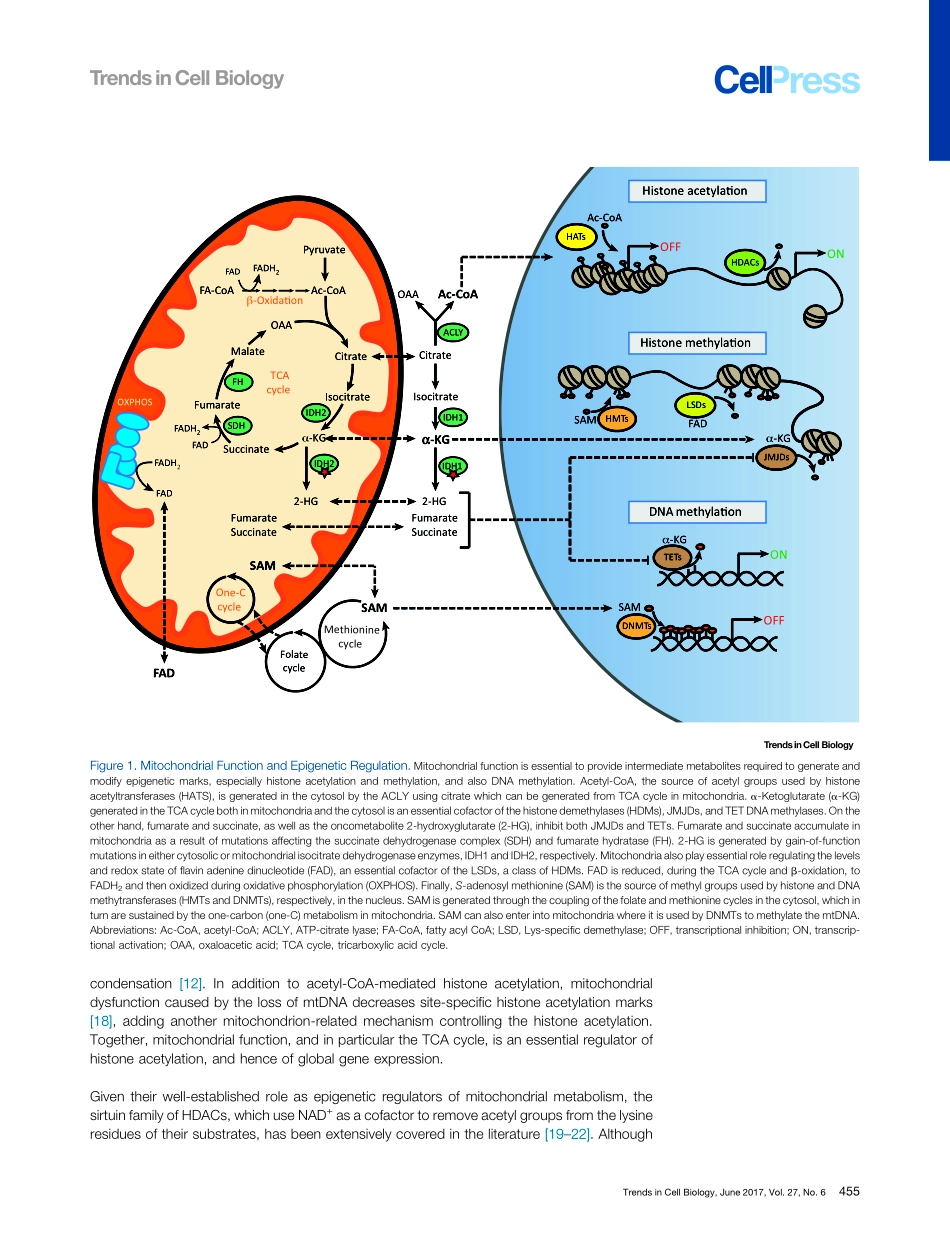
SpecialSeries:MitochondriaReviewMitochondriaandEpigenetics–CrosstalkinHomeostasisandStressOlliMatilainen,1,2PedroM.Quirós,1,2andJohanAuwerx1,*Throughepigeneticmechanismscellsintegrateenvironmentalstimulitofine-tunegeneexpressionlevels.Mitochondrialfunctionisessentialtoprovidetheintermediatemetabolitesnecessarytogenerateandmodifyepigeneticmarksinthenucleus,whichinturncanregulatetheexpressionofmitochondrialproteins.Inthisreviewwesummarizethefunctionofmitochondriaintheregulationofepigeneticmechanismsasanewaspectofmitonuclearcommu-nication.Wefocusinparticularonthemostcommonepigeneticmodifications–histoneacetylationandhistoneandDNAmethylation.WealsodiscusstheemergingfieldofmitochondrialDNA(mtDNA)methylation,whosephysiologicalroleremainsunknown.Finally,wedescribetheessentialroleofsomehistonemodificationsinregulatingthemitochondrialunfoldedproteinresponse(UPRmt)andthemitochondrialstress-dependentlifespanextension.MitochondrialGeneticsandFunctionMitochondriaarethecentralcoreofenergymetabolismwithinthecell,producingATPthroughoxidativephosphorylation(OXPHOS)andanintricatesystemthatcoordinatesfattyacidandglucoseoxidation.Inaddition,mitochondriaregulateintermediatemetabolism,controllingthelevelsofmanydifferentmetabolitesessentialfordiversecellularfunctions[1].Mitochondriahavetheirownindependentgenome–themtDNA–arelicfromtheirbacterialorigin,whichhasbeensignificantlyreducedinsizeasaresultofmillionsofyearsofcoevolutionwithineukaryoticcells.MammalianmtDNAencodesonly37genes:tworibosomalRNAs,22transferRNAs,and13proteinsthatarepartofthemitochondrialOXPHOScomplexes[2].Theremainderofthemitochondrialproteome,comprisingmorethan1000proteins,isencodedinthenucleus.WhereascircularmtDNAexistsinmultiplescopiesineachmitochondrion,andismaternallyinheritedandredundant[3],nuclearDNA(nDNA)iswrappedaroundnucleosomesconsistingofeighthistoneproteincores.Mitochondrialfunctiondependsonthecoordinationofnuclearandmitochondrialgenomes,andthereforethetranscriptionandtranslationofbothgenomesarecoregul...