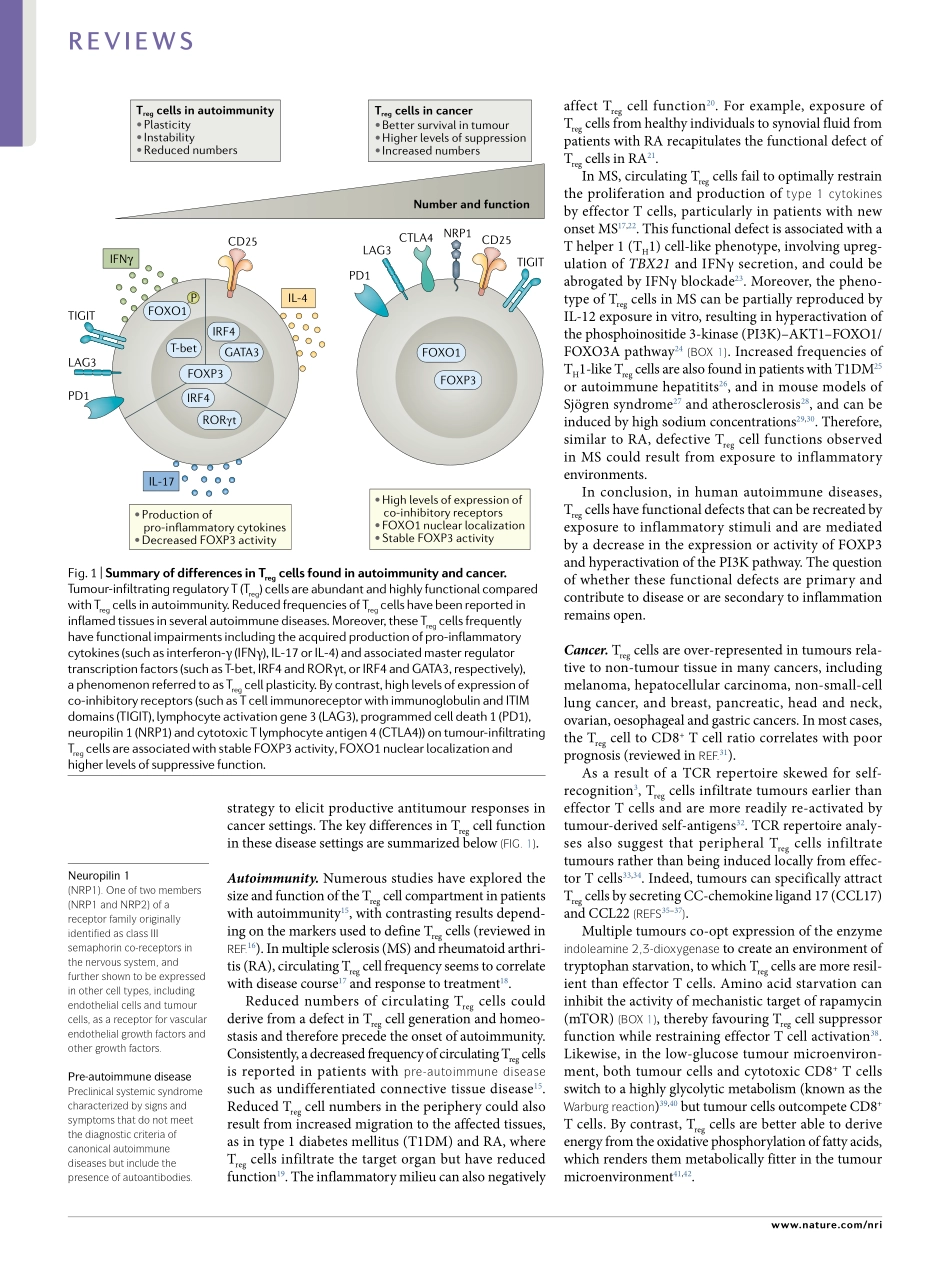
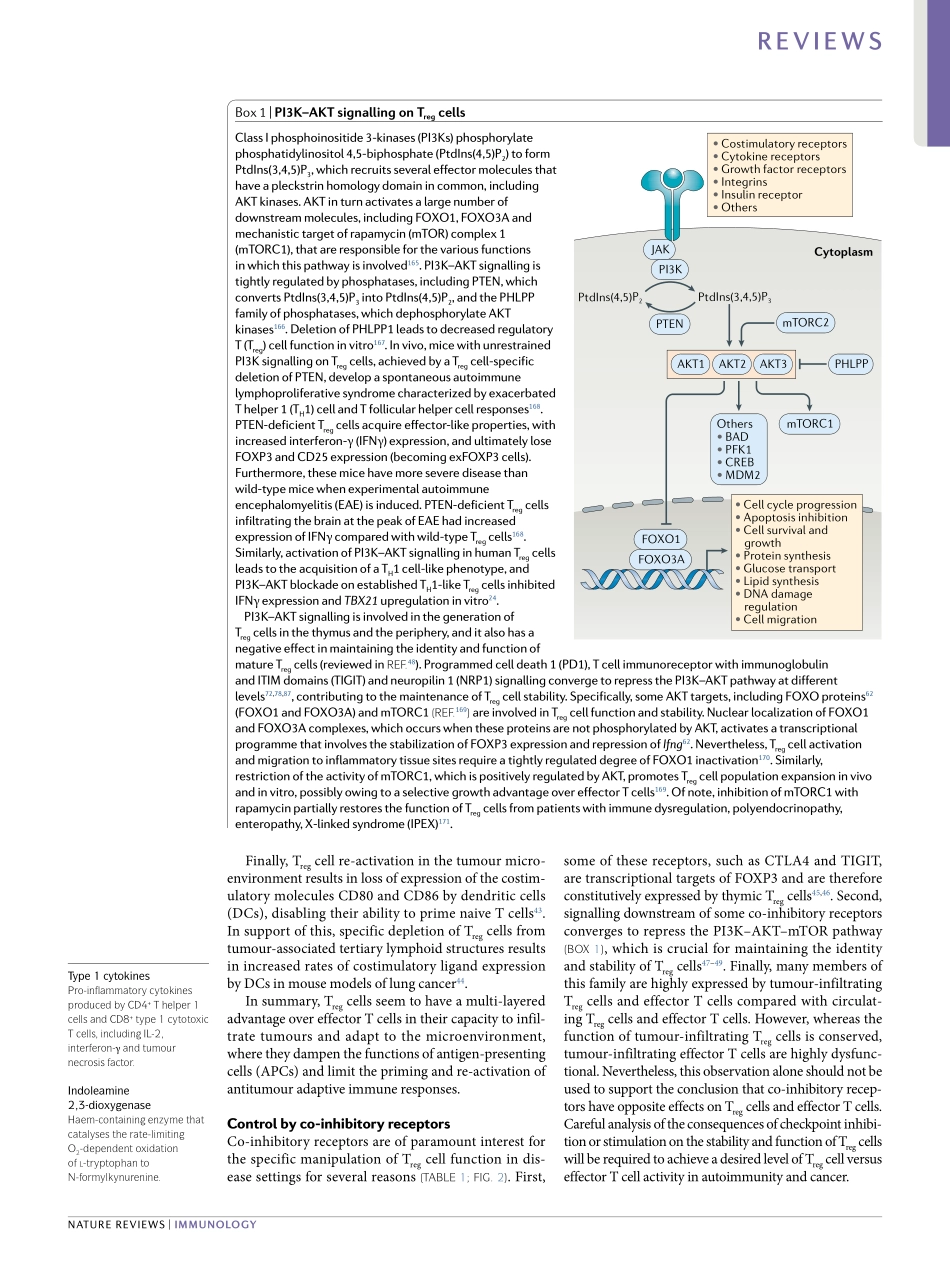
RegulatoryT(Treg)cellsareanintegralpartoftheimmunesystemandtheirfunctionsgobeyondthecon-trolofphysiologicalandpathologicalimmuneresponses.Tregcellscanbegeneratedinthethymusuponrecog-nitionofself-antigenswithintermediateavidityorfromnaiveCD4+Tcellsinspecializedperipheraltis-suessuchastheintestinallaminapropria1.BecausetheTcellreceptor(TCR)repertoireofTregcellsismostlyskewedtowardsrecognitionofself2,3,TCR-dependentfunctionsofTregcellsareessentialforthemaintenanceofself-tolerance.However,recentfindingshavehigh-lightedaroleforTregcellsbeyondthecontrolofimmuneresponses,namelyinwoundhealingandtissuerepair,mediatedbothbytheorchestrationofotherimmunecellpopulationsandbythedirectproductionoftissuegrowthfactors4–6.Tregcellsarethereforekeyplayersinthepreventionofautoimmunityandinthedevelopmentofthetumourmicroenvironment.Tregcellsarecharacterizedinmiceandhumansbyhighlevelsofexpressionoftheα-subunitoftheIL-2receptor(CD25),lackofexpressionoftheIL-7receptorα-subunit(CD127)7andexpressionofthetranscriptionfactorFOXP3,whichisessentialforTregcelldevelop-mentandfunction8.TheTregcellfunctionalprogrammeisestablishedbyboththeexpressionofFOXP3(ref.8)andthegenerationofaspecificepigeneticsignaturethatisacquiredduringTregcelldevelopment9.AlterationofeitherofthesetwofeaturesasaconsequenceoftheinteractionbetweenTregcellsandtheirenvironmentorneighbouringcellscanleadtoTregcellinstabilityandplasticity10.Thus,inflammatoryconditionscaninducetheinstabilityofasubpopulationofTregcellsthatloseFOXP3expressionandconvertintoeffectorcellsthatproducepro-inflammatorycytokinesandarepatho-genicinmousemodelsofautoimmunity11–13.Tregcellscanalsoacquiretheexpressionofpro-inflammatorycytokinessuchasinterferon-γ(IFNγ),IL-13orIL-17,whilemaintainingFOXP3expressionininflamma-torysettings10,14(fig.1).ThemolecularmechanismsresponsibleforthesedynamicchangesinTregcellphe-notypeandfunctionarenotcompletelyunderstood,butnumerousrecentworkshavehighlightedthecon-tributionofseveralco-inhibitoryreceptors(alsoknownascheckp...