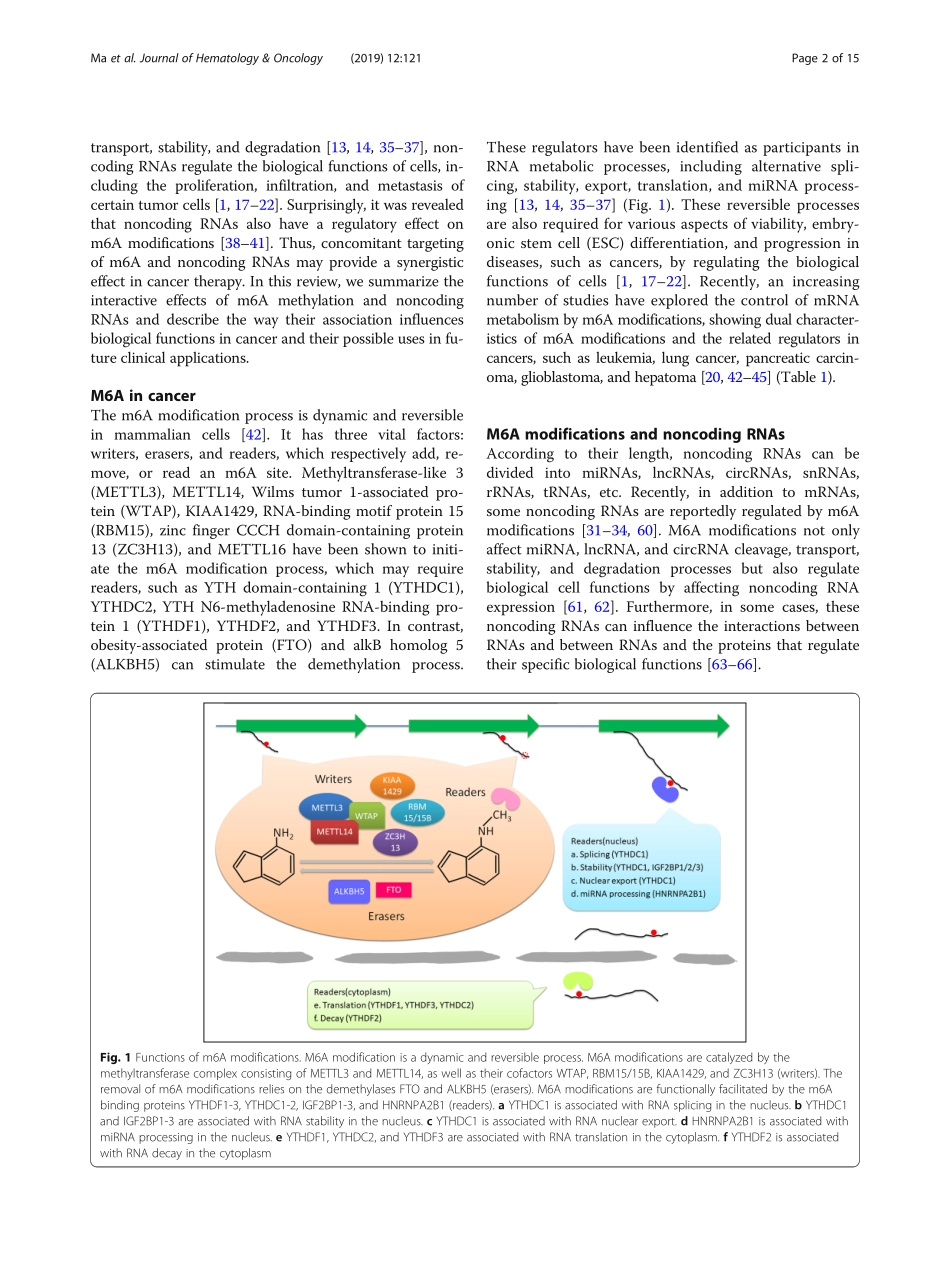
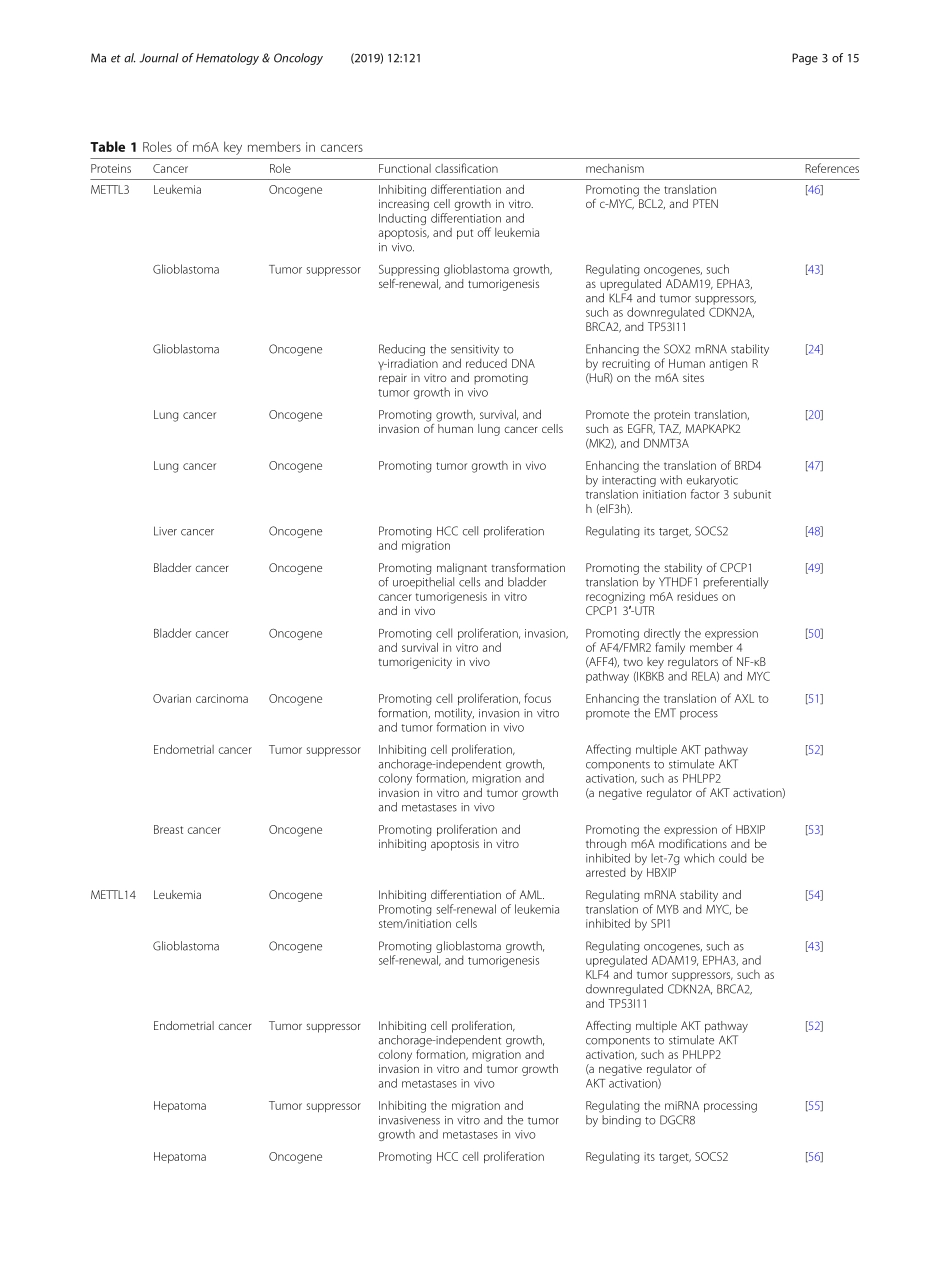
REVIEWOpenAccessTheinterplaybetweenm6ARNAmethylationandnoncodingRNAincancerShuaiMa1†,ChenChen1,2†,XiangJi1†,JinboLiu1,QuanboZhou1,GuixianWang1,WeitangYuan1*,QuanchengKan3*andZhenqiangSun1,2,3*AbstractN6-methyladenosine(m6A)methylation,oneofthemostcommonRNAmodifications,hasbeenreportedtoexecuteimportantfunctionsthataffectnormallifeactivitiesanddiseases.Moststudieshavesuggestedthatm6Amodificationcanaffectthecomplexityofcancerprogressionbyregulatingbiologicalfunctionsrelatedtocancer.M6AmodificationofnoncodingRNAsregulatesthecleavage,transport,stability,anddegradationofnoncodingRNAsthemselves.Italsoregulatescellproliferationandmetastasis,stemcelldifferentiation,andhomeostasisincancerbyaffectingthebiologicalfunctionofcells.Interestingly,noncodingRNAsalsoplaysignificantrolesinregulatingthesem6Amodifications.Additionally,itisbecomingincreasinglyclearthatm6AandnoncodingRNAspotentiallycontributetotheclinicalapplicationofcancertreatment.Inthisreview