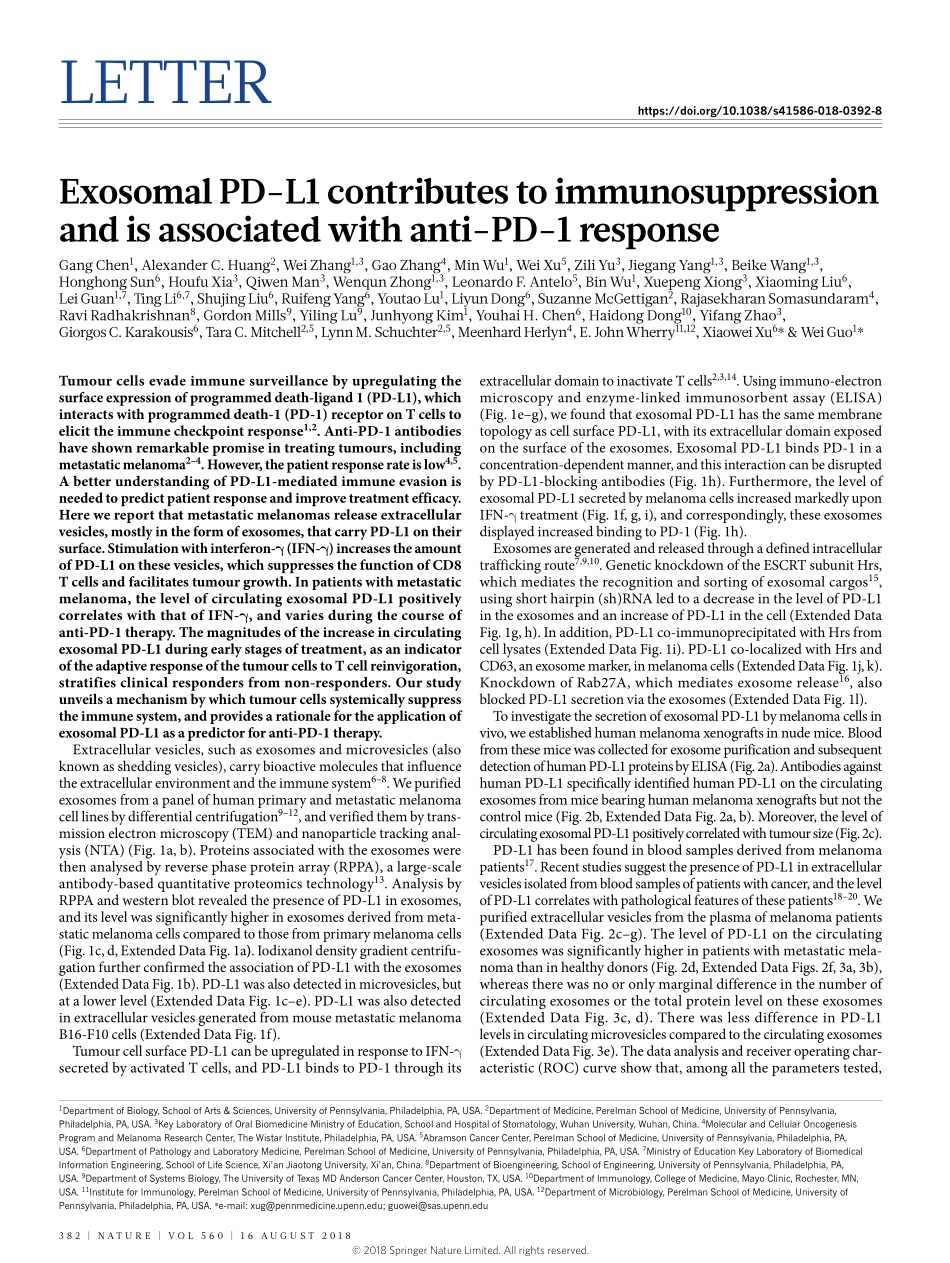
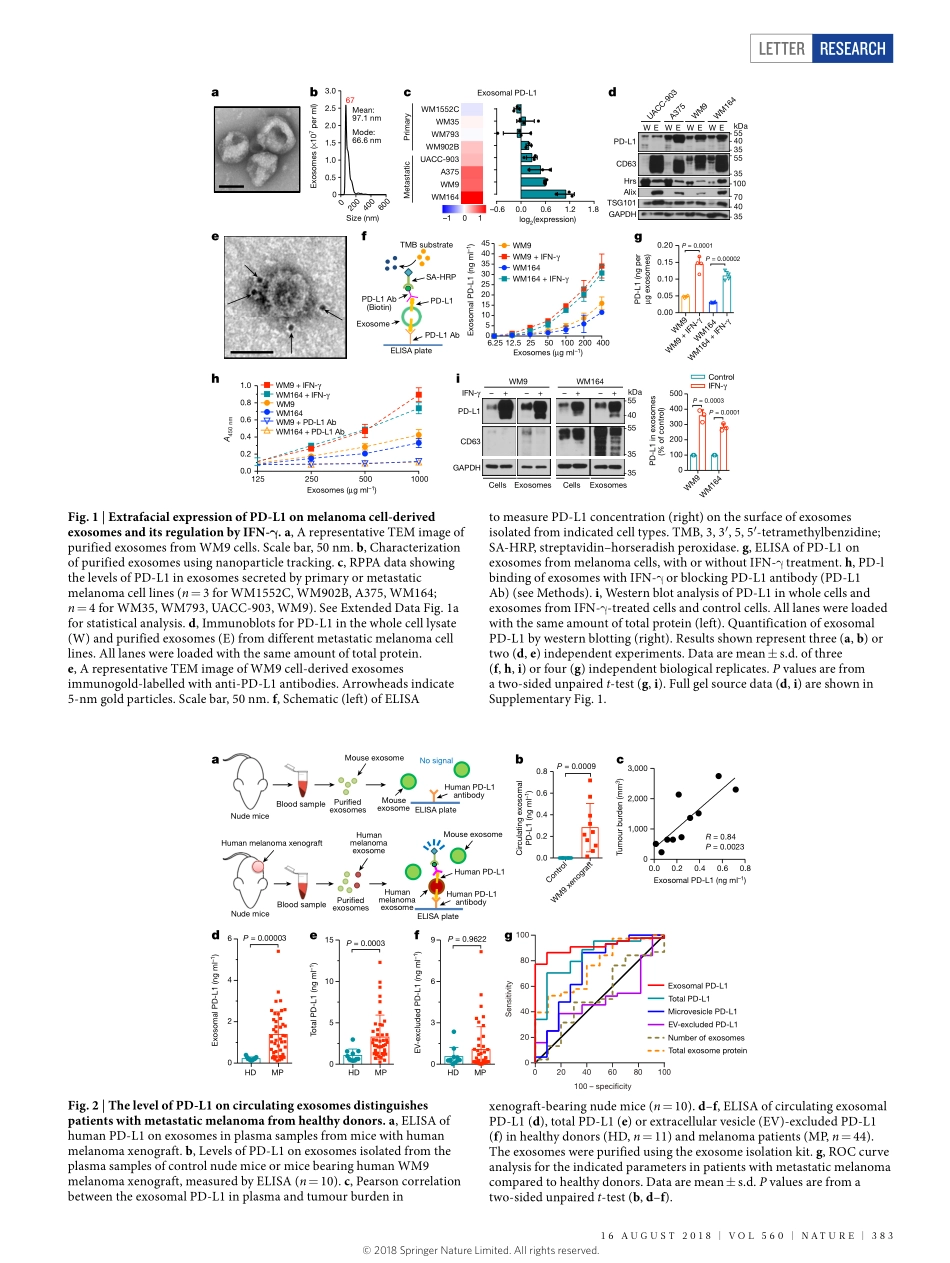
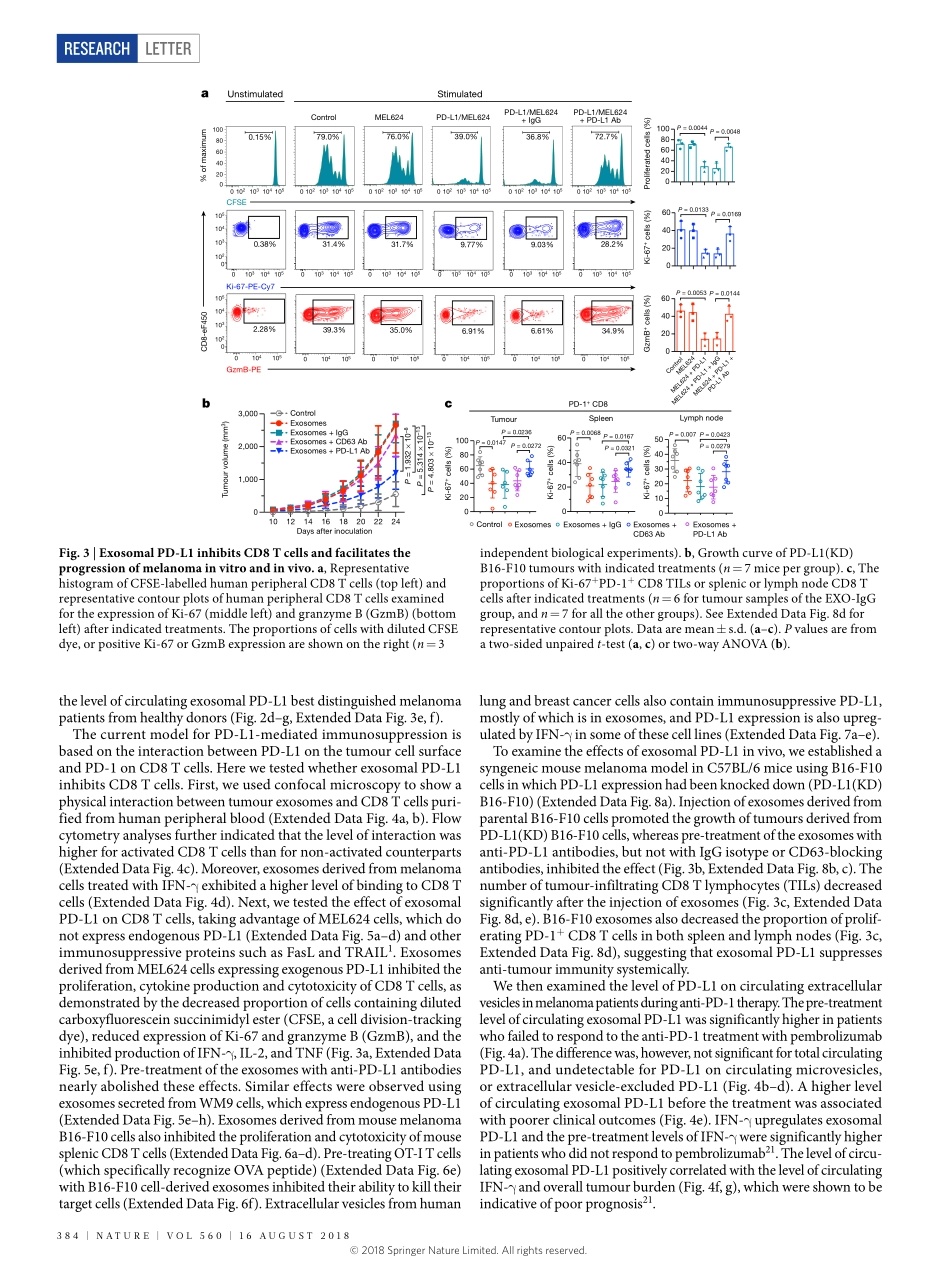
Letterhttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0392-8ExosomalPD-L1contributestoimmunosuppressionandisassociatedwithanti-PD-1responseGangChen1,AlexanderC.Huang2,WeiZhang1,3,GaoZhang4,MinWu1,WeiXu5,ZiliYu3,JiegangYang1,3,BeikeWang1,3,HonghongSun6,HoufuXia3,QiwenMan3,WenqunZhong1,3,LeonardoF.Antelo5,BinWu1,XuepengXiong3,XiaomingLiu6,LeiGuan1,7,tingLi6,7,ShujingLiu6,ruifengYang6,YoutaoLu1,LiyunDong6,SuzanneMcGettigan2,rajasekharanSomasundaram4,raviradhakrishnan8,GordonMills9,YilingLu9,JunhyongKim1,YouhaiH.Chen6,HaidongDong10,YifangZhao3,GiorgosC.Karakousis6,taraC.Mitchell2