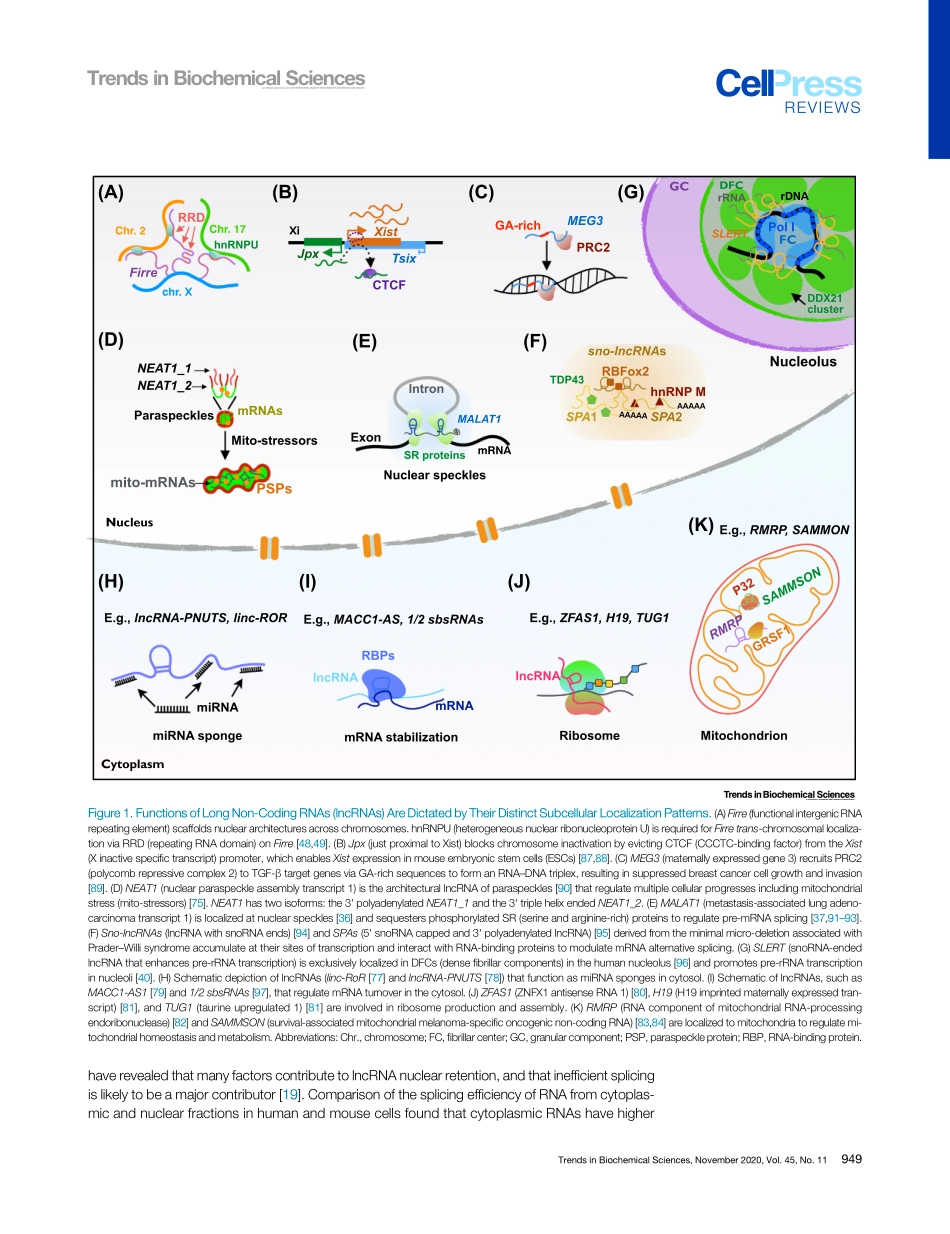
ReviewMechanismsofLongNoncodingRNANuclearRetentionChun-JieGuo,1GuangXu,1andLing-LingChen1,2,3,*LongnoncodingRNAs(lncRNAs)arecrucialregulatorsindiversecellularcontextsandbiologicalprocesses.ThesubcellularlocalizationoflncRNAsdeterminestheirmodesofaction.ComparedtomRNAs,however,manymRNA-likelncRNAsarepreferentiallylocalizedtothenucleuswheretheyregulatechromatinorganization,transcription,anddifferentnuclearcondensates.RecentstudieshaverevealedthecomplexmechanismsthatgovernlncRNAnuclearretention.WereviewcurrentunderstandingofhowthetranscriptionandprocessingoflncRNAs,motifswithinlncRNAs,andtrans-factorscoordinatelycontributetotheirnuclearreten-tioninmammaliancells.ManylncRNAsAreLocalizedtotheNucleusLarge-scaletranscriptomicanalyseshaveuncoveredthatlncRNAsarepervasivelytranscribedbyRNApolymeraseII(PolII)[1–3].Mostwell-characterizedlncRNAsareprocessedtoproducemRNA-likemoleculesthatcontaina5'methylguanylatecap(m7G)anda3'poly(A)tail[3,4],whilesomearegeneratedviaunusualprocessingpathwaysandarestabilizedbyforminguniquestructuresattheirends(reviewedin[5,6]).AlthoughsomeannotatedlncRNAtranscriptscanin-deedbetranslatedintofunctionalpolypeptides[7–9],anincreasinglistofnon-protein-codinglncRNAsplaykeyrolesindiversecellularcontextsandbiologicalprocesses(reviewedin[10–12]).Theseactivitiesareassociatedwiththeirdistinctsubcellularfates(reviewedin[5,13]).AlthoughsomelncRNAsareexportedtothecytoplasmtocarryouttheirfunctions(Box1),manyothersarelocalizedinthenucleus[3,4,14],wheretheyassociatewithchromatintomodulatechromatinstatus(Figure1A)andinterferewithPolIItranscription(Figure1B,C),oraccumulateinnuclearcondensatestoregulatetheirassembliesandfunctions(Figure1D–G).ComparedtomRNAs,howagroupofmRNA-likelncRNAsareacquiredtheirdistinctsub-cellularfatesorfunctionshasremainedintriguing.Ontheonehand,theexportofmRNA-likelncRNAsmaycopymRNAmechanisms[15]ordisplayselectivelocalizationsimilarlytomRNAsinvolvedinbiologicalprocessessuchasDNArepair,proliferation,andcellsurvival[16].Ontheotherhand,re...