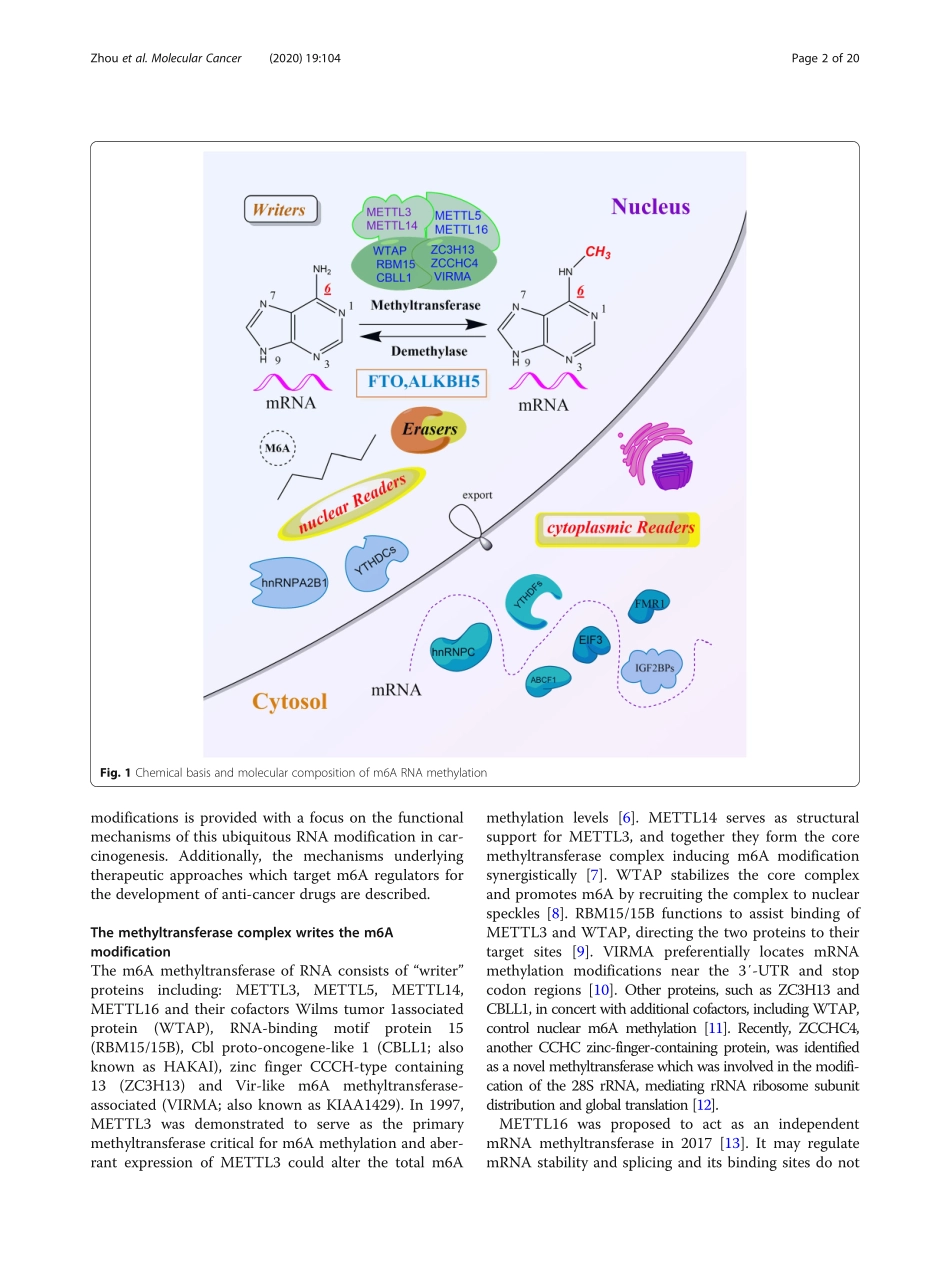
REVIEWOpenAccessMechanismofRNAmodificationN6-methyladenosineinhumancancerZijianZhou†,JianchengLv†,HaoYu†,JieHan,XiaoYang,DexiangFeng,QikaiWu,BaoruiYuan,QiangLu*andHaiweiYang*AbstractSincethebreakthroughdiscoveriesofDNAandhistonemodifications,thefieldofRNAmodificationshasgainedincreasinginterestinthescientificcommunity.ThediscoveryofN6-methyladenosine(m6A),apredominantlyinternalepigeneticmodificationineukaryotesmRNA,heraldedthecreationofthefieldofepi-transcriptomics.Thispost-transcriptionalRNAmodificationisdynamicandreversible,andisregulatedbymethylases,demethylasesandproteinsthatpreferentiallyrecognizem6Amodifications.Alteredm6AlevelsaffectRNAprocessing,degradationandtranslation,therebydisruptinggeneexpressionandkeycellularprocesses,ultimatelyresultingintumorinitiationandprogression.Furthermore,inhibitorsandregulatorsofm6A-relatedfactorshavebeenexploredastherapeuticapproachesfortreatingcancer.Inthepresentreview,themechanismsofm6ARNAmodification,theclinicopathologicalrelevanceofm6Aalterations,thetypeandfrequencyofalterationsandthemultiplefunctionsitregulatesindifferenttypesofcancerarediscussed.Keywords:N6-methyladenosine,RNAmethylation,CancerTheN6-methyladenosine(m6A)RNAmodificationM6ARNAmodification,describesamethylationattheN6positionofadenosine,andisthemostabundantin-ternalmodificationineukaryotesmRNA[1].Sinceitsdiscoveryin1974[1],researchonm6Ahasflourishedowingtoimprovementsindetectionmethodsandtheidentificationofimportantregulatoryproteinsanditre-centlyreportedthatm6AmodificationsregulatethegenerationandfunctionoftransferRNA(tRNA),riboso-malRNA(rRNA)andnon-codingRNAs(ncRNAs),suchasmicroRNA(miRNAs),longnon-codingRNA(lncRNAs),andcircularRNAs(circRNAs).Geneexam-inationtechnologyandhigh-throughputsequencingmethodshavedemonstratedthatthem6Amodificationisnotrandomlydistributed,butisenrichednearstopcodonsand3′-untranslatedterminalregions(UTRs)andtranslatednear5′-UTRorinlongexons[2].Them6AmodificationofRNAisdynamicallyandreversiblyregu-latedbytwoimportantcatalyt...