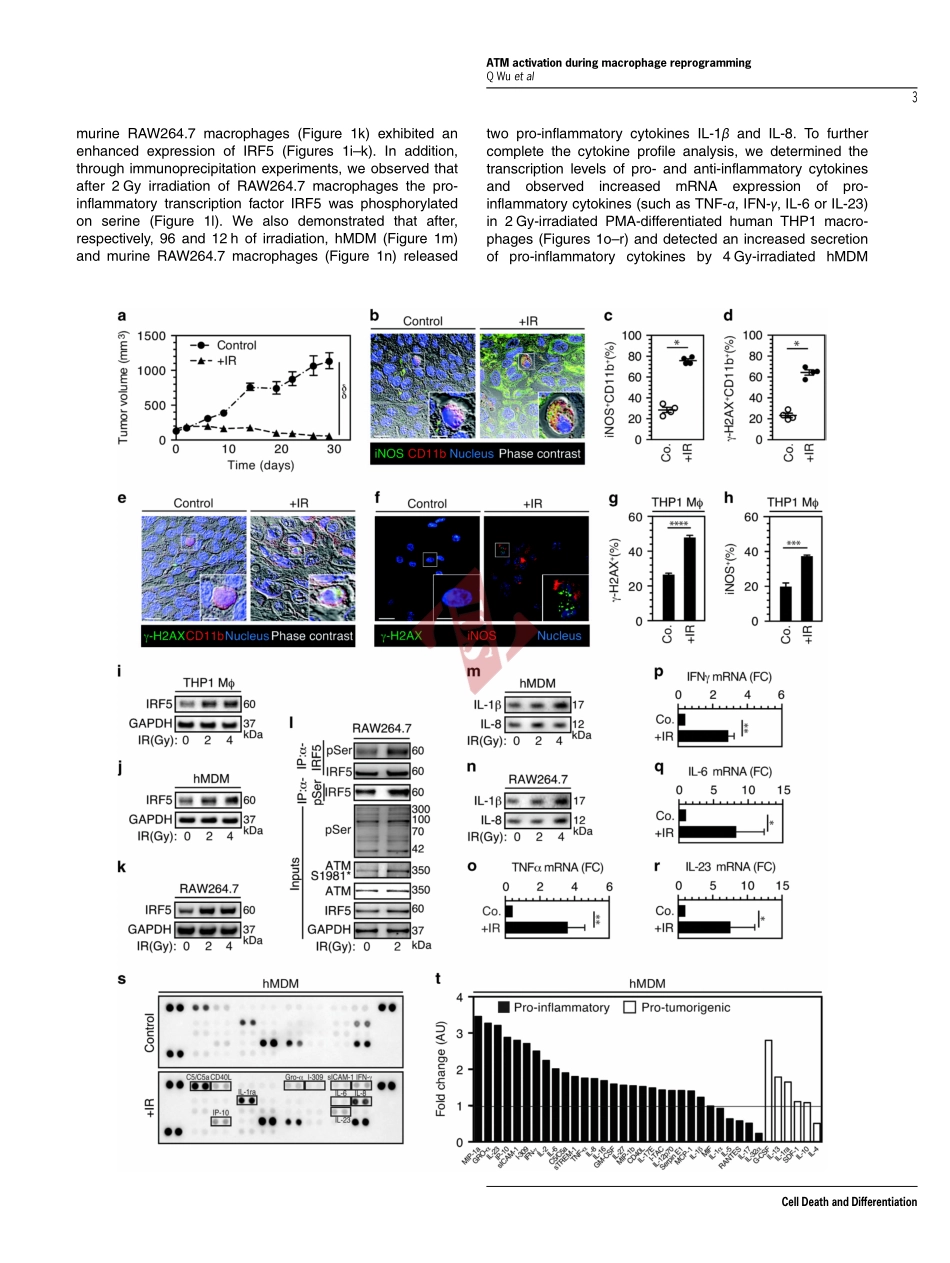
NOX2-dependentATMkinaseactivationdictatespro-inflammatorymacrophagephenotypeandimproveseffectivenesstoradiationtherapyQiujiWu1,2,3,4,5,6,AwatefAllouch1,2,3,4,AudreyPaoletti1,2,3,4,CelineLeteur2,3,4,CelineMirjolet7,IsabelleMartins1,2,3,4,LaurentVoisin1,2,3,4,FrédéricLaw1,2,3,4,HaithemDakhli1,2,3,4,ElodieMintet1,2,3,4,MaximeThoreau1,2,3,4,ZeinafMuradova1,2,3,4,MélanieGauthier7,OlivierCaron3,FabienMilliat8,DavidMOjcius9,FilippoRosselli10,EricSolary11,NazanineModjtahedi2,3,4,EricDeutsch2,3,4,12andJean-LucPerfettini*,1,2,3,4,12Althoughtumor-associatedmacrophageshavebeenextensivelystudiedinthecontrolofresponsetoradiotherapy,themolecularmechanismsinvolvedintheionizingradiation-mediatedactivationofmacrophagesremainelusive.Hereweshowthationizingradiationinducestheexpressionofinterferonregulatoryfactor5(IRF5)promotingthusmacrophageactivationtowardapro-inflammatoryphenotype.Werevealthattheactivationoftheataxiatelangiectasiamutated(ATM)kinaseisrequiredforionizingradiation-elicitedmacrophageactivation,butalsoformacrophagereprogrammingaftertreatmentswithγ-interferon,lipopolysaccharideorchemotherapeuticagent(suchascisplatin),underscoringthefactthatthekinaseATMplaysacentralroleduringmacrophagephenotypicswitchingtowardapro-inflammatoryphenotypethroughtheregulationofmRNAlevelandpost-translationalmodificationsofIRF5.WefurtherdemonstratethatNADPHoxidase2(NOX2)-dependentROSproductionisupstreamtoATMactivationandisessentialduringthisprocess.Wealsoreportthattheinhibitionofanycomponentofthissignalingpathway(NOX2,ROSandATM)impairspro-inflammatoryactivationofmacrophagesandpredictsapoortumorresponsetopreoperativeradiotherapyinlocallyadvancedrectalcancer.Altogether,ourresultsidentifyanovelsignalingpathwayinvolvedinmacrophageactivationthatmayenhancetheeffectivenessofradiotherapythroughthereprogrammingoftumor-infiltratingmacrophages.CellDeathandDifferentiationadvanceonlinepublication,2June2017;doi:10.1038/cdd.2017.91Approximately,halfofallcancerpatientsaretreatedwithradiotherapyaloneorinco...