,5,LynnM.Schuchter2,5,MeenhardHerlyn4,e.JohnWherry11,12,XiaoweiXu6*&WeiGuo1*Tumourcellsevadeimmunesurveillancebyupregulatingthesurfaceexpressionofprogrammeddeath-ligand1(PD-L1),whichinteractswithprogrammeddeath-1(PD-1)receptoronTcellstoelicittheimmunecheckpointresponse1,2.Anti-PD-1antibodieshaveshownremarkablepromiseintreatingtumours,includingmetastaticmelanoma2–4.However,thepatientresponserateislow4,5.AbetterunderstandingofPD-L1-mediatedimmuneevasionisneededtopredictpatientresponseandimprovetreatmentefficacy.Herewereportthatmetastaticmelanomasreleaseextracellularvesicles,mostlyintheformofexosomes,thatcarryPD-L1ontheirsurface.Stimulationwithinterferon-γ(IFN-γ)increasestheamountofPD-L1onthesevesicles,whichsuppressesthefunctionofCD8Tcellsandfacilitatestumourgrowth.Inpatientswithmetastaticmelanoma,thelevelofcirculatingexosomalPD-L1positivelycorrelateswiththatofIFN-γ,andvariesduringthecourseofanti-PD-1therapy.ThemagnitudesoftheincreaseincirculatingexosomalPD-L1duringearlystagesoftreatment,asanindicatoroftheadaptiveresponseofthetumourcellstoTcellreinvigoration,stratifiesclinicalrespondersfromnon-responders.Ourstudyunveilsamechanismbywhichtumourcellssystemicallysuppresstheimmunesystem,andprovidesarationalefortheapplicationofexosomalPD-L1asapredictorforanti-PD-1therapy.Extracellularvesicles,suchasexosomesandmicrovesicles(alsoknownassheddingvesicles),carrybioactivemoleculesthatinfluencetheextracellularenviron...