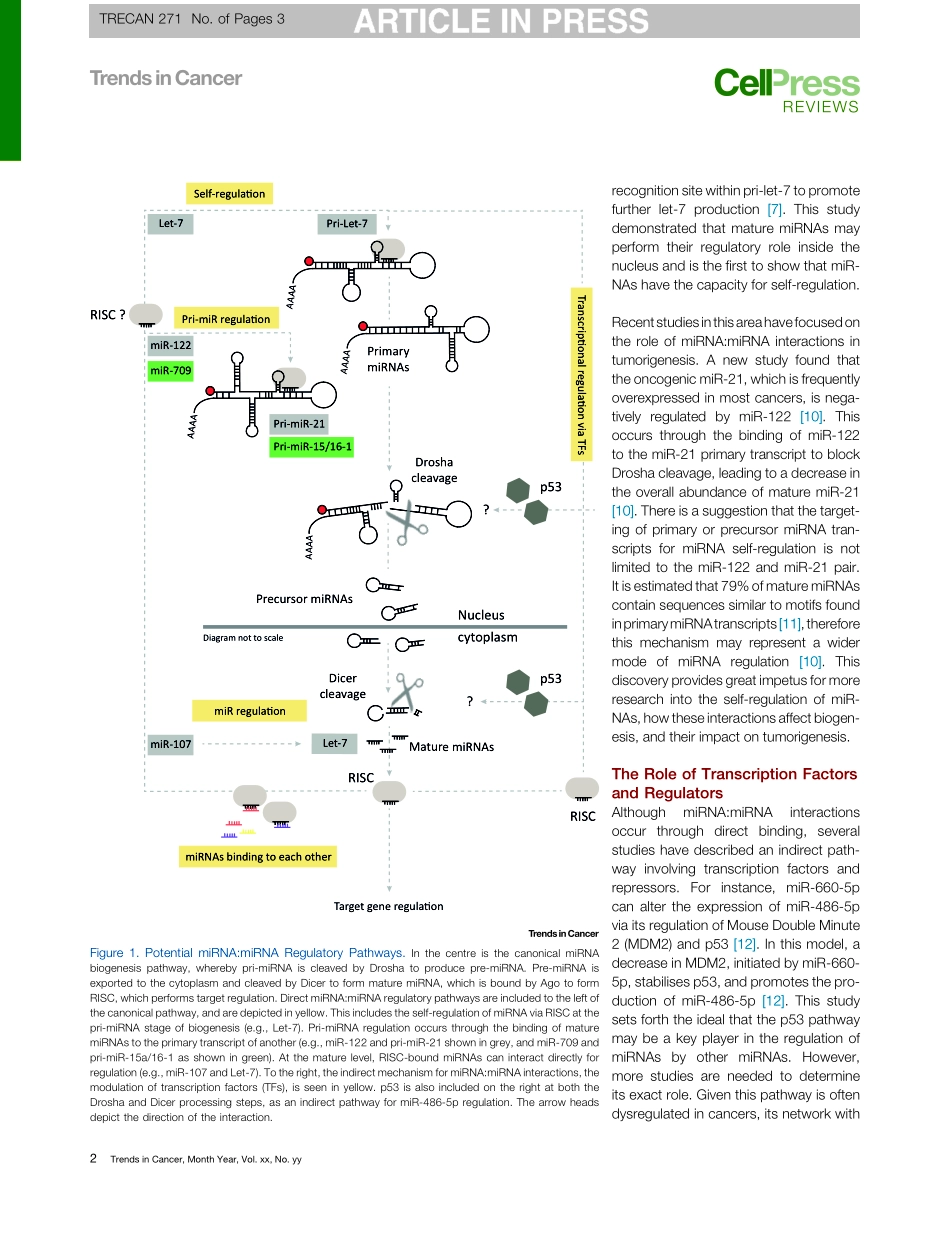
ForumMicroRNAsRegulatingMicroRNAsinCancerMeredithHill1andNhamTran1,2,*MicroRNAs(miRNA)arecapableofself-regulation,termedmiRNAtomiRNAinteraction.Verylittleisknownabouttheseinteractionsandtheirimpactonthecellularmilieu.We[45_TD$DIF]discussknownmiRNAtomiRNAinteractions,potentialmechanisms,andtheirroleincancer.TheFunctionofMiRNAsMiRNAsareclassifiedasnoncodingRNAsthatregulatetheexpressionofmessengerRNA(mRNA)bybindingtocomplementarysequenceswithinthe30untranslatedregion(30UTR)[1].Thetran-scribedprimaryRNAtranscriptunder-goescleavagebytheenzymesDroshaandDicertoproduceprecursorandmaturemiRNA,respectively[1].MaturemiRNAsareboundtoArgonaute(Ago)toformtheRNAinducedsilencingcom-plex(RISC)forgeneregulation.Duetotheirrole,alterationsinmiRNAexpressioncandisruptmRNAexpression,includingthatofoncogenesandtumoursuppres-sorgenes,leadingtopotentialoncogenicchanges[1,2].Thus,itisimportantthatmoreisknownabouttheregulationofmiRNAstofurtherunderstandtheirinflu-enceinacellularsystem.ThepurposeofthisarticleistohighlightanemergingareaofmiRNAregulation,wherebyonemiRNAcontrolstheexpressionofanother.MiRNAtoMiRNARegulationSeveralprocessesareinvolvedinregulat-ingthebiogenesisofmiRNAsandtheirendogenouslevels.However,recentstudieshaveshownthatmiRNAscanbindtoandcontrolothernoncodingRNAs,includingmiRNAs.[46_TD$DIF]ThisprocessisknownasamiRNA:miRNAinteraction.TheoverallresultofthisinteractionistheregulationofamiRNA’sabundanceandbiogenesisbyanothermiRNA,withsub-sequenteffectsonmRNAregulation.ThisphenomenonwasfirstobservedbyLaietal.,whofoundtwomiRNApairsinDrosophila,miR-5:miR-6andmiR-9:miR-79,basedonnucleotidesequencecomplementarity[3].ThissuggestedthatmiRNAscouldbindandregulatebothmRNAandnoncodingRNA.However,sincethesemiRNApairswereidentifiedthroughsequencingandwerenotexperi-mentallyvalidated,itisuncertainwhetherthesemiRNAcomplexesareformedinbiologicalsystems.IthasbeenproposedthatmiRNApairingbetweensimilarmiR-NAsincreasestheirindividualstability[3].Additionally,thebindingofmiRNApairspreventsthecontrol...