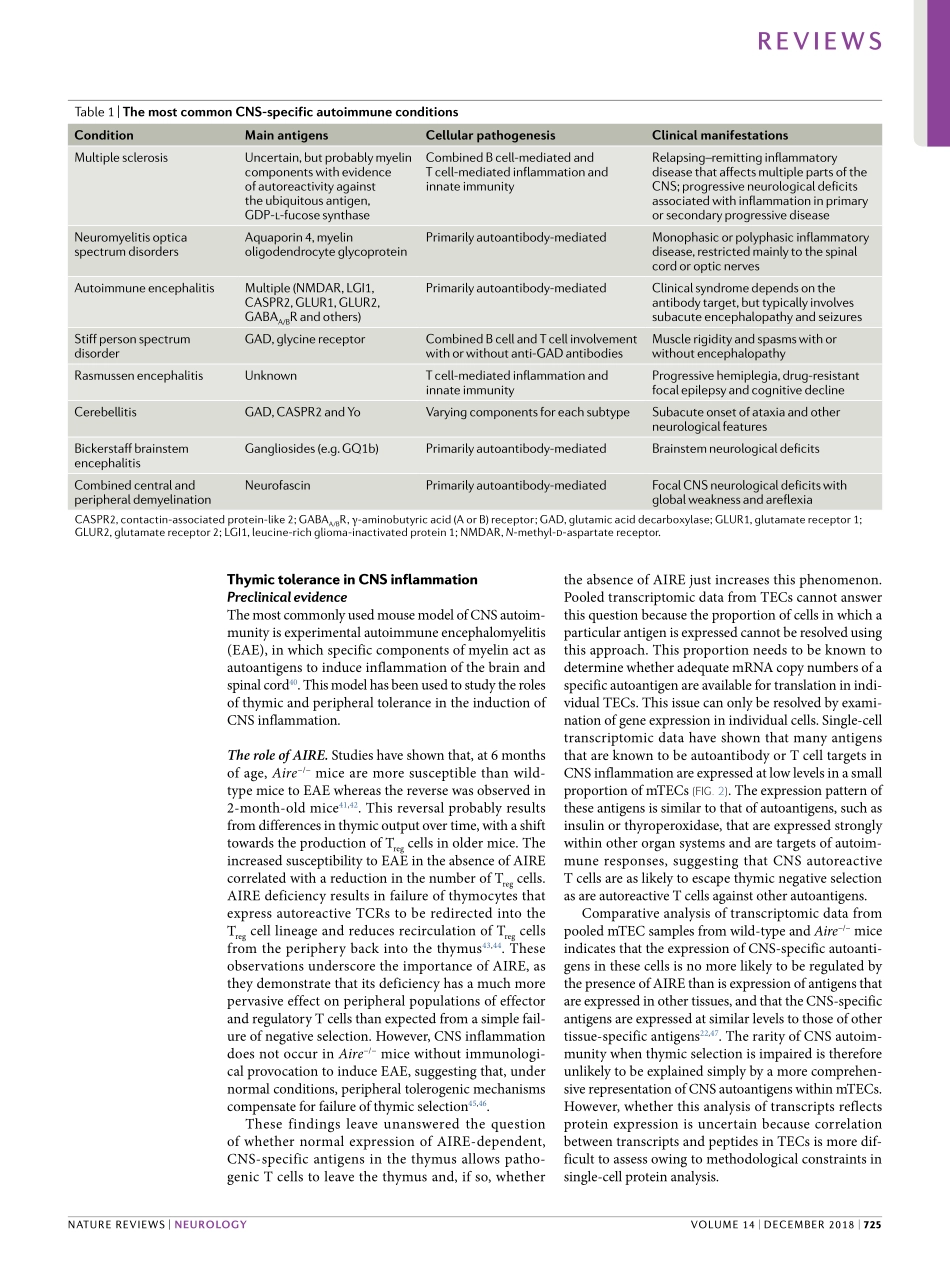
AutoimmunedisordersthataffecttheCNSareanimpor-tantcauseofneurologicalmorbidityandmortalitythatareassociatedwithconsiderableeconomiccosts1.TheseconditionscanbeCNS-specificdisorders2–7(Table1)orsystemicinflammatorydisordersthatresultinCNSdiseaseviaadirectreactionagainstthebrainorspinalcordparenchymaorviaCNSvasculitis.PathologicalfailureofimmunetoleranceleadstoCNSinflammation,andthisscenariorequiresfailureofthemechanismsthatensurethattheadaptiveimmunesystemrespondstoforeignantigensbutistolerantofautoantigens.Tcelltoleranceisgenerallymaintainedbyinductionoftolerance,thefirststagesofwhichoccurinthethymusandthefinalstagesinperipheraltissues.ThismechanismshapestherepertoireofantigensthatarerecognizedbyTcells8.Similarly,severalcheck-pointsinbothearlyandlatestagesofBcelldifferen-tiationestablishBcelltolerance.AlthoughearlyBcellcheckpointsoccurindependentlyofTcellmodulation,autoreactiveBcellclonesthatescapenegativeselec-tioninthebonemarrowarelikelytobesuppressedbyTcellsintheperiphery9–11.ResearchintotherelationshipbetweenimmunetoleranceandCNSinflammationhaslargelyfocusedonmechanismsthatestablishandmaintainperipheralimmunologicaltolerance12.Lessconsiderationhasbeengiventothecontributionofthethymustothepathogen-esisofCNSautoimmunity.InthisReview,weanalyseourcurrentunderstandingofthymictolerance(alsoknownascentraltolerance)inCNSautoimmunity,atthecellular,molecularandclinicallevels,andconsiderwhythemechanismsarelikelytobecomeimportantandhavetherapeuticimplications.ThymicTcelltolerancePositiveandnegativeselectionThedevelopmentofthymictoleranceindevelopingTcells(thymocytes)reliesonthymicepithelialcells(TECs).TECsderivefromtheendodermalliningofthethirdpharyngealpouchearlyduringgestation.Overtime,thesecellsformanintricate3Dscaffoldthat,togetherwithdendriticcells,intrathymicBcells,macrophagesandotherstromalcells,createsanexclu-sivemicroenvironmentthatenablestheformationandselectionofTcells13,14(Fig.1).TheouterregionofthethymusisknownasthecortexandcontainsTcellsintheearlystagesofd...