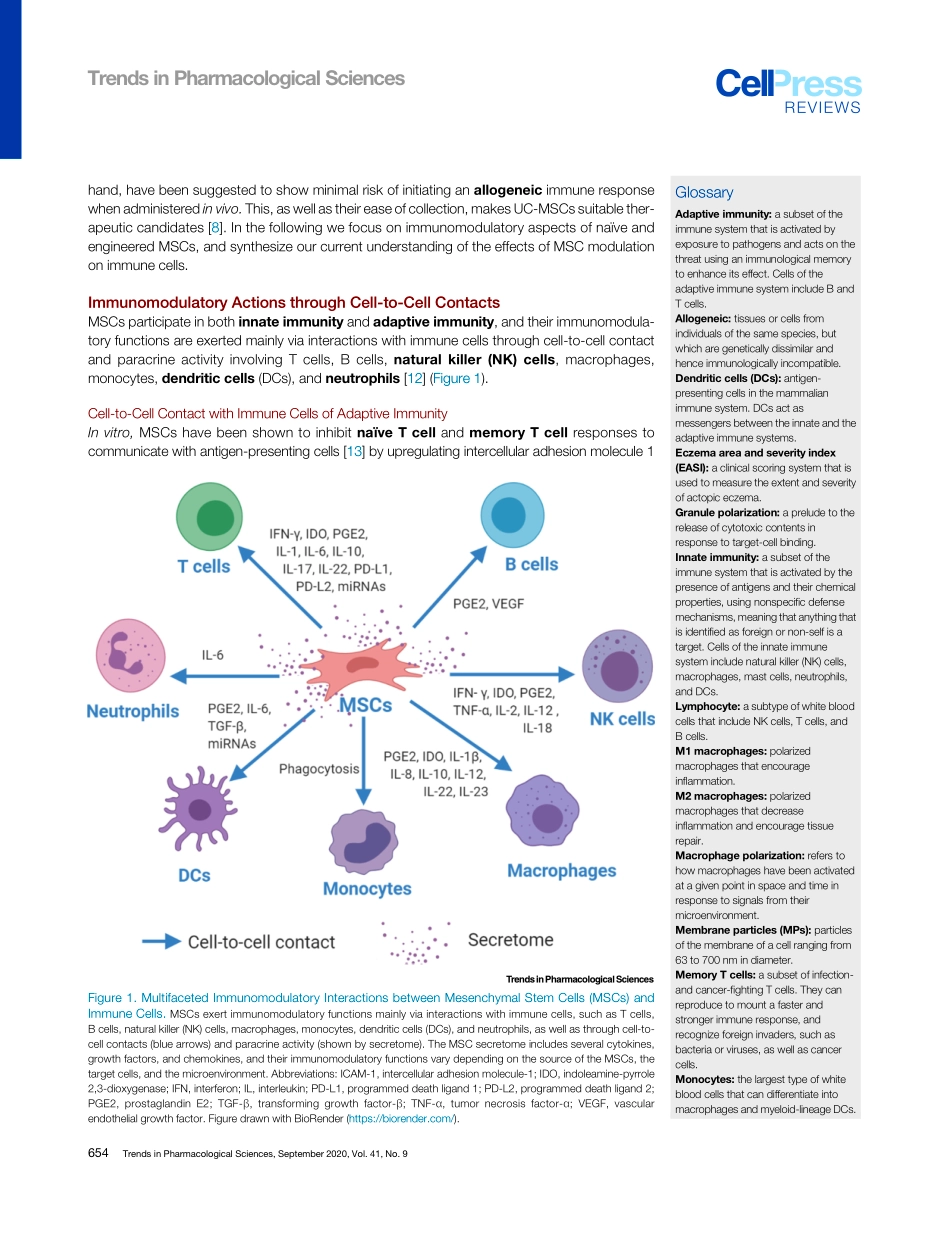
ReviewMesenchymalStemCellImmunomodulation:MechanismsandTherapeuticPotentialNaSong,1,2,3MartijnScholtemeijer,1,2andKhalidShah1,2,4,*Mesenchymalstem/stromalcells(MSCs)aremultipotentcellsthatareemergingasthemostpromisingmeansofallogeneiccelltherapy.MSCshaveinherentimmunomodulatorycharacteristics,trophicactivity,highinvitroself-renewalability,andcanbereadilyengineeredtoenhancetheirimmunomodulatoryfunc-tions.MSCsaffectthefunctionsofmostimmuneeffectorcellsviadirectcontactwithimmunecellsandlocalmicroenvironmentalfactors.PreviousstudieshaveconfirmedthattheimmunomodulatoryeffectsofMSCsaremainlycommuni-catedviaMSC-secretedcytokines;however,apoptoticandmetabolicallyinactivatedMSCshavemorerecentlybeenshowntopossessimmunomodula-torypotential,inwhichregulatoryTcellsandmonocytesplayakeyrole.WereviewtheimmunomodulatoryaspectsofnaïveandengineeredMSCs,anddiscussstrategiesforincreasingthepotentialofsuccessfullyusingMSCsinclinicalsettings.MesenchymalStemCellsMSCsarepluripotentTcellsthathaveself-renewing,differentiation,andimmunomodulatoryproperties.Theirtwomostattractivefeaturesareplasticity(seeGlossary)andtropism.Theyaredistinguishedfromothercelltypesbytheexpressionofcell-surfacemarkersincludingCD73,CD90,andCD105,andbythelackofexpressionofCD45,CD34,CD14,CD19,CD11b,andhumanleukocyteantigenDRisotype(HLA-DR)[1],andplayacentralroleintissuerepairinadditiontotheirantitumorigenic,antifibrotic,antiapoptotic,anti-inflammatory,proangiogenic,neuroprotective,antibacterial,andchemoattractiveeffects[2,3].ThisuniquesetofcharacteristicsmakesMSCsattractivefortheirtherapeuticpotentialinthefieldsofregenerativemedicine[4],inflammatorydisorders[2],and,increasingly,cancertherapy[5,6].Initially,MSCsweremainlyusedfortissuerepairandregeneration[3].However,theyhavebeenincreasinglyusedfordiseasesincludinggraft-versus-hostdisease(GVHD)andautoimmunediseasessuchaslupusandCrohn’sdisease[2].Inaddition,theclinicalpotentialofMSCshasbeenextendedtothetreatmentofmyocardialinfarction,stroke,multiplesclerosis,livercir...