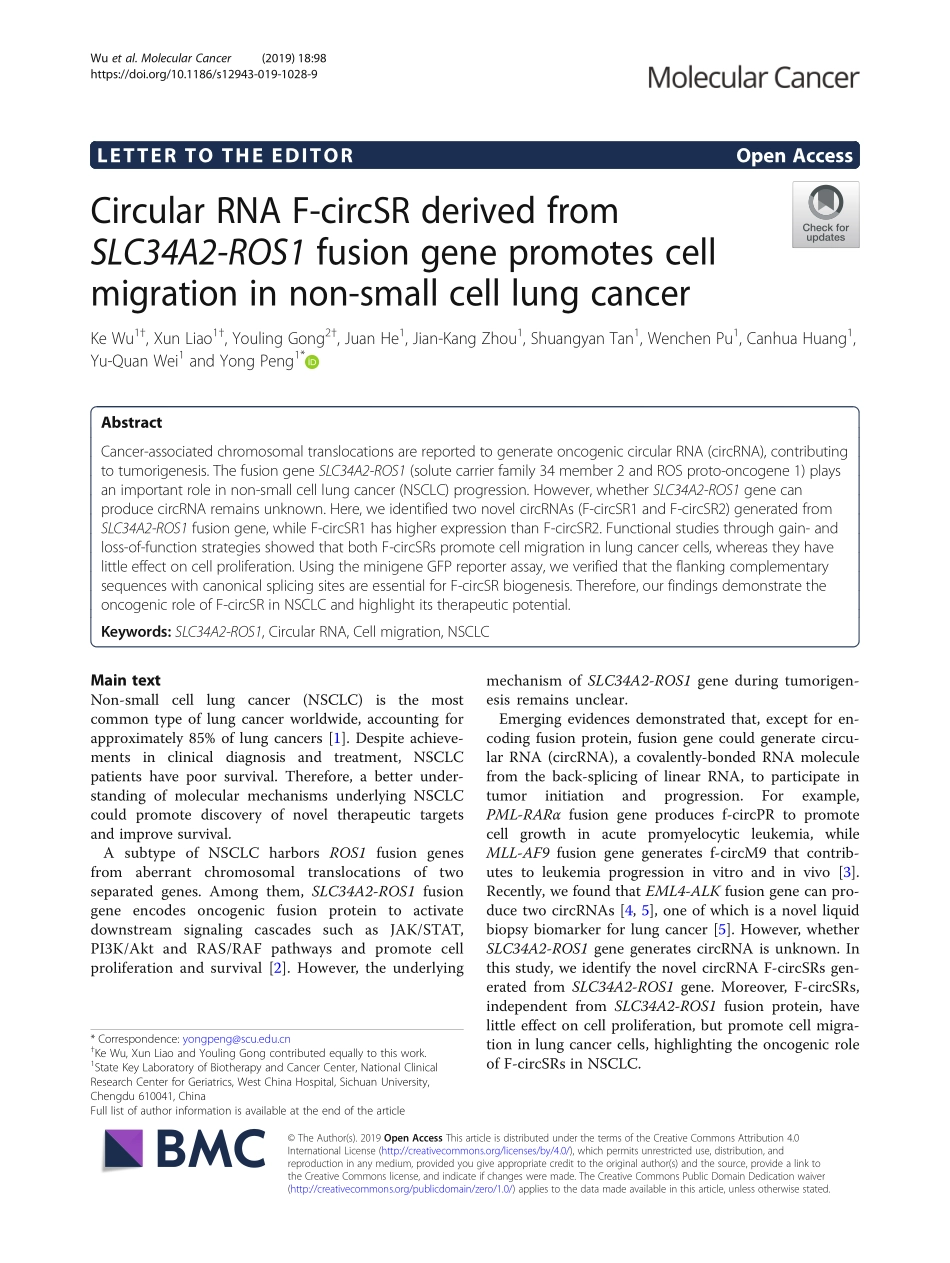
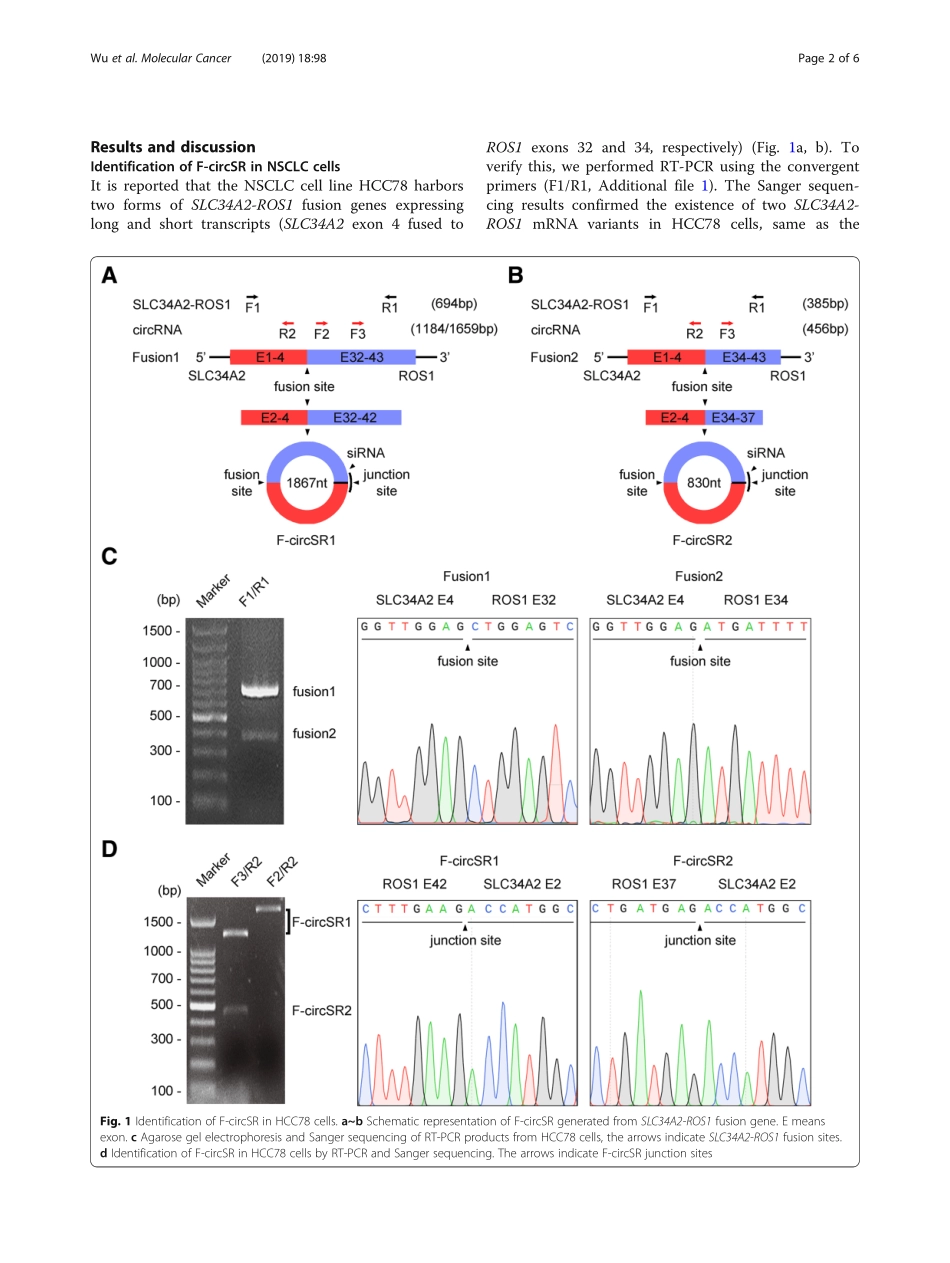
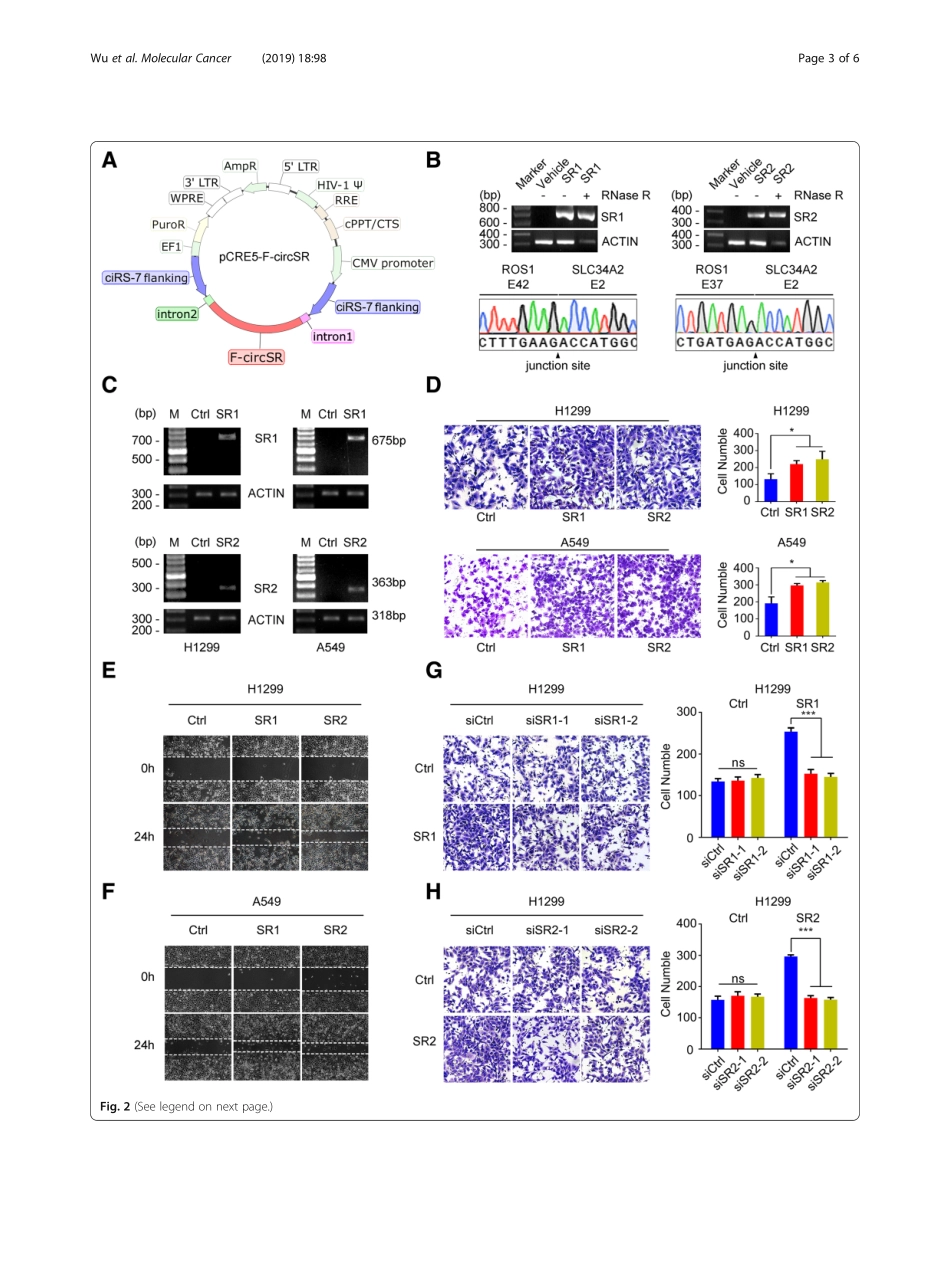
LETTERTOTHEEDITOROpenAccessCircularRNAF-circSRderivedfromSLC34A2-ROS1fusiongenepromotescellmigrationinnon-smallcelllungcancerKeWu1†,XunLiao1†,YoulingGong2†,JuanHe1,Jian-KangZhou1,ShuangyanTan1,WenchenPu1,CanhuaHuang1,Yu-QuanWei1andYongPeng1*AbstractCancer-associatedchromosomaltranslocationsarereportedtogenerateoncogeniccircularRNA(circRNA),contributingtotumorigenesis.ThefusiongeneSLC34A2-ROS1(solutecarrierfamily34member2andROSproto-oncogene1)playsanimportantroleinnon-smallcelllungcancer(NSCLC)progression.However,whetherSLC34A2-ROS1genecanproducecircRNAremainsunknown.Here,weidentifiedtwonovelcircRNAs(F-circSR1andF-circSR2)generatedfromSLC34A2-ROS1fusiongene,whileF-circSR1hashigherexpressionthanF-circSR2.Functionalstudiesthroughgain-andloss-of-functionstrategiesshowedthatbothF-circSRspromotecellmigrationinlungcancercells,whereastheyhavelittleeffectoncellproliferation.UsingtheminigeneGFPreporterassay,weverifiedthattheflankingcomplementarysequenceswithcanonicalsplicingsitesareessentialforF-circSRbiogenesis.Therefore,ourfindingsdemonstratetheoncogenicroleofF-circSRinNSCLCandhighlightitstherapeuticpotential.Keywords:SLC34A2-ROS1,CircularRNA,Cellmigration,NSCLCMaintextNon-smallcelllungcancer(NSCLC)isthemostcommontypeoflungcancerworldwide,accountingforapproximately85%oflungcancers[1].Despiteachieve-mentsinclinicaldiagnosisandtreatment,NSCLCpatientshavepoorsurvival.Therefore,abetterunder-standingofmolecularmechanismsunderlyingNSCLCcouldpromotediscoveryofnoveltherapeutictargetsandimprovesurvival.AsubtypeofNSCLCharborsROS1fusiongenesfromaberrantchromosomaltranslocationsoftwoseparatedgenes.Amongthem,SLC34A2-ROS1fusiongeneencodesoncogenicfusionproteintoactivatedownstreamsignalingcascadessuchasJAK/STAT,PI3K/AktandRAS/RAFpathwaysandpromotecellproliferationandsurvival[2].However,theunderlyingmechanismofSLC34A2-ROS1geneduringtumorigen-esisremainsunclear.Emergingevidencesdemonstratedthat,exceptforen-codingfusionprotein,fusiongenecouldgeneratecircu-larRNA(circRNA),acovalently-bo...