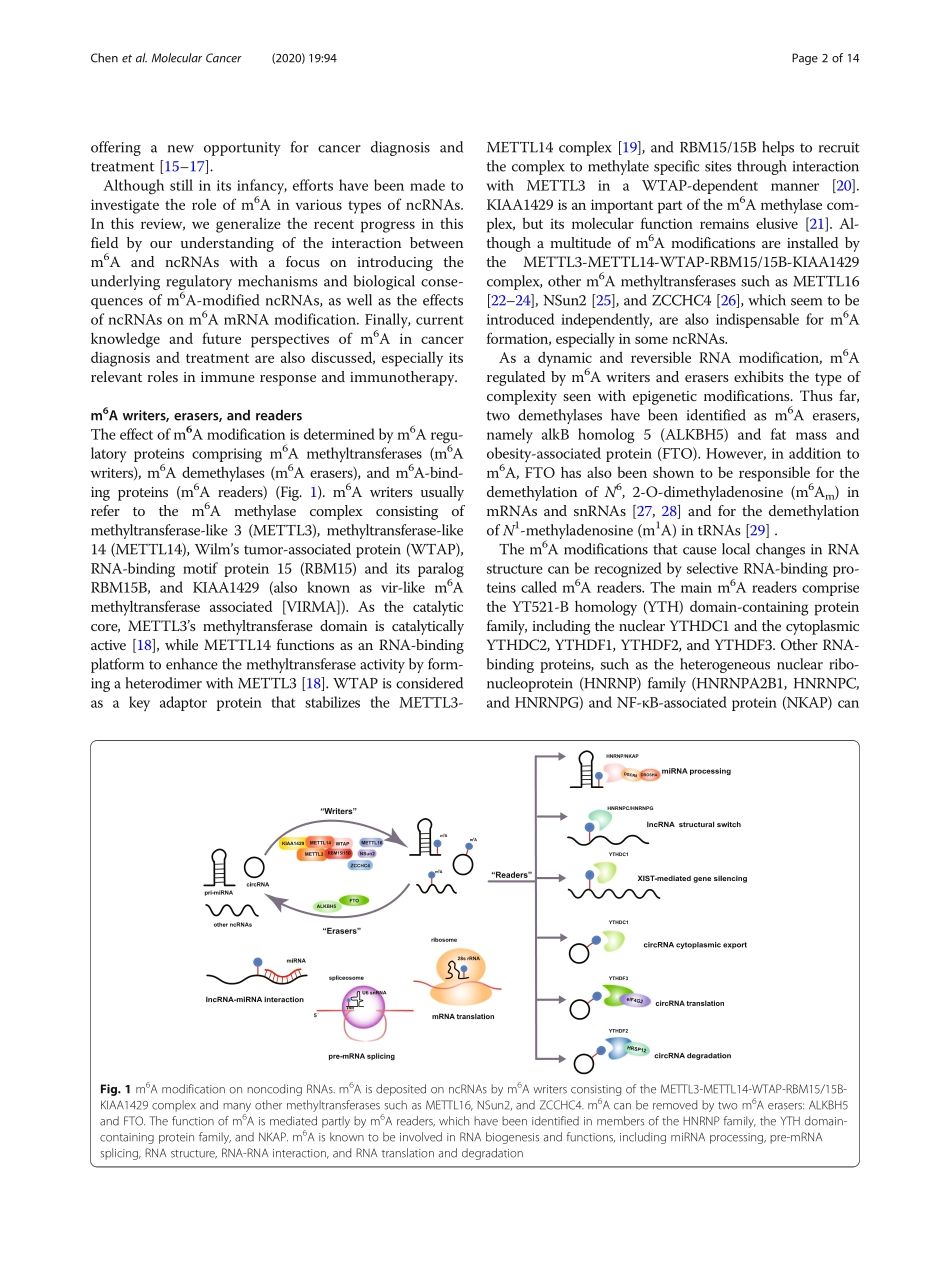
REVIEWOpenAccessInteractionbetweenN6-methyladenosine(m6A)modificationandnoncodingRNAsincancerYiChen,YuLin,YongqianShu*,JingHe*andWenGao*AbstractAsacriticalinternalRNAmodificationinhighereukaryotes,N6-methyladenosine(m6A)hasbecomethehotspotofepigeneticsresearchinrecentyears.ExtensivestudiesonmessengerRNAshaverevealedthatm6AaffectsRNAfateandcellfunctionsinvariousbioprocesses,suchasRNAsplicing,export,translation,andstability,someofwhichseemtobedirectlyorindirectlyregulatedbynoncodingRNAs.Intriguingly,abundantnoncodingRNAssuchasmicroRNAs,longnoncodingRNAs,circularRNAs,smallnuclearRNAs,andribosomalRNAsarealsohighlymodifiedwithm6Aandrequirem6Amodificationfortheirbiogenesisandfunctions.Here,wediscusstheinteractionbetweenm6AmodificationandnoncodingRNAsbyfocusingonthefunctionalrelevanceofm6Aincancerprogression,metastasis,drugresistance,andimmuneresponse.Furthermore,theinvestigationofm6Aregulatoryproteinsanditsinhibitorsprovidesnewopportunitiesforearlydiagnosisandeffectivetreatmentofcancer,especiallyincombinationwithimmunotherapy.Keywords:m6Amodification,NoncodingRNAs,CancerBackgroundN6-methyladenosine(m6A),firstdescribedin1974[1,2],isawell-knowninternalmodificationofmessengerRNAs(mRNAs)andnoncodingRNAs(ncRNAs);itiswidelyconservedamongeukaryotesrangingfromyeast,plants,andfliestomammalsandevenoccursinviralRNAswithanuclearphase[3,4].AsthemostabundantandimportantmRNAmodificationinmammals,m6Amodificationaccountsforapproximately50%ofthetotalmethyl-labeledribonucleosides[5]and0.1–0.4%ofalladenosinesintotalcellularRNAswithabout3–5m6AsitespermRNA[6].m6AisenrichedintheconsensussequenceRRACH(whereR:AorGandH:A,C,orU)andhighlyoccursin3′untranslatedregions(3′-UTRs),stopcodons,andinternallongexons[4,7],thusshowinganeffectonmRNAmetabolism,includingsplicing,ex-port,translation,anddecay[8].Notably,approximately67%of3′UTRswithm6ApeaksalsocontainbindingsitesforncRNAssuchasmicroRNAs(miRNAs)[7],thussuggestingapossiblemechanismbywhichm6AandncRNAsco-regulatetargetmRNAsthroughcooperationorco...