,wesummarizetheeffectoftheinteractionsbetweenm6AmodificationsandnoncodingRNAsonthebiologicalfunctionsinvolvedincancerprogression.Inparticular,wediscusstheroleofm6AandnoncodingRNAsaspossiblepotentialbiomarkersandtherapeutictargetsinthetreatmentofcancers.Keywords:M6Amodification,NoncodingRNAs,Cancer,ClinicalperspectivesBackgroundThegenome-widedistributionofn6-methyladenosine(m6A)wasunclearuntil2012,butm6Aisthemostcom-monRNAmodificationofmRNAs.Itisenrichedinmanyeukaryoticspeciesofmammals,plants,andyeast[1–8]andisfoundinprokaryotes,includingbacteriaandmycoplasma[9,10].ThemRNAsof7676mammaliangeneswerefoundtobemodifiedbym6A[11].Moreover,therearemorethan7000humangeneswith12,000m6AsitesthatareenrichedintheconsensussequenceRRACH(R=GorAandH=A,C,orU),whichtendstobefoundinstopcodonsand3′untranslatedregions(3′UTRs)[12].M6Amodificationsoccurviathem6Amethyltransferasescalled“writers”;theyareremovedbythedemethylasescalled“erasers”andarerecognizedbym6A-bindingproteinscalled“readers”[13–16].M6Amodificationsarequiteprevalent,andthedyn...