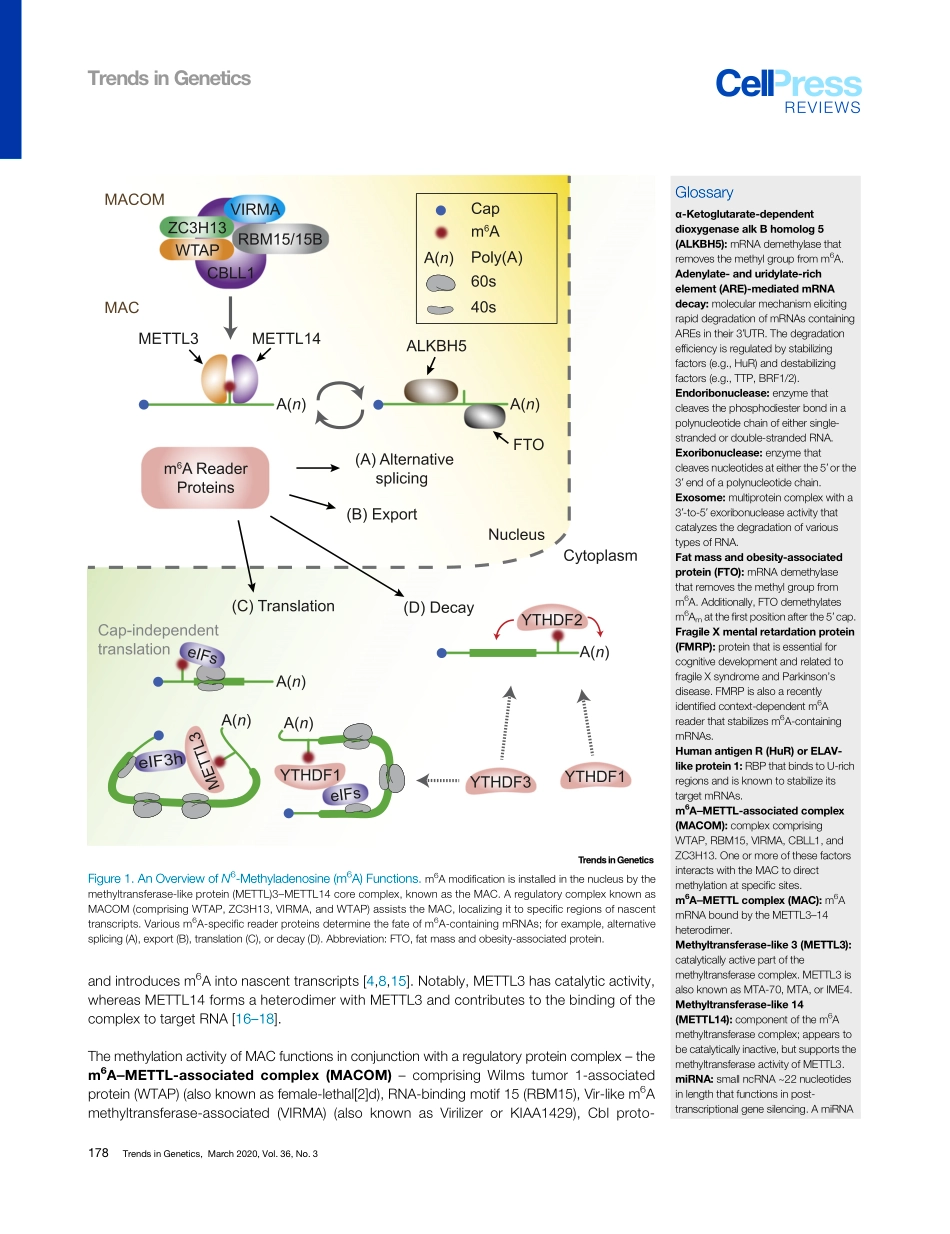
ReviewMolecularMechanismsDrivingmRNADegradationbym6AModificationYujinLee,1,2,5JunhoChoe,3,4,5OkHyunPark,1,2andYoonKiKim1,2,*N6-Methyladenosine(m6A),themostprevalentinternalmodificationassociatedwitheukaryoticmRNAs,influencesmanystepsofmRNAmetabolism,includingsplicing,export,andtranslation,aswellasstability.Recentstudieshaverevealedthatm6A-containingmRNAsundergooneoftwodistinctpathwaysofrapiddegra-dation:deadenylationviatheYT521-Bhomology(YTH)domain-containingfamilyprotein2(YTHDF2;anm6Areaderprotein)–CCR4/NOT(deadenylase)complexorendoribonucleolyticcleavagebytheYTHDF2–HRSP12–ribonuclease(RNase)P/mitochondrialRNA-processing(MRP)(endoribonuclease)complex.Somem6A-containingcircularRNAs(circRNAs)arealsosubjecttoendoribonucleolyticcleavagebyYTHDF2–HRSP12–RNaseP/MRP.Here,wehighlightrecentprogressonthemolecularmechanismsunderlyingrapidmRNAdegradationviam6Aandde-scribeourcurrentunderstandingofthedynamicregulationofm6A-mediatedmRNAdecaythroughthecrosstalkbetweenm6A(orYTHDF2)andothercellularfactors.RNAModification:AnEmergingLayerofPost-TranscriptionalGeneRegulationManyrecentstudiespointtotheroleofRNAmodificationasamodeofpost-transcriptionalgeneregulationandthisfieldhasbeentermed‘epitranscriptomics’[1–4].Todate,approximately150post-transcriptionalmodificationshavebeenassociatedwithvariousRNAspecies,includingmRNAs,tRNAs,rRNAs,noncodingRNAs(ncRNAs),andviralRNAgenomes[5–7].Inthisreview,wesummarizerecentreportsonm6Adepositionandfunction.Inparticular,wediscussrecentfindingsregardinghowm6AcontributestomRNAstabilityatthemolecularlevel.FeaturesandDynamicsofthem6AModificationAlthoughfirstdiscoveredinthe1970s,m6AmodificationrecentlyreturnedtothespotlightwiththedevelopmentofRNA-seqtechniquesandthecharacterizationoftheproteinsinvolvedinthem6Amodification[4,8].ThismodificationisfoundinmRNAexpressedinvariousmammaliancelltypesincludingblood,muscle,liver,intestinal,andneuronalcells.Atthemolecularlevel,them6AmodificationfunctionsatalmostallstagesofthemRNAlifecycle,includingsplicing,...