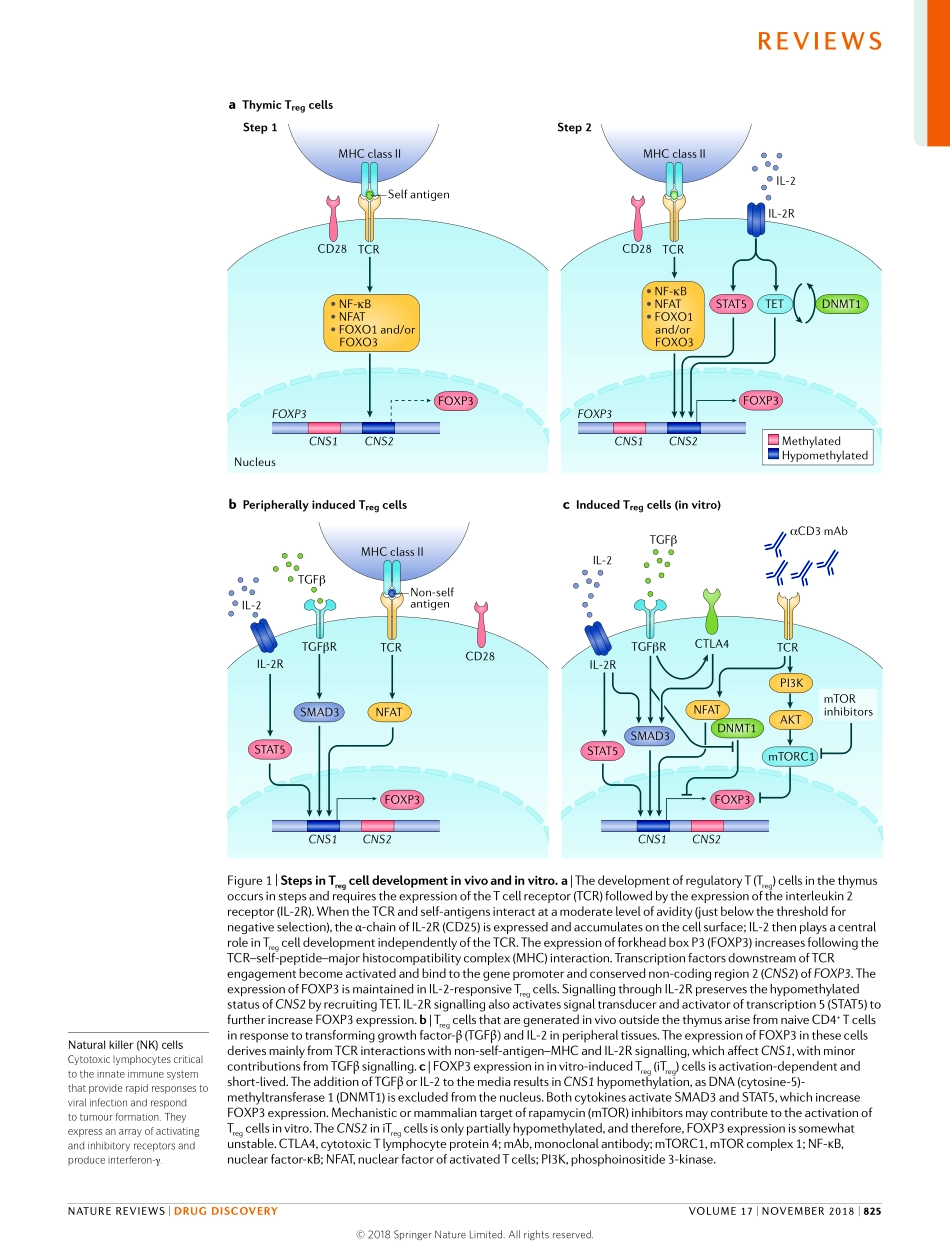
TheimmunesystememploysnumerousmechanismstoregulateTcell-dependentimmuneresponses.Downregulationofanimmuneresponsefollowinginfectioniscriticaltoavoiduncontrolledclonalexpan-sionandexcessivecytokineproduction,andreducingtheimmuneresponsetoself-antigensisnecessarytopreventorgandamageinautoimmunediseases.Ontheflipside,thesuppressionoftheimmuneresponsethatoccursinpatientswithcancerisdetrimental,asitallowsuncheckedtumourgrowth.Muchofourunderstandingoftheseprocessescomesfromuncoveringthecellularandmolecularmecha-nismsbywhichresponsestoself-antigensareregulated.Numerousdifferentcellsharboursuppressiveactiv-itythatcontributestoself-tolerance(SupplementaryBox1).Themostimportantcellsinthesuppressionofself-reactiveTcellsaretheCD4+Tcellsthatexpressfork-headboxP3(FOXP3)(hereinreferredtoasregulatoryT(Treg)cells).ThecriticalroleofTregcellsinthedevel-opmentofautoimmunityhasbeenhighlightedbythemulti-organautoinflammatorysyndromethatdevelopsinFOXP3-deficientmice1,2andtheimmunedysregula-tion,polyendocrinopathy,enteropathy,X-linked(IPEX)syndromeseeninhumans3,4,whichoccursinindividualswhoharbourmutationsinFOXP3.ApproachestoincreasethenumberandfunctionofTregcellscouldclearlybenefitpatientswithautoimmunedisorders.Someoftheseapproachesarenowinclinicaltrials.OnesucheffortinvolvesadoptiveTregcelltherapy5–7andincludesthepotentialtoengineerantigenspecific-ityintothetransferredTregcells;inanother,low-doseinterleukin(IL)-2isadministeredtoselectivelyexpandTregcellpopulations,astrategythatcouldbeappliedtomanypatientswithautoimmunediseases8–10.Inaddi-tion,strategiestoreducethefunctionand/ornumberofTregcellsarebeinginvestigatedtopromoteantitumourimmunity.InthisReview,wefocusontherapiesthattargetTregcellsandarenowbeingexploitedtotreatautoimmunediseasesandcancer.WediscussthebiologyandfunctionofTregcellsandthenhighlightthecurrenttherapeuticapproachesbeinginvestigatedtoeitherempowerthemorlimittheirsuppressivecapacityandexpansion.BiologyofTregcellsDevelopmentalheterogeneityTregcellsaremarkedbythetran...