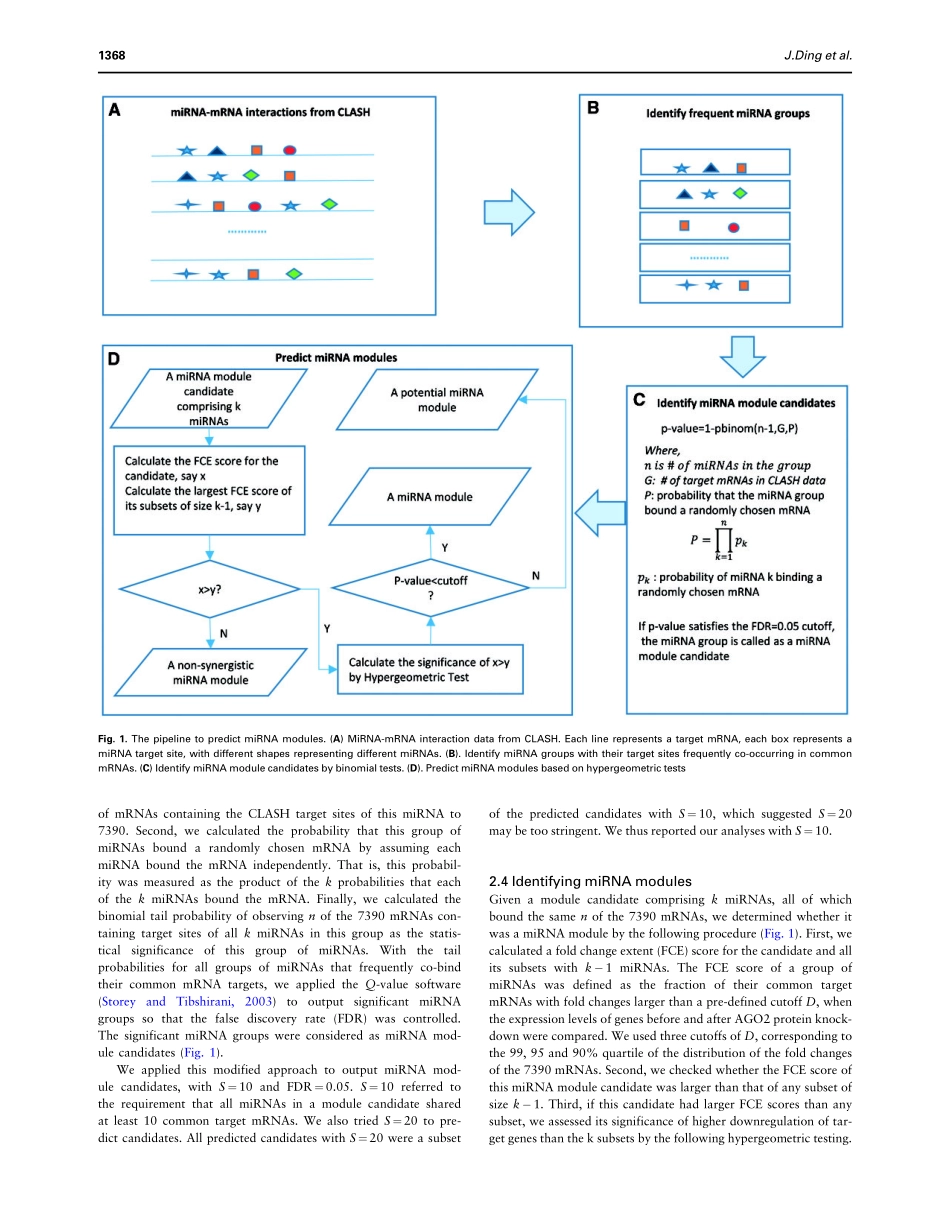
SequenceanalysisMicroRNAmodulesprefertobindweakandunconventionaltargetsitesJunDing1,XiaomanLi2,*andHaiyanHu1,*1DepartmentofElectricalEngineeringandComputerScienceand2BurnettSchoolofBiomedicalScience,CollegeofMedicine,UniversityofCentralFlorida,Orlando,FL32816,USA*Towhomcorrespondenceshouldbeaddressed.AssociateEditor:IvoHofackerReceivedonAugust21,2014;revisedonDecember1,2014;acceptedonDecember13,2014AbstractMotivation:MicroRNAs(miRNAs)playcriticalrolesingeneregulation.AlthoughitiswellknownthatmultiplemiRNAsmayworkasmiRNAmodulestosynergisticallyregulatecommontargetmRNAs,theunderstandingofmiRNAmodulesisstillinitsinfancy.Results:WeemployedtherecentlygeneratedhighthroughputexperimentaldatatostudymiRNAmodules.Wepredicted181miRNAmodulesand306potentialmiRNAmodules.WeobservedthatthetargetsitesofthesepredictedmoduleswereingeneralweakercomparedwiththosenotboundbymiRNAmodules.WealsodiscoveredthatmiRNAsinpredictedmodulespreferredtobindunconventionaltargetsitesratherthancanonicalsites.Surprisingly,contrarytoapreviousstudy,wefoundthatmostadjacentmiRNAtargetsitesfromthesamemiRNAmoduleswerenotwithintherangeof10–130nucleotides.Interestingly,thedistanceoftargetsitesboundbymiRNAsinthesamemoduleswasshorterwhenmiRNAmodulesboundunconventionalinsteadofcanonicalsites.OurstudyshednewlightonmiRNAbindingandmiRNAtargetsites,whichwilllikelyad-vanceourunderstandingofmiRNAregulation.Availabilityandimplementation:ThesoftwaremiRModulecanbefreelydownloadedathttp://hulab.ucf.edu/research/projects/miRNA/miRModule.Supplementaryinformation:SupplementarydataareavailableatBioinformaticsonline.Contact:haihu@cs.ucf.eduorxiaoman@mail.ucf.edu.1IntroductionMicroRNAs(miRNAs)playcriticalrolesingeneregulation(Bartel,2004,2009).MiRNAsareafamilyofsmall(�22nucleo-tides)non-codingRNAs.TheycanbindmRNAsat50untranslatedregions(UTRs),codingsequences(CDSs),and30UTRs.Thebindingistraditionallythoughttobethroughbase-pairingoftheseedregionsinmiRNAswiththepartiallycomplementarysequencesintargetmRNAs(Bartel,2009).Theseedreg...