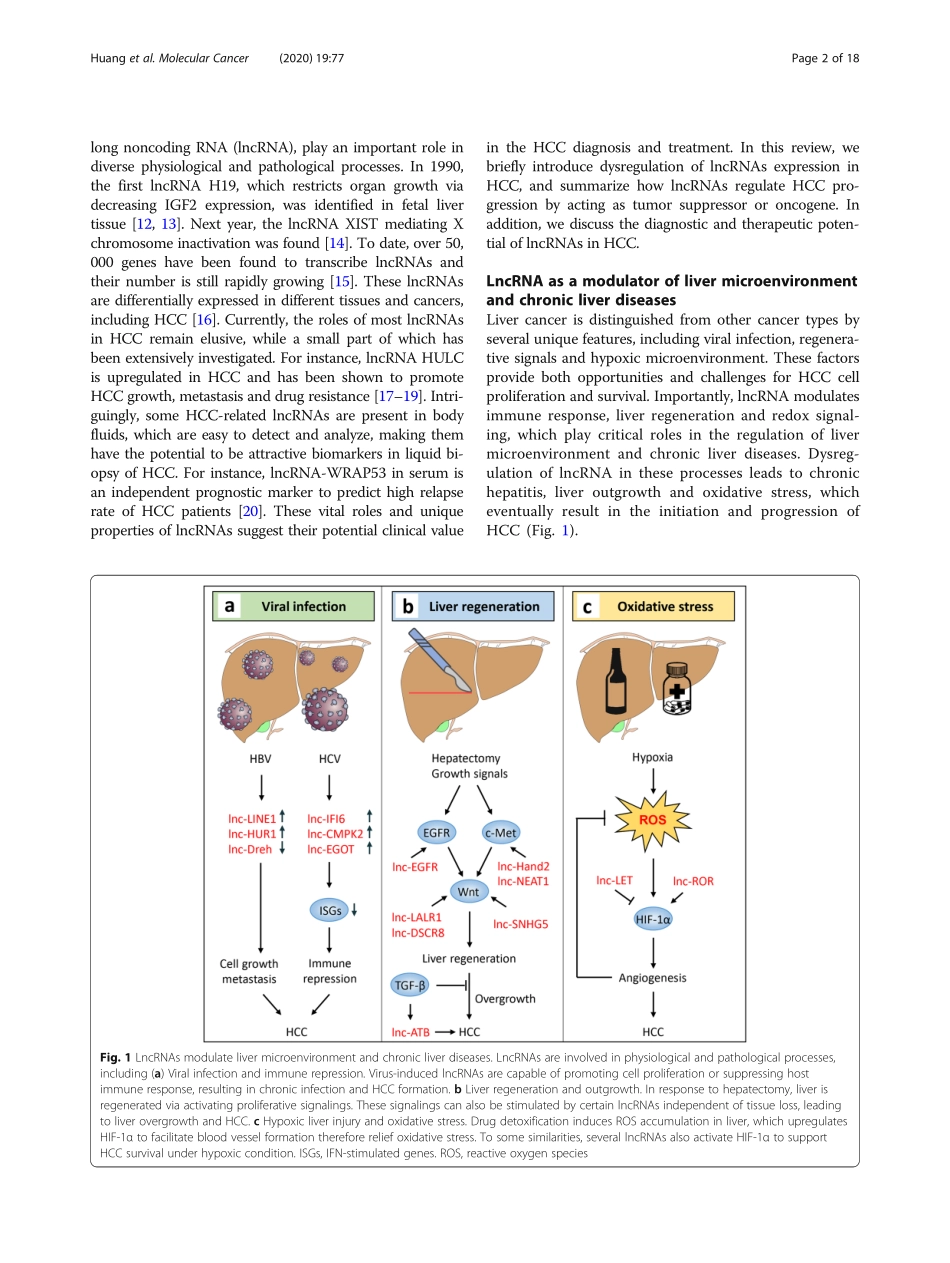
REVIEWOpenAccessTheroleoflongnoncodingRNAsinhepatocellularcarcinomaZhaoHuang1†,Jian-KangZhou1†,YongPeng1,WeifengHe2*andCanhuaHuang1*AbstractHepatocellularcarcinoma(HCC)isthemostfrequentsubtypeofprimarylivercancerandoneoftheleadingcausesofcancer-relateddeathworldwide.However,themolecularmechanismsunderlyingHCCpathogenesishavenotbeenfullyunderstood.EmergingevidenceshaverecentlysuggestedthecrucialroleoflongnoncodingRNAs(lncRNAs)inthetumorigenesisandprogressionofHCC.VariousHCC-relatedlncRNAshavebeenshowntopossessaberrantexpressionandparticipateincancerousphenotypes(e.g.persistentproliferation,evadingapoptosis,acceleratedvesselformationandgainofinvasivecapability)throughtheirbindingwithDNA,RNAorproteins,orencodingsmallpeptides.Thus,adeeperunderstandingoflncRNAdysregulationwouldprovidenewinsightsintoHCCpathogenesisandnoveltoolsfortheearlydiagnosisandtreatmentofHCC.Inthisreview,wesummarizethedysregulationoflncRNAsexpressioninHCCandtheirtumorsuppressiveoroncogenicrolesduringHCCtumorigenesis.Moreover,wediscussthediagnosticandtherapeuticpotentialsoflncRNAsinHCC.Keywords:LongnoncodingRNA,Hepatocellularcarcinoma,Biomarker,TargetedtherapyIntroductionHepatocellularcarcinoma(HCC)isoneofthemostcommonmalignanciesworldwideandranksasthethirdmostcommoncauseofcancer-relateddeath,especiallyinAfricaandEasternAsiaduetothelackofsurveillanceandtreatmentoptions[1].TheriskfactorsunderlyingHCCpathogenesisarehighlyvariable,includingchronichepatitisB(HBV)andhepatitisCvirus(HCV)infection,alcoholconsumption,non-alcoholicfattyliverdisease(NAFLD),andaflatoxinB1intake[2].ThesefactorsmayinduceDNAdamage,epigeneticalterationsandcancer-relatedmutations,leadingtothesilencingoftumorsup-pressors(e.g.TP53,CDH1,RASSF1)andtheactivationofoncogenes(e.g.MYC,VEGFA,MAPK7),whicheventuallycontributetoHCCprogression[3–6].Todate,severalpreventiveandtherapeuticstrategieshavebeenimplicatedinthemanagementofHCC,asexampledbytheadminis-trationofanti-hepatitisvaccine,specifickinaseinhibitors(e.g.SorafenibandRegorafenib),...