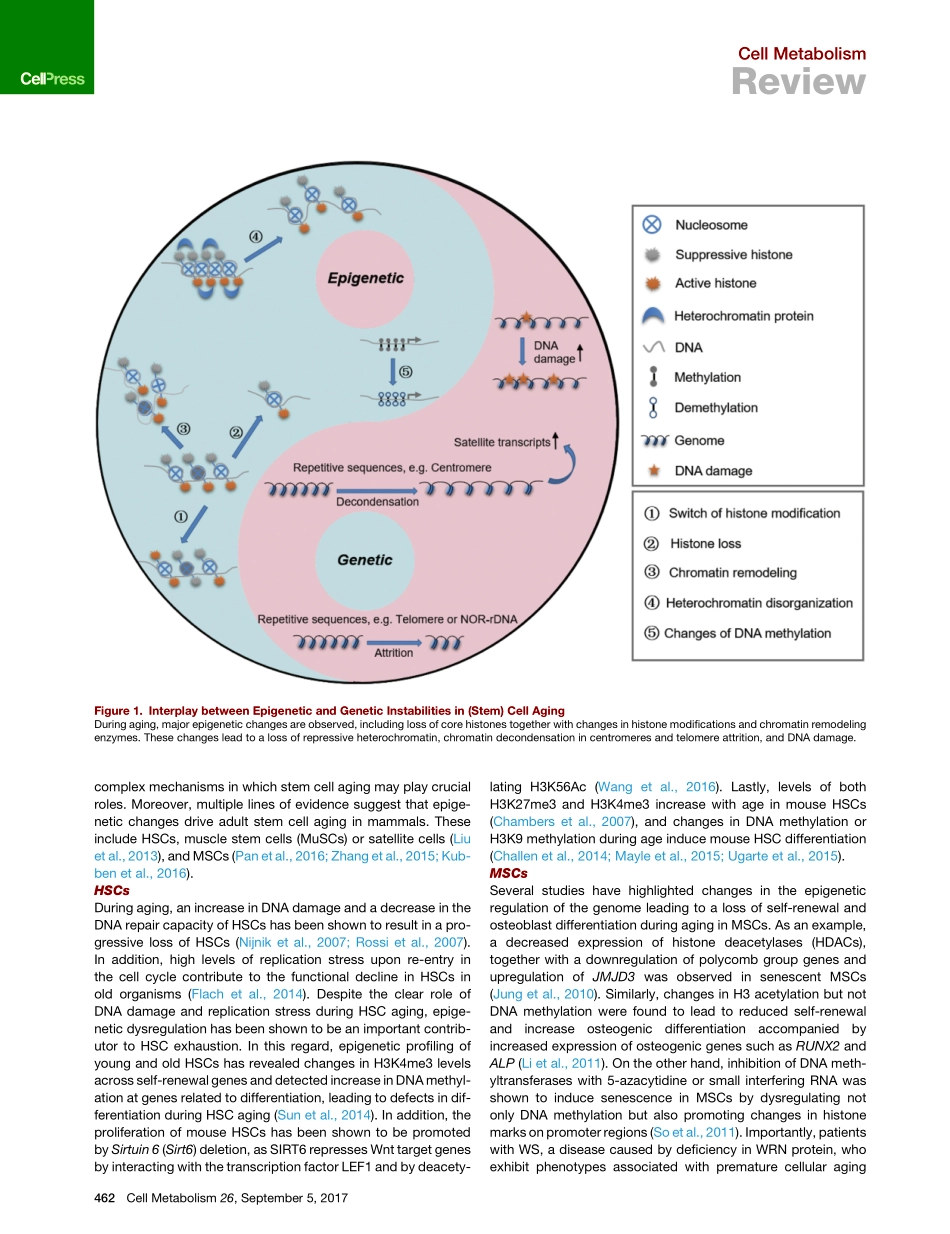
CellMetabolismReviewRegulationofStemCellAgingbyMetabolismandEpigeneticsRuotongRen,1,2,3AlejandroOcampo,4Guang-HuiLiu,1,2,3,5,*andJuanCarlosIzpisuaBelmonte4,*1NationalClinicalResearchCenterforGeriatricDisorders,XuanwuHospitalofCapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100053,China2NationalLaboratoryofBiomacromolecules,CASCenterforExcellenceinBiomacromolecules,InstituteofBiophysics,ChineseAcademyofSciences,Beijing100101,China3UniversityofChineseAcademyofSciences,Beijing100049,China4GeneExpressionLaboratory,SalkInstituteforBiologicalStudies,10010NorthTorreyPinesRoad,LaJolla,CA92037,USA5BeijingInstituteforBrainDisorders,Beijing100069,China*Correspondence:ghliu@ibp.ac.cn(G.-H.L.),belmonte@salk.edu(J.C.I.B.)http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.07.019Stemcellagingandexhaustionareconsideredimportantdriversoforganismalaging.Age-associateddeclinesinstemcellfunctionarecharacterizedbymetabolicandepigeneticchanges.Understandingthemechanismsunderlyingthesechangeswilllikelyrevealnoveltherapeutictargetsforamelioratingage-asso-ciatedphenotypesandforprolonginghumanhealthspan.Recentstudieshaveshownthatmetabolismplaysanimportantroleinregulatingepigeneticmodificationsandthatthisregulationdramaticallyaffectstheagingprocess.Thisreviewfocusesoncurrentknowledgeregardingthemechanismsofstemcellaging,andthelinksbetweencellularmetabolismandepigeneticregulation.Inaddition,wediscusshowtheseinteractionssenseandrespondtoenvironmentalstressinordertomaintainstemcellhomeostasis,andhowenviron-mentalstimuliregulatestemcellfunction.Additionally,wehighlightrecentadvancesinthedevelopmentoftherapeuticstrategiestorejuvenatedysfunctionalagedstemcells.IntroductionAgingcanbedefinedasacomplex,time-dependentprocessthataffectsmultipletissuesandorgansleadingtoaprogressivereductioninphysiologicalintegrityandthedegenerationoftis-sue,organ,andorganismalfunction.Understandingthecauseofaginghasbeenanareaofinterestthroughouthumanhistory.Duringthepast30years,agingresearchhasdramaticallyadvanced,beginningwiththeinitialdiscoverie...