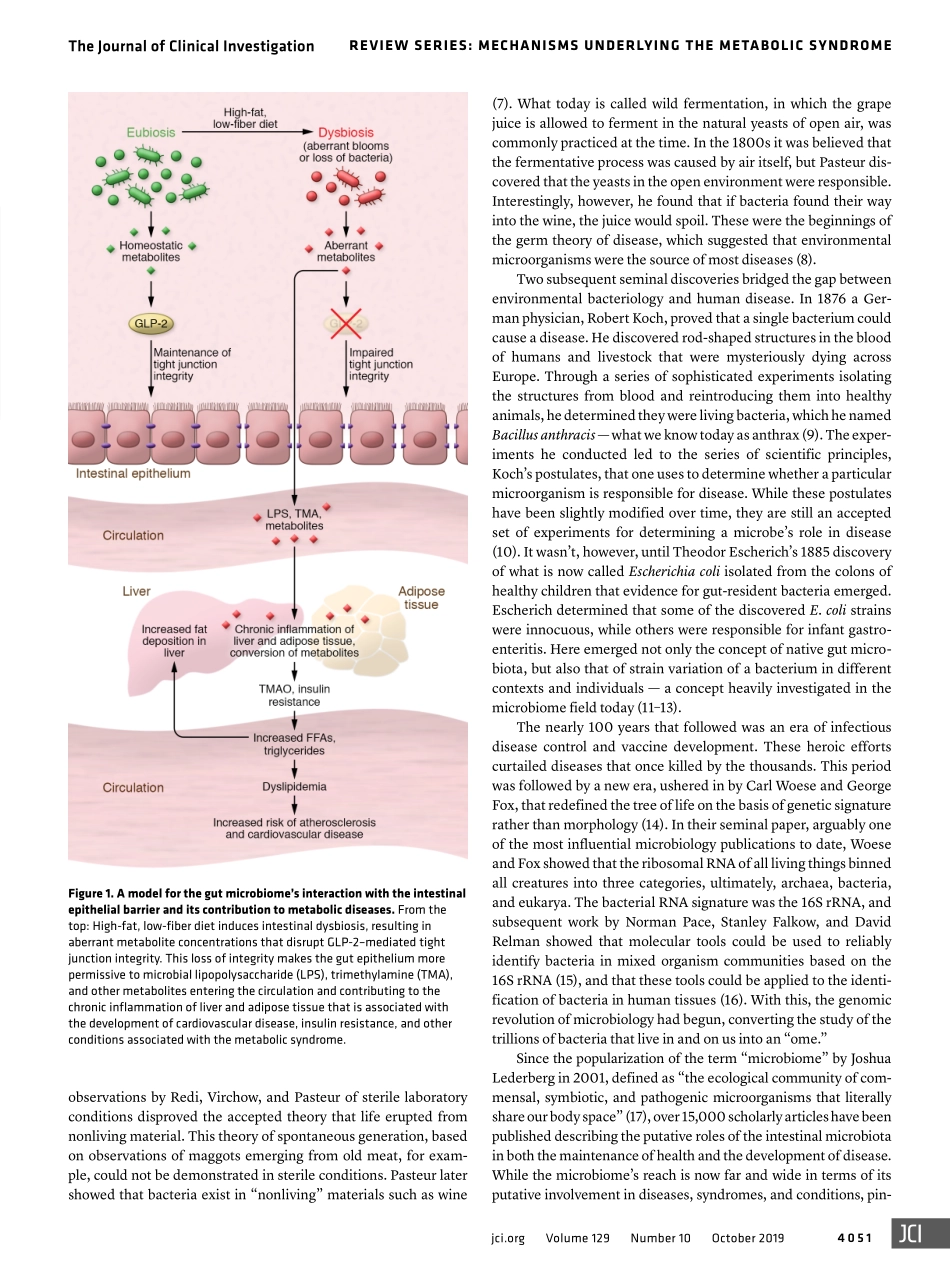
TheJournalofClinicalInvestigation4050jci.orgVolume129Number10October2019REVIEWSERIES:MECHANISMSUNDERLYINGTHEMETABOLICSYNDROMESeriesEditor:PhilippE.SchererIntroductionThegutmicrobiomehasbeenimplicatedintheetiopathogenesisofmultiplediseasesrangingfromtheintestinal(inflammatoryboweldiseases,coloncancer)totheneurological(Parkinson’sdisease,autism).However,definitionofthemicrobiome’sroleinmetabolicdiseaseshasremainedelusive.Theprimaryreasonisthattheveryfactorsbelievedtobecentraldriversofdysmetabolismarealsobelievedtobetheprimarydriversofourgutmicrobiomecompo-sition:dietandlifestyle.Whileitisconceptuallyintuitivethatthegutmicrobiomeandhostmetabolismwouldbeinterrelated,dis-entanglingcauseandeffectremainsachallenge.InthisReviewwewillexploretheevidenceforalinkbetweenthegutmicrobiomeandmetaboliceventsthatcontributetothemetabolicsyndrome(MetS).Inparticular,wewilltakeagut-centricviewofMetSthatrootsitselfinthehypothesisthatchronicsystemicdefects,suchasMetS,maybeginhere,whereimmune,hormonal,nervous,andmicrobialsignalsconverge(Figure1).DefiningandredefiningthemetabolicsyndromeTheterm“metabolicsyndrome”wasfirstcoinedinthe1970sbyHermanHaller,whowasstudyingthevariousrisksassociatedwithatherosclerosis.However,theassociationofdysmetabolismwithcardiovascularriskfactorswasdocumentedasearlyasthe1920s;thelinkbetweenthesecardiovascularriskfactorsandandroidadiposity(theaccompanyingphenotype,characterizedbyfatdistributioninthetrunkandupperbody)wasdescribedshortlythereafter.Then,in1988,GeraldReavenofferedanewnameforMetS,“syndromeX,”whichnowemphasizedinsulinresistanceamongtheconstellationofriskfactors(1).Despiteobservationoftheseclinicalfindingsforover80years,developingastandarddefinitionforMetShasprovedchallenging.Multipleorganizations,suchastheWorldHealthOrganization,theAmericanAssociationforClinicalEndocrinology,andtheInternationalDiabetesFederation,havesincecomeoutwiththeirowndefinitionsforMetSthat,whileoverlapping,arenotidentical(2,3).Thesedefinitionsallincludecentralobesity,dysli...