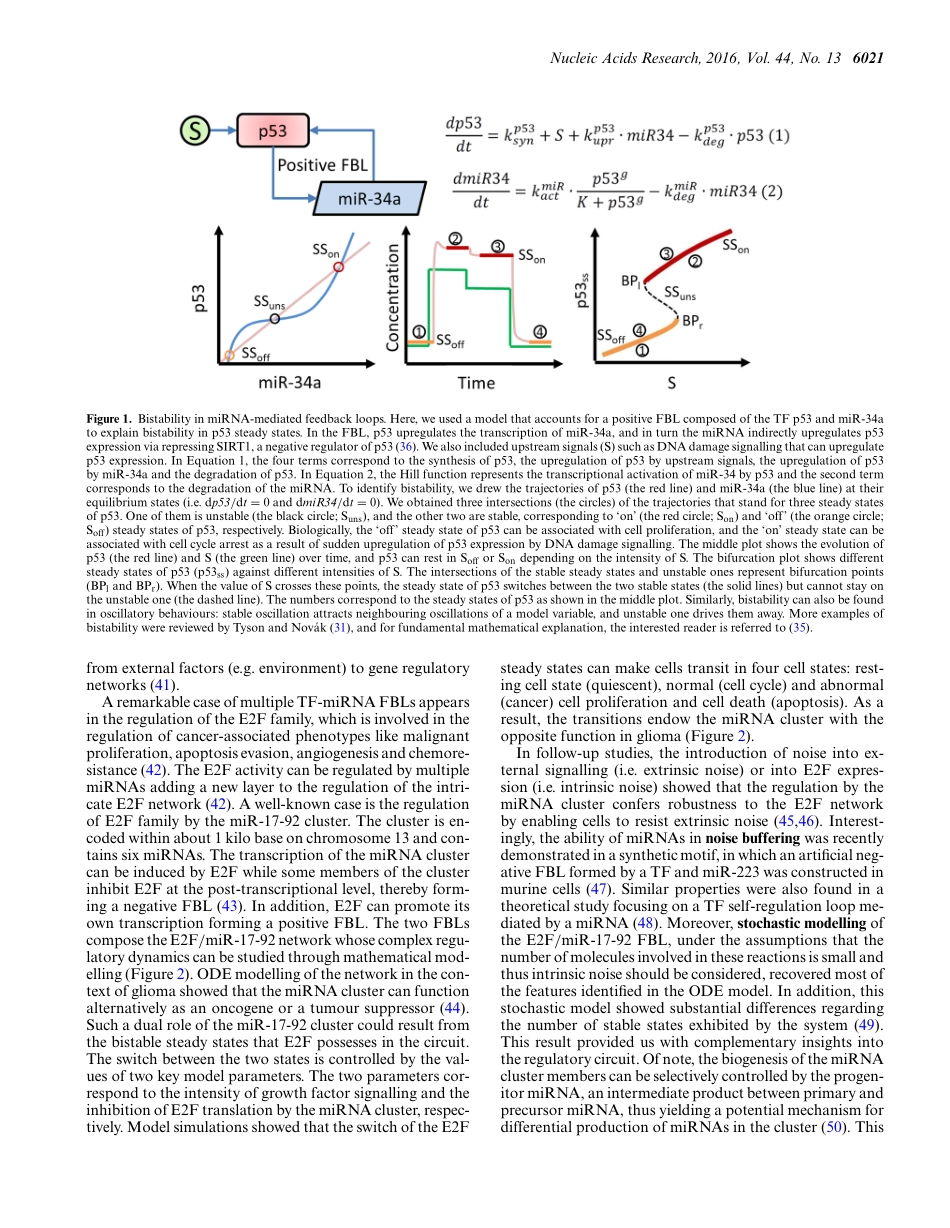
Publishedonline17June2016NucleicAcidsResearch,2016,Vol.44,No.136019–6035doi:10.1093/nar/gkw550SURVEYANDSUMMARYUnderstandingmicroRNA-mediatedgeneregulatorynetworksthroughmathematicalmodellingXinLai1,*,OlafWolkenhauer2,3andJulioVera1,*1LaboratoryofSystemsTumourImmunology,DepartmentofDermatology,ErlangenUniversityHospitalandFriedrich-AlexanderUniversityErlangen-Nuremberg,Erlangen,91054,Germany,2DepartmentofSystemsBiology&Bioinformatics,UniversityofRostock,Rostock,18051,Germanyand3StellenboschInstituteforAdvancedStudy,WallenbergResearchCentreatStellenboschUniversity,7600,SouthAfricaReceivedDecember29,2015;RevisedJune2,2016;AcceptedJune6,2016ABSTRACTThediscoveryofmicroRNAs(miRNAs)hasaddedanewplayertotheregulationofgeneexpression.Withtheincreasingnumberofmolecularspeciesin-volvedingeneregulatorynetworks,itishardtoob-tainanintuitiveunderstandingofnetworkdynam-ics.MathematicalmodellingcanhelpdissectingtheroleofmiRNAsingeneregulatorynetworks,andweshallherereviewthemostrecentdevelopmentsthatutilisedifferentmathematicalmodellingapproachestoprovidequantitativeinsightsintothefunctionofmiRNAsintheregulationofgeneexpression.KeymiRNAregulationfeaturesthathavebeenelucidatedviamodellinginclude:(i)theroleofmiRNA-mediatedfeedbackandfeedforwardloopsinfine-tuningofgeneexpression;(ii)themiRNA–targetinteractionpropertiesdeterminingtheeffectivenessofmiRNA-mediatedgenerepression;and(iii)thecompetitionforsharedmiRNAsleadingtothecross-regulationofgenes.However,thereisstilllackofmechanisticunderstandingofmanyotherpropertiesofmiRNAregulationlikeunconventionalmiRNA–targetinter-actions,miRNAregulationatdifferentsub-cellularlocationsandfunctionalmiRNAvariant,whichwillneedfuturemodellingeffortstodealwith.Thisre-viewprovidesanoverviewofrecentdevelopmentsandchallengesinthisfield.INTRODUCTIONMicroRNAs(miRNAs)areaclassofsmallendogenousnon-codingRNAs(ncRNAs)withalengthof∼22nt(1,2).MiRNAsfunctionasevolutionarilyconservedpost-transcriptionalgeneregulatorsthat,inmostcases,decreasethestabilityorinhibi...