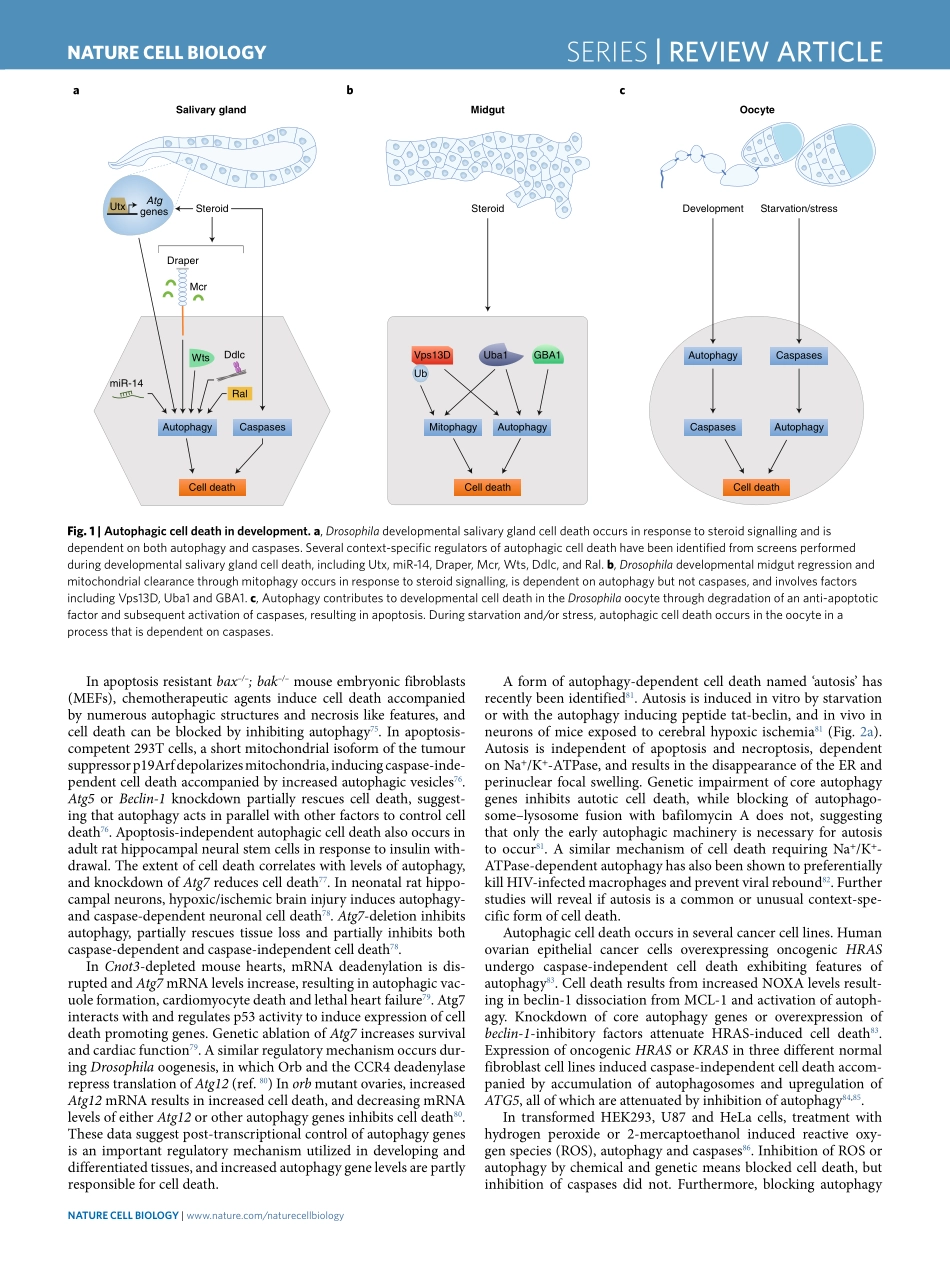
SERIES|ReviewARticlehttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0201-5DepartmentofMolecular,CellandCancerBiology,UniversityofMassachusettsMedicalSchool,Worcester,MA,USA.*e-mail:Eric.Baehrecke@umassmed.eduCelldeathoccursbymultiplemechanisms,butoriginaldescriptionswerebasedonmorphologicalfeaturesandhowdeadcellsandtheirfragmentsarecleared.Morphologically,threebroadclassificationsofcelldeathoccurunderphysiologicalconditionsduringdevelopment:apoptosis,autophagiccelldeathandnecrosis1.Apoptosisischaracterizedbycellshrinkage,chromatincon-densation,nuclearfragmentation,plasmamembraneblebbinganddebrisclearancebyneighbouringphagocytes1,2.Twomolecu-larmechanismscontrolapoptosis,theintrinsicpathwayinitiatedbyintracellularstimulisuchasDNAdamage,andtheextrinsicpathwayinitiatedbyextracellulardeathreceptors;bothpathwaysdependoncaspaseactivation2–4.Celldeaththatdependsonautophagyisdistinguishedbycyto-plasmicvacuolization,autophagosomeformationandclearanceofmaterialviathelysosome1,3.Duringmacroautophagy(hereinreferredtoasautophagy),cytoplasmicmaterialsandorganellesaresequesteredandengulfedbyadoublemembranedstructure,termedtheautophagosome,thendeliveredtothelysosomefordegradationandrecycling3,5.Necrosisresultsinorganelleswellingandlysis,inflammation,andreleaseofintracellularcomponents.Incontrasttoapoptosisandautophagiccelldeath,necrosisgenerallyoccurswhencellsareexposedtopathologicalconditions3,6.Themolecularmachineryunderlyingthesedifferentformsofcelldeatharepromiscuousandrecentevidenceindicatesthereiscomplexinterplayamongthem,makingitdifficulttounambigu-ouslydistinguishoneformofcelldeathfromanother7.Themecha-nismbywhichacelldiesisoftenspecifictothecelltype,stimulus,contextandenvironment.Therecentexplosionindiscoveriesofcelldeathsubtypeshighlightsthemanywaysacellcandie3.InthisReview,weaddressthecrosstalkbetweenautophagy,apoptosisandnecrosis,highlightingtheemergingandcontext-specificrolesofautophagyduringcelldeath.DefiningautophagiccelldeathAutophagy(‘selfeating’)sequesters,degradesandrec...