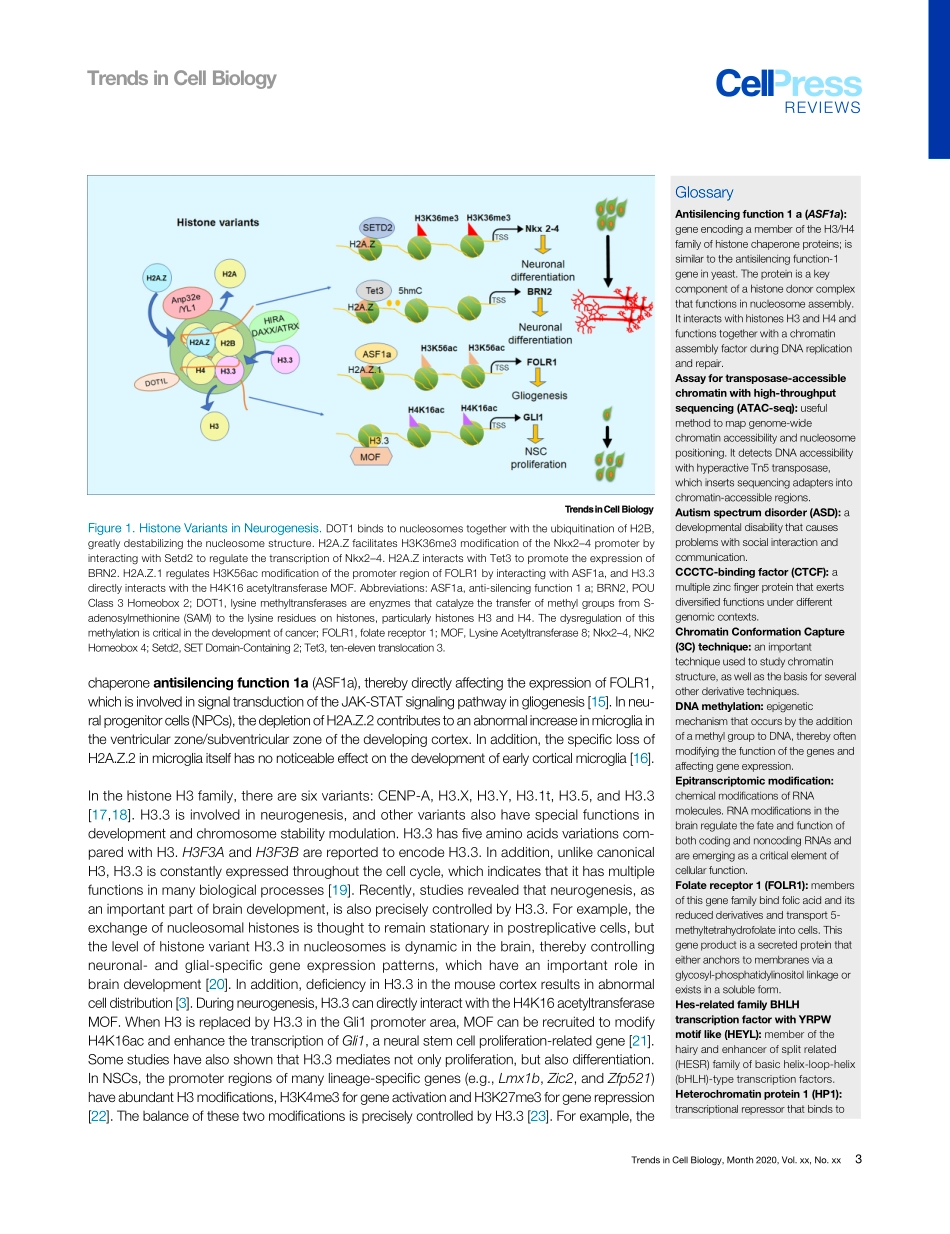
ReviewHistoneVariantsandHistoneModificationsinNeurogenesisMengtianZhang,1,2,3,5JinyueZhao,1,2,3,5YuqingLv,1,2,3,5WenwenWang,1,4,5ChaoFeng,1,3WenzhengZou,1,2,3LiboSu,1,2,3andJianweiJiao1,2,3,*Duringembryonicbraindevelopment,neurogenesisrequirestheorchestrationofgeneexpressiontoregulateneuralstemcell(NSC)fatespecification.Epigeneticregulationwithspecificemphasisonthemodesofhistonevariantsandhistonepost-translationalmodificationsareinvolvedininteractivegeneregulationofcentralnervoussystem(CNS)development.Here,weprovideabroadoverviewoftheregulatorysystemofhistonevariantsandhistonemodificationsthathavebeenlinkedtoneurogenesisanddiseases.Wealsoreviewthecrosstalkbetweendifferenthistonemodificationsanddiscusshowthe3Dgenomeaffectscellfatedynamicsduringbraindevelopment.Understandingthemechanismsofepige-neticregulationinneurogenesishasshiftedtheparadigmfromsinglegeneregu-lationtosynergisticinteractionstoensurehealthyembryonicneurogenesis.HistoneVariantsandHistoneModificationsAreCriticalfortheDynamicModulationofNeurogenesisIneukaryotes,nucleosomesformthebasicrepeatingunitsofchromatinandcomprisecorehistones(H2A,H2B,H3,andH4).Thenucleosomesprovidefunctionalcomplexityviatheincorpo-rationofhistonevariants,whichinturnregulatechromatinarchitectureandgeneexpression.Histonevariantscontributetoextendingtheinformationpotentialofthegeneticcode.Theyalsoregulatenor-malbrainfunction,andotherformsofhistonemodificationshavebeenlinkedtoneurogenesisandneuralplasticity[1].Incorporationoftiming-specifichistonevariantsgenerallyleadstoDNA–proteininteractions,whichallowchangesinchromosomalarchitectureinglobalreplacement.Recently,H2A.ZandH3.3werefoundtohavespecializedfunctionsthatregulatelineagecommitmentduringembryonicneurodevelopment[2,3].Histonesaredecoratedbyavarietyofmodifications,includingmethylation,acetylation,phosphorylation,ubiquitination,crotonylation,andglycosylation.Thesemodificationsaffecttheaccessoftranscriptionfactors(TFs)andarecriticalforthedynamicmod-ulationofchromatinfunction,